Control of an electric machine
a technology of electric machines and electric motors, applied in the direction of electronic commutators, dynamo-electric machines, synchronous motor starters, etc., can solve the problems of becoming increasingly difficult to drive power into electric machines, and achieve the effect of increasing the advance tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
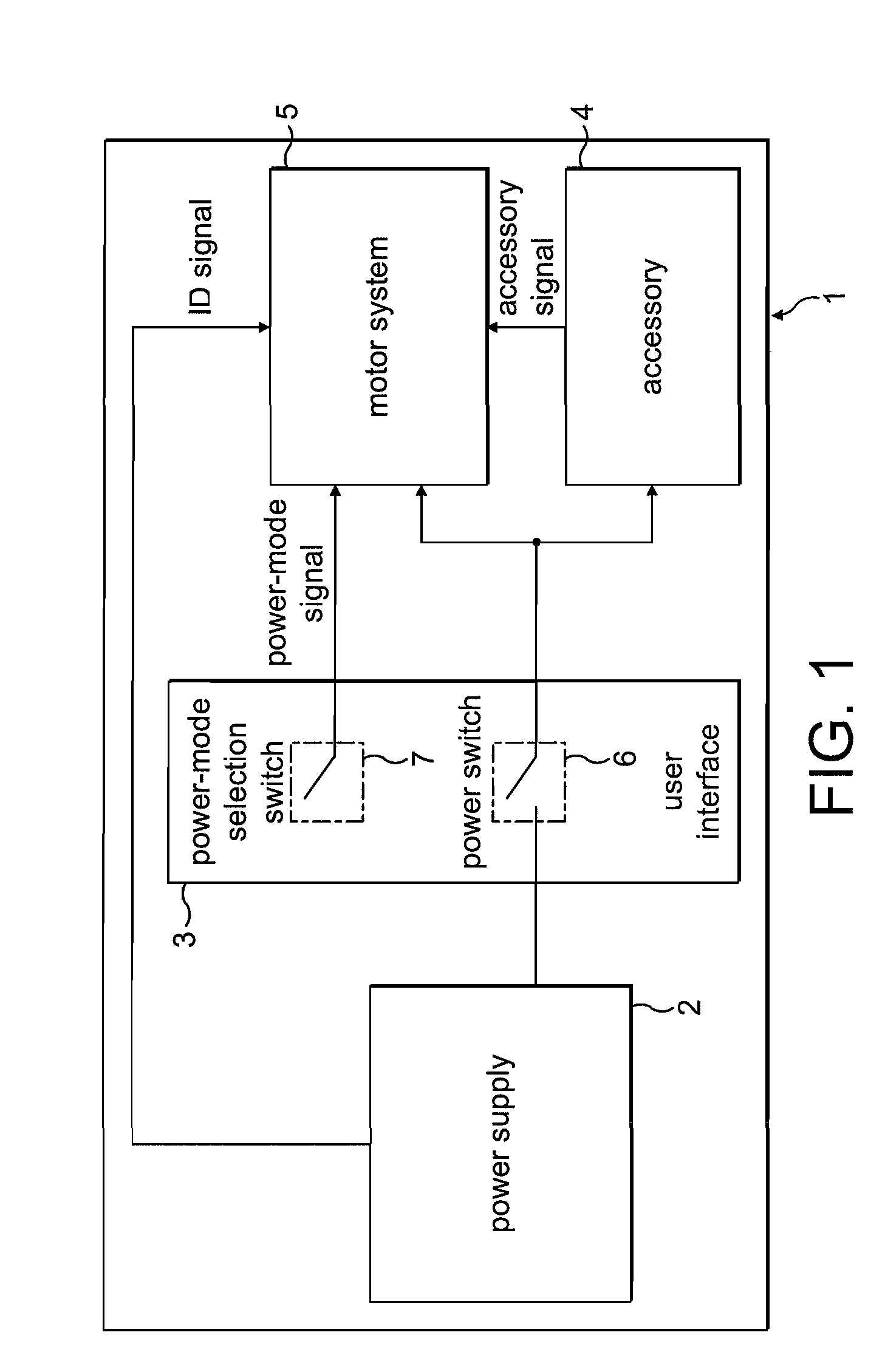
[0034]The product 1 of FIG. 1 comprises a power supply 2, a user interface 3, an accessory 4, and a motor system 5.
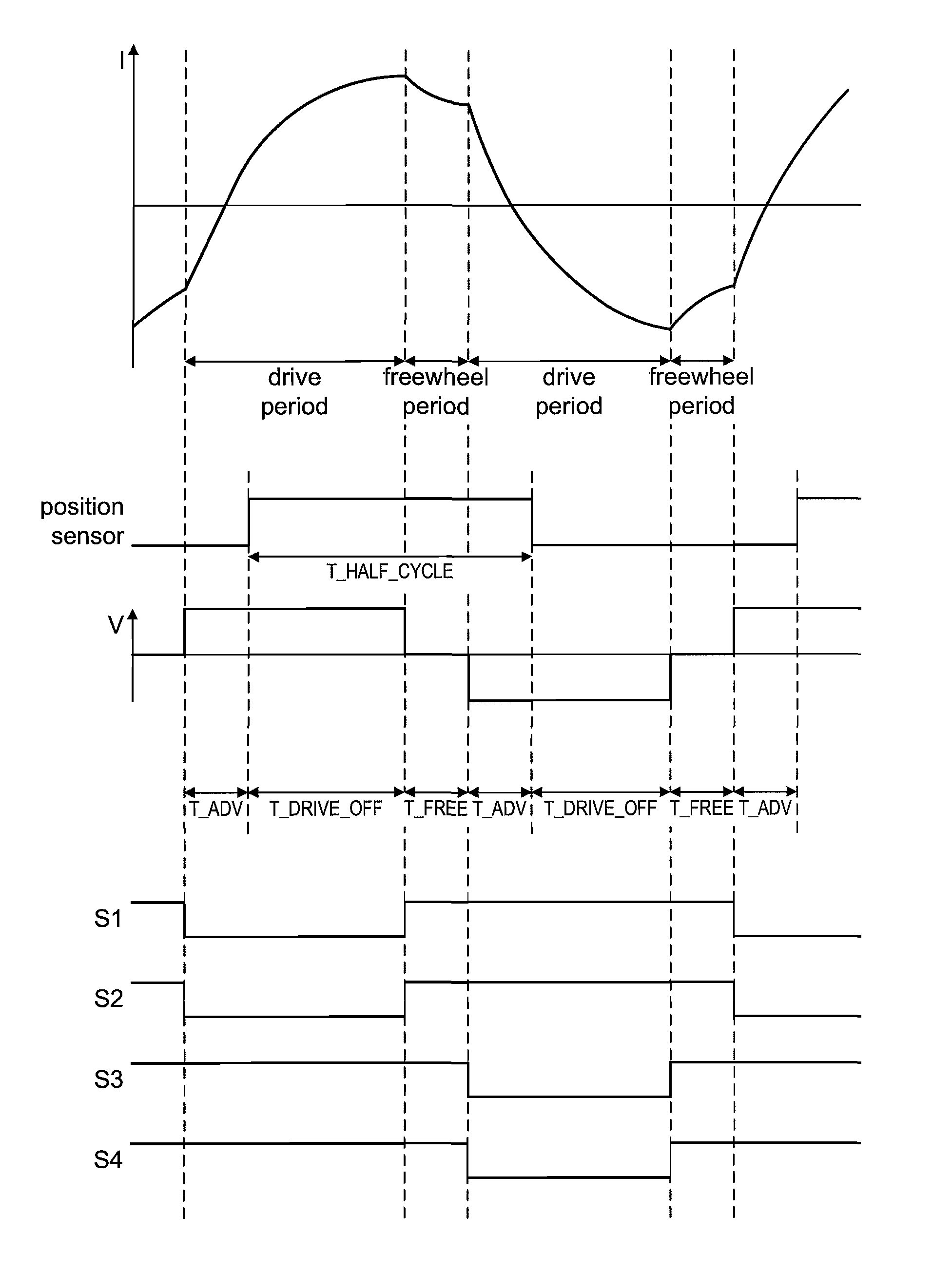
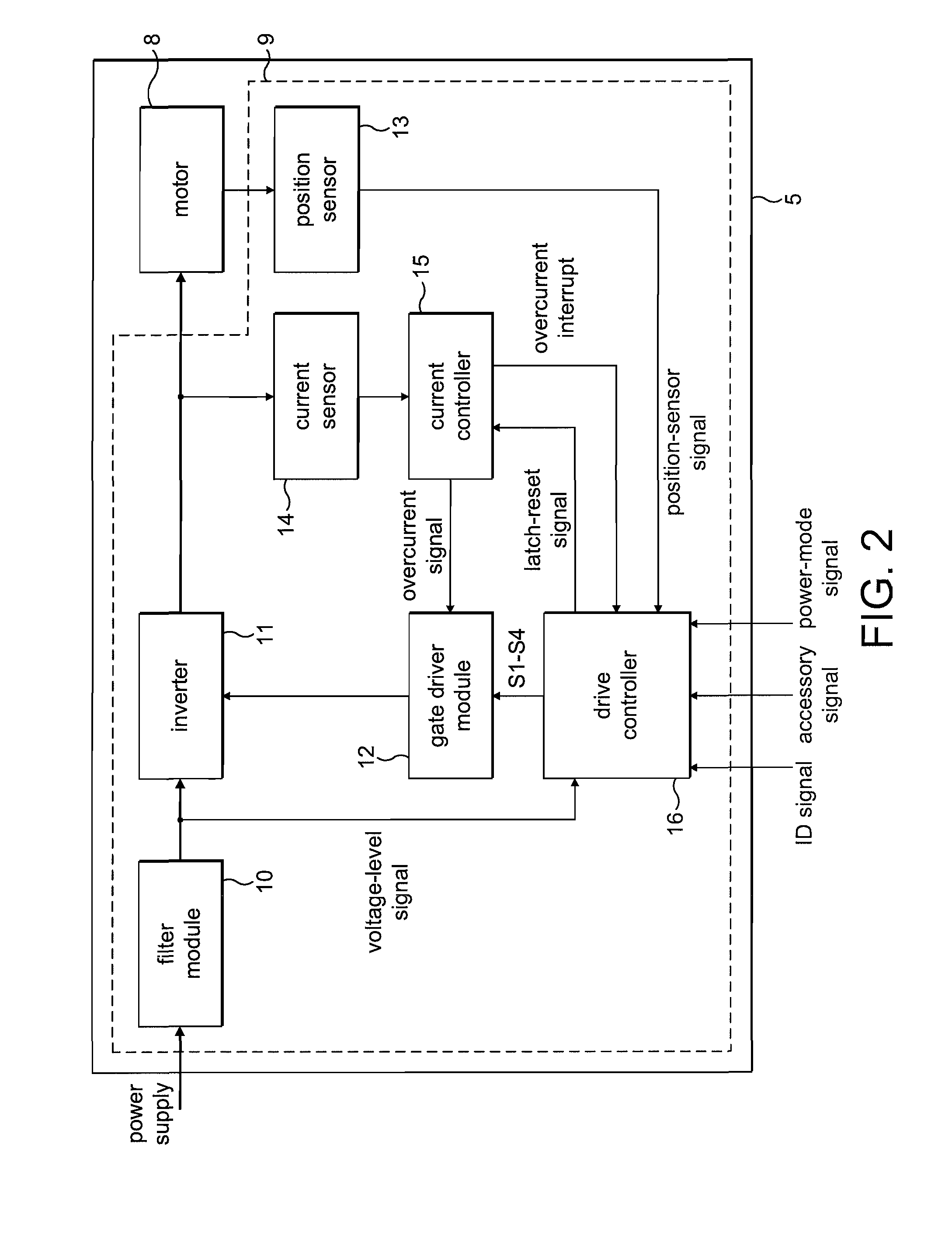
[0035]The power supply 2 comprises a battery pack that supplies a DC voltage to both the accessory 4 and the motor system 5. The power supply 2 is removable from the product 1 such that the product 1 may be used with different battery packs. For the purposes of the present description, the power supply 2 is either a 4-cell battery pack providing a 16.4 V DC supply or 6-cell battery pack providing a 24.6 V DC supply. In addition to providing a supply voltage, the power supply outputs an identification signal that is unique to the type of battery pack. The ID signal takes the form of a square-wave signal having a frequency that varies according to the type of battery pack. In the present example, the 4-cell battery pack outputs an ID signal having a frequency of 25 Hz (20 ms pulse length), while the 6-cell battery pack outputs an ID signal having a frequency of 50 Hz (10 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com