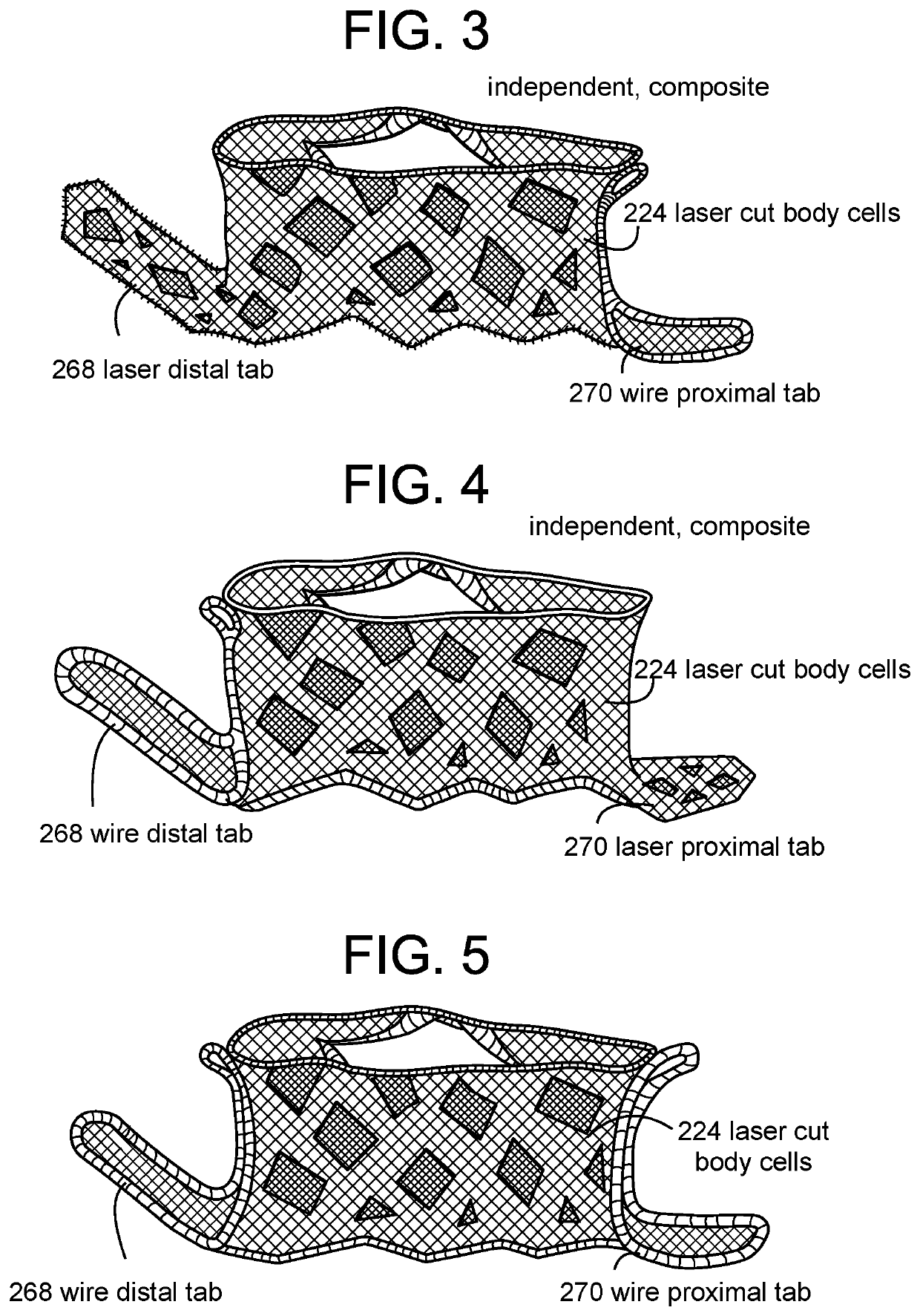
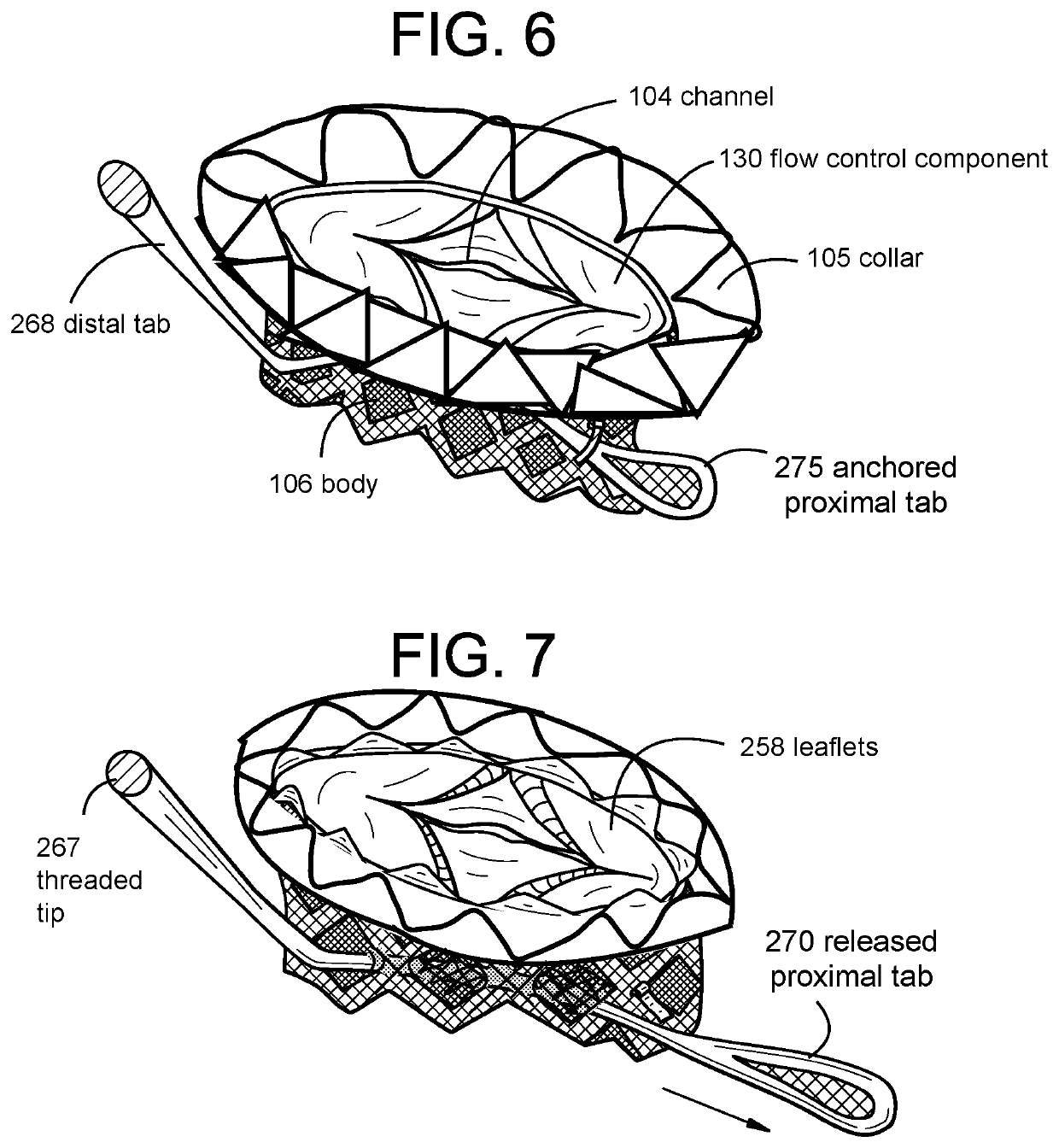
Proximal Tab for Side-Delivered Transcatheter Heart Valve Prosthesis
a transcatheter heart valve and prosthesis technology, applied in the field of prosthesis, can solve the problems of prone to fracture of the strut of the valve, inability to fully correct the valve problem, etc., to achieve the effect of convenient rolling, folding, and compressing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Compression Methods
[0190]In another preferred embodiment, there is provided a method of compressing, wherein the implantable prosthetic heart valve is rolled or folded into a compressed configuration using a step selected from the group consisting of:
[0191](i) unilaterally rolling into a compressed configuration from one side of the annular support frame;
[0192](ii) bilaterally rolling into a compressed configuration from two opposing sides of the annular support frame;
[0193](iii) flattening the annular support frame into two parallel panels that are substantially parallel to the long-axis, and then rolling the flattened annular support frame into a compressed configuration; and
[0194](iv) flattening the annular support frame along a vertical axis to reduce a vertical dimension of the valve from top to bottom.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com