Hypertonic Saline Solutions: Application in Respiratory Therapy
Hypertonic Saline Evolution
The evolution of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy has been marked by significant advancements and a growing understanding of their therapeutic potential. Initially, the use of hypertonic saline was primarily limited to treating cystic fibrosis patients, where it was found to improve mucociliary clearance and lung function.
As research progressed, the application of hypertonic saline expanded to other respiratory conditions. In the early 2000s, studies began to explore its efficacy in treating bronchiolitis, particularly in infants. This marked a crucial turning point in the evolution of hypertonic saline therapy, broadening its potential patient base.
The mid-2000s saw an increased focus on optimizing the concentration and delivery methods of hypertonic saline. Researchers experimented with various concentrations, ranging from 3% to 7%, to determine the most effective and safe options for different respiratory conditions. Concurrently, advancements in nebulizer technology improved the delivery of hypertonic saline, enhancing its efficacy and patient comfort.
By the 2010s, hypertonic saline had gained recognition as a valuable tool in managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Its ability to reduce airway inflammation and improve mucus clearance made it an attractive option for these chronic respiratory conditions.
Recent years have seen a surge in research exploring the potential of hypertonic saline in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and COVID-19-related respiratory complications. These investigations have opened new avenues for its application in critical care settings, potentially expanding its role in managing severe respiratory conditions.
The evolution of hypertonic saline solutions has also been characterized by efforts to mitigate potential side effects. Researchers have developed strategies to reduce bronchospasm and airway irritation, such as combining hypertonic saline with bronchodilators or using stepwise concentration increases.
Looking ahead, the future of hypertonic saline in respiratory therapy appears promising. Ongoing research is focusing on personalized treatment approaches, considering factors such as individual patient characteristics and specific respiratory conditions. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring long-term outcomes and the potential for hypertonic saline to modify disease progression in chronic respiratory disorders.
Respiratory Therapy Market
The respiratory therapy market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases and the growing aging population worldwide. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and therapeutic interventions designed to diagnose, treat, and manage various respiratory conditions.
One of the key factors contributing to the market's expansion is the rising incidence of chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and sleep apnea. These conditions affect millions of people globally and require ongoing management and treatment, creating a sustained demand for respiratory therapy products and services.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, highlighting the critical importance of respiratory care and driving innovation in this field. The sudden surge in demand for ventilators, oxygen therapy devices, and other respiratory support equipment during the pandemic has led to increased investment and research in respiratory therapy technologies.
In terms of product segments, the market can be broadly categorized into therapeutic devices, monitoring devices, diagnostic devices, and consumables. Therapeutic devices, including ventilators, nebulizers, and oxygen concentrators, represent a significant portion of the market. The monitoring devices segment, comprising pulse oximeters and capnographs, has also seen substantial growth due to the increasing focus on continuous patient monitoring.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally dominated the respiratory therapy market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising awareness of respiratory diseases.
The competitive landscape of the respiratory therapy market is characterized by the presence of several large multinational corporations as well as numerous smaller, specialized companies. Key players in this market are continuously investing in research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market share.
Looking ahead, the respiratory therapy market is poised for continued growth, with technological advancements playing a crucial role in shaping its future. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in respiratory care devices, the development of portable and home-use devices, and the increasing adoption of telemedicine in respiratory therapy are some of the trends expected to drive market expansion in the coming years.
Challenges in Saline Use
The use of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy presents several challenges that require careful consideration. One of the primary concerns is the potential for bronchospasm, particularly in patients with reactive airway disease. The high salt concentration can irritate the airways, leading to coughing, wheezing, and in severe cases, respiratory distress. This risk necessitates close monitoring and may limit the use of hypertonic saline in certain patient populations.
Another significant challenge is the optimal dosing and administration protocol. The concentration of saline solution, frequency of administration, and duration of treatment can vary widely depending on the specific respiratory condition being treated. Determining the most effective regimen for each patient requires a delicate balance between therapeutic benefit and potential side effects. This variability in treatment protocols can lead to inconsistencies in clinical practice and outcomes across different healthcare settings.
The potential for systemic effects is also a concern when using hypertonic saline solutions. While the primary target is the respiratory system, the absorption of sodium and chloride ions can impact fluid balance and electrolyte levels in the body. This is particularly problematic for patients with pre-existing cardiac or renal conditions, who may be more susceptible to fluid overload or electrolyte imbalances. Careful monitoring of serum electrolytes and fluid status is essential to mitigate these risks.
Additionally, the long-term effects of repeated hypertonic saline use on the respiratory epithelium are not fully understood. There are concerns about potential damage to the ciliary function and alterations in the composition of airway surface liquid over time. This uncertainty raises questions about the safety of prolonged or frequent use, especially in chronic respiratory conditions that may require ongoing treatment.
The preparation and storage of hypertonic saline solutions also present practical challenges. Ensuring the correct concentration and sterility of the solution is crucial for patient safety and treatment efficacy. Healthcare facilities must have robust protocols in place for the preparation, labeling, and storage of these solutions to prevent errors and contamination.
Lastly, patient compliance and comfort can be significant hurdles in the use of hypertonic saline therapy. The salty taste and potential for throat irritation can be unpleasant for patients, potentially leading to poor adherence to treatment regimens. This is particularly challenging in pediatric populations or in patients requiring long-term therapy. Developing strategies to improve palatability and reduce discomfort without compromising therapeutic efficacy remains an ongoing challenge in the field of respiratory therapy.
Current Hypertonic Methods
01 Composition and preparation of hypertonic saline solutions
Hypertonic saline solutions are prepared with higher concentrations of sodium chloride than physiological saline. These solutions typically contain 3% to 7% sodium chloride and may include additional electrolytes or other components to enhance their therapeutic effects. The preparation process involves careful mixing and sterilization to ensure safety and efficacy.- Medical applications of hypertonic saline solutions: Hypertonic saline solutions are used in various medical applications, including treatment of edema, respiratory conditions, and as a nasal irrigation solution. These solutions can help reduce inflammation, improve mucus clearance, and provide osmotic effects beneficial in certain medical conditions.
- Formulation and preparation of hypertonic saline solutions: The formulation of hypertonic saline solutions involves careful consideration of salt concentration, pH balance, and additives. Preparation methods may include sterile manufacturing processes, precise measurement of ingredients, and quality control measures to ensure consistency and safety for medical use.
- Delivery systems for hypertonic saline solutions: Various delivery systems are used for administering hypertonic saline solutions, including nebulizers, nasal sprays, and intravenous infusion devices. These systems are designed to ensure accurate dosing, proper distribution, and effective application of the solution to target areas.
- Combination therapies using hypertonic saline solutions: Hypertonic saline solutions are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents or treatments to enhance their effectiveness. This may include combining saline solutions with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or using them as part of a broader treatment regimen for various medical conditions.
- Industrial and environmental applications of hypertonic saline solutions: Beyond medical uses, hypertonic saline solutions have applications in industrial processes and environmental remediation. These may include water treatment, desalination, and certain manufacturing processes where high salt concentrations are beneficial.
02 Medical applications of hypertonic saline solutions
Hypertonic saline solutions have various medical applications, including treatment of edema, intracranial pressure reduction, and management of cystic fibrosis. They are also used in wound care, nasal irrigation, and as a mucolytic agent. The high osmolarity of these solutions helps draw fluid from tissues and improve mucus clearance in respiratory conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Delivery methods for hypertonic saline solutions
Hypertonic saline solutions can be administered through various routes, including intravenous infusion, nebulization, nasal sprays, and topical application. Specialized delivery devices and techniques have been developed to optimize the effectiveness of these solutions for different medical conditions and patient populations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Formulation enhancements for hypertonic saline solutions
Researchers have developed enhanced formulations of hypertonic saline solutions by incorporating additional components such as antimicrobial agents, antioxidants, or pH buffers. These modifications aim to improve the stability, efficacy, and patient tolerability of the solutions while maintaining their primary therapeutic effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of hypertonic saline solutions
Beyond medical uses, hypertonic saline solutions find applications in various industrial processes. These include water treatment, desalination, and as a component in certain manufacturing processes. The high salt concentration of these solutions can be utilized for specific chemical reactions or physical processes in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Respiratory Players
The application of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for respiratory care devices is expanding, driven by rising respiratory disorders and aging populations. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Fisher & Paykel Healthcare, Medtronic, and ResMed leading innovation in respiratory therapy devices. Pharmaceutical giants such as Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novartis are actively developing new formulations and delivery methods for hypertonic saline solutions. Emerging players like Parion Sciences and Pulmatrix are focusing on novel approaches, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape with varying levels of technological maturity across different aspects of this therapy.
Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Corp. Ltd.
Medtronic, Inc.
Saline Therapy Innovations
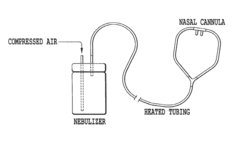
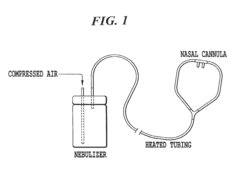
- A nasal cannula system connected to a nebulizer delivers aerosolized osmolytes, such as hypertonic saline, allowing for prolonged treatment periods, including overnight hydration, using a large volume nebulizer capable of continuous operation without refilling for several hours, with heated tubing to prevent fluid condensation and ensure aerosol delivery.
- Combining neuronal agonists such as menthol or capsaicin with hypertonic saline to stimulate the nervous system, thereby increasing airway surface liquid volume and mucociliary clearance, and enhancing the hydration and efficacy of airway surface liquid treatment.
Safety and Efficacy Studies
The safety and efficacy of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy have been extensively studied, with numerous clinical trials and meta-analyses providing valuable insights. These studies have primarily focused on patients with cystic fibrosis, bronchiolitis, and other chronic respiratory conditions.
For cystic fibrosis patients, long-term use of hypertonic saline has demonstrated significant improvements in lung function and quality of life. A landmark study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that regular inhalation of 7% hypertonic saline over 48 weeks resulted in sustained improvement in lung function and reduced pulmonary exacerbations. Subsequent studies have confirmed these findings, with meta-analyses indicating a consistent positive effect on FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second) and reduced frequency of pulmonary exacerbations.
In the context of bronchiolitis, particularly in infants, the efficacy of hypertonic saline has been more controversial. While some studies have shown reduced hospital stay duration and improved clinical scores, others have found no significant benefit over standard care. A Cochrane review analyzing multiple randomized controlled trials concluded that nebulized 3% hypertonic saline may moderately reduce the length of hospital stay in infants with acute bronchiolitis, but emphasized the need for further high-quality studies.
Safety profiles of hypertonic saline solutions have generally been favorable across various patient populations. Reported adverse events are typically mild and transient, including cough, throat irritation, and chest tightness. These effects are often mitigated by pre-treatment with bronchodilators. Serious adverse events are rare, with no significant differences in occurrence compared to isotonic saline in most studies.
However, it's important to note that the optimal concentration and administration protocol for hypertonic saline can vary depending on the specific respiratory condition and patient characteristics. While 3% and 7% solutions are most commonly studied, some research has explored higher concentrations up to 10%, with varying results in terms of efficacy and tolerability.
Recent studies have also begun to explore the potential of hypertonic saline in other respiratory conditions, such as non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Preliminary results suggest possible benefits in mucus clearance and symptom improvement, but larger, well-designed trials are needed to establish definitive efficacy and safety profiles in these populations.
In conclusion, while the safety of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy is well-established, their efficacy varies depending on the specific condition and patient population. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of optimal use and potential applications in a broader range of respiratory disorders.
Patient Compliance Factors
Patient compliance is a critical factor in the successful application of hypertonic saline solutions in respiratory therapy. The effectiveness of this treatment modality heavily relies on patients' adherence to prescribed regimens and proper administration techniques. Several key factors influence patient compliance in this context.
Firstly, the frequency and duration of treatments can significantly impact adherence. Hypertonic saline solutions often require multiple daily administrations, which can be challenging for patients to incorporate into their routines. The time-consuming nature of nebulizer treatments may lead to reduced compliance, especially among individuals with busy schedules or those who find the process disruptive to their daily activities.
The taste and sensation of hypertonic saline solutions can also affect patient compliance. Some patients report a salty or unpleasant taste, which may discourage regular use. Additionally, the initial bronchoconstrictive effect experienced by some individuals can be uncomfortable and may lead to treatment avoidance if not properly managed or explained by healthcare providers.
Equipment-related factors play a crucial role in compliance. The complexity of nebulizer devices, maintenance requirements, and the need for proper cleaning and disinfection can be overwhelming for some patients. Difficulties in operating the equipment or concerns about contamination may result in reduced adherence to prescribed treatments.
Patient education and understanding of the treatment's benefits are vital compliance factors. Inadequate knowledge about the mechanism of action, expected outcomes, and the importance of consistent use can lead to poor adherence. Healthcare providers must ensure that patients comprehend the long-term benefits of hypertonic saline therapy, even when immediate improvements may not be apparent.
Side effects and perceived efficacy also influence compliance. Some patients may experience temporary irritation, coughing, or bronchospasm, which can discourage continued use if not properly managed. Conversely, patients who perceive immediate benefits from the treatment are more likely to adhere to the prescribed regimen.
Financial considerations can impact compliance, particularly in healthcare systems where patients bear a significant portion of treatment costs. The expense of nebulizer equipment, replacement parts, and ongoing supplies of hypertonic saline solution may pose barriers to consistent use for some individuals.
Lastly, psychosocial factors, including motivation, self-efficacy, and social support, play crucial roles in patient compliance. Patients who feel confident in their ability to manage their condition and those with strong support systems are more likely to adhere to hypertonic saline treatments. Conversely, depression, anxiety, or lack of social support can negatively impact compliance.