Infinitely variable transmission for differentially steered vehicles
a technology of variable transmission and differential steering, which is applied in mechanical equipment, transportation and packaging, and gearing, etc., can solve the problem of low torque loading of the variable ratio pulley system driving the sun gear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
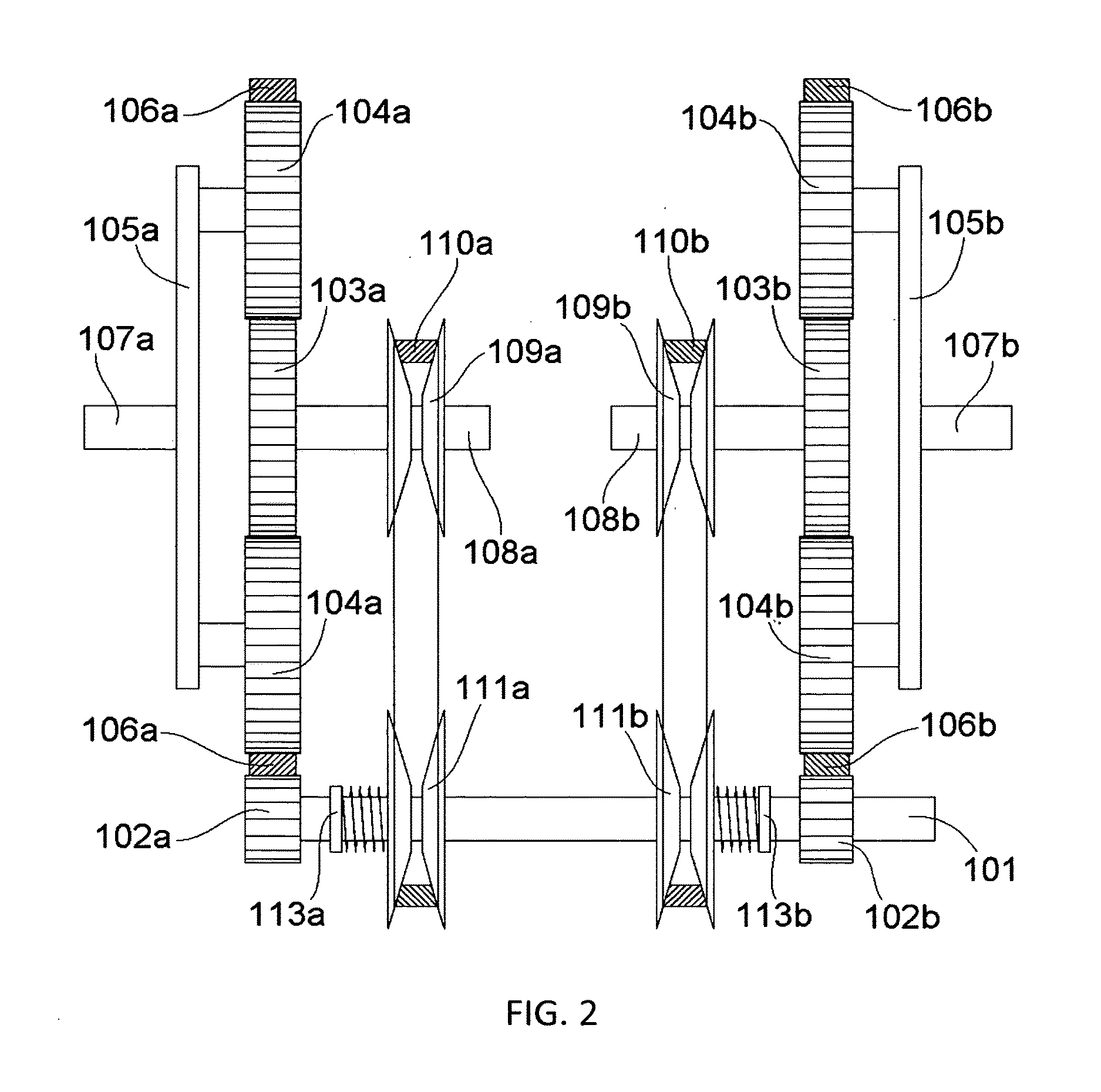
[0044]FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 illustrate an Infinitely Variable Transmission in accordance with this invention. The engine shaft 101, driven by the engine, drives the ring gears 106a 106b of both planetary gearboxes via the respective fixed gear ratio drivers 102a 102b. Hence, both ring gears 106a 106b are driven at the same speed relative to each other. The engine shaft 101 is also coupled with the two spring loaded 113a 113b variable ratio driver pulleys 111a 111b, each of which is coupled with a respective variable ratio driven pulley 109a 109b via a respective belt 110a 110b, to form two variable ratio belt drive systems. The springs 113a 113b maintain a force load on one or both flanges of both of the driver pulleys 111a 111b, pushing the flanges towards each other. Within each variable ratio belt drive system, the gearing ratio of the driven pulley 109a(109b) is controllably varied, while the ratio of the driver pulley 111a(111b) is, in response, controlled by the spring 113a(113b) ...
second embodiment
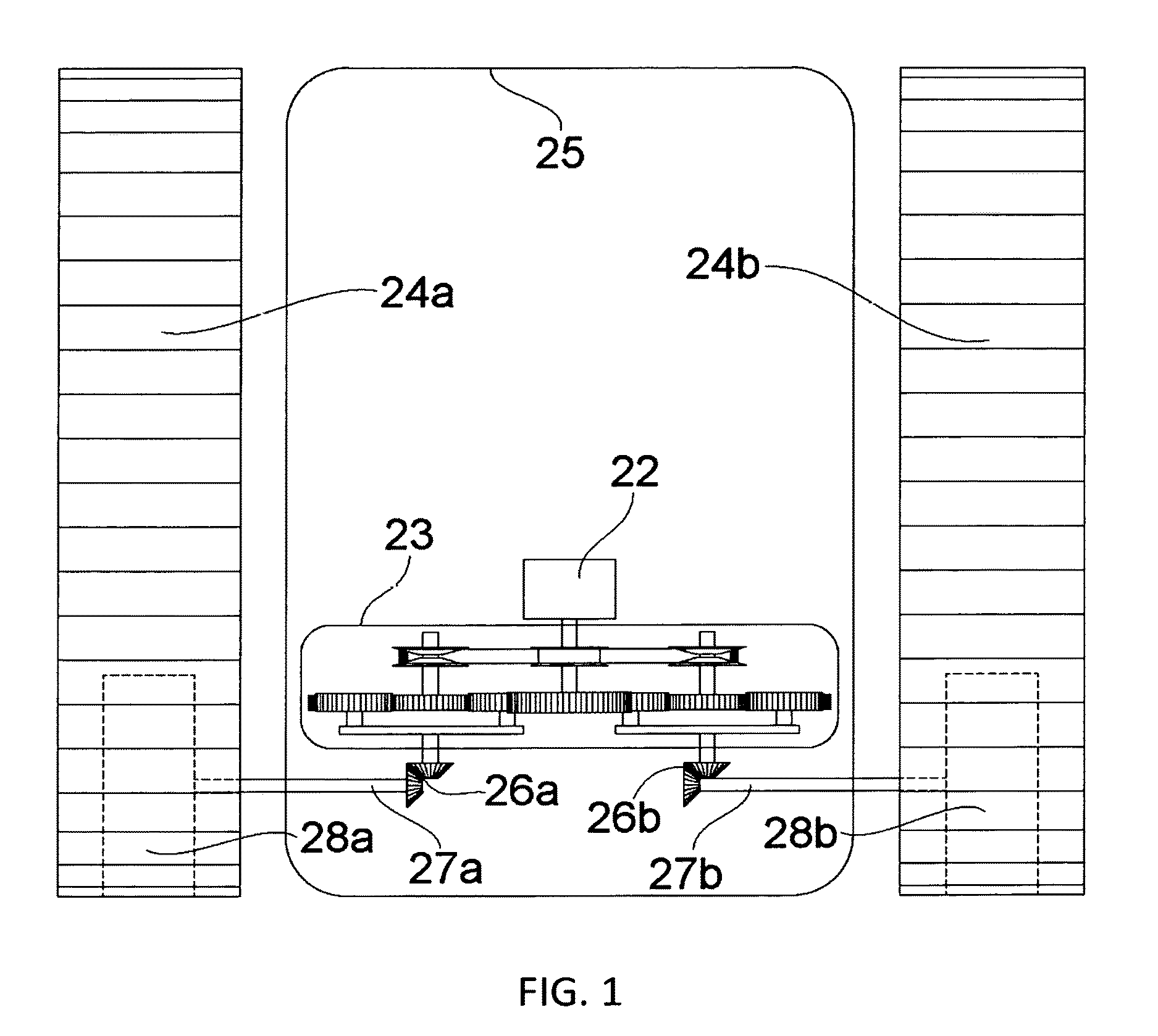
[0048]Referring to FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 as this invention, an engine 22 is drivingly connected to a fixed ratio driver pulley 211, and to a fixed gear ratio driver 202 via the engine shaft 201. A single belt 210 couples the fixed ratio pulley 211 with two variable ratio driven pulleys 209a 209b. The fixed ratio driver gear 202 is drivingly connected to the ring gears 206a 206b of both planetary gearboxes. Similar to embodiment one, planet gear sets 204a 204b of both planetary gearboxes are each coupled to drive the respective output shafts 207a 207b via the respective carrier elements 205a 205b, which in turn drive the respective tracks of the vehicle. Again similar to embodiment one, sun gears 203a 203b are drivingly connected to the respective driven pulleys 209a 209b via the respective shafts 208a 208b. Also operationally similar to embodiment one, by controllably varying the distances between the flanges, hence the gearing ratios, of both variable ratio driven pulleys 209a 209b in ...
third embodiment
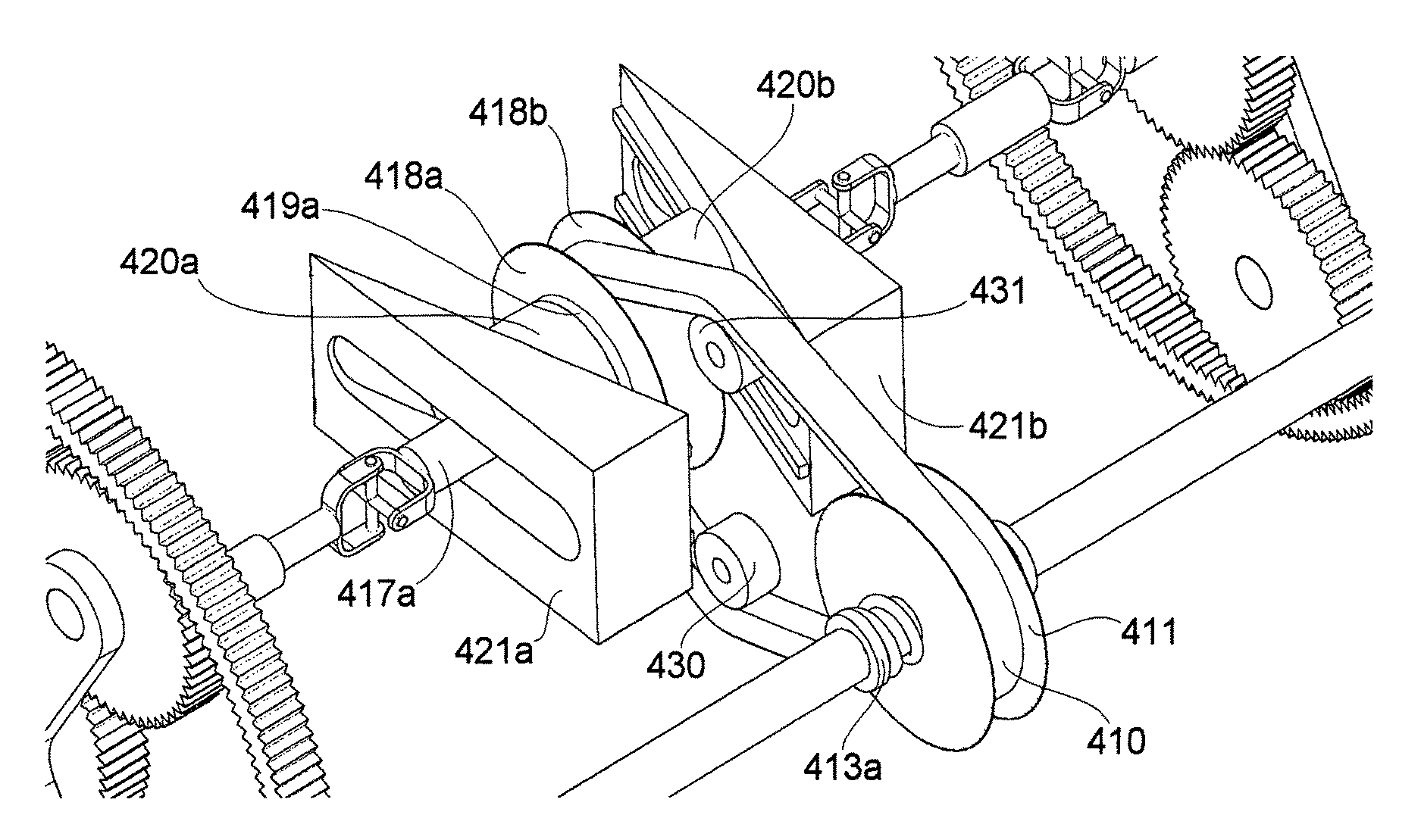
[0049]A third embodiment as outlined in FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 is similar to embodiment two, however differs from embodiment two by the fact that it utilizes a spring loaded 313 variable ratio driver pulley 311, in place of the fixed ratio driver pulley 211 of embodiment two, and the tensioner pulley 212 is absent. Similar to the spring loaded 113a 113b driver pulleys 111a 111b in embodiment one, the spring load 313 for the driver pulley 311 maintains a force load on one or both flanges towards each other. As the gearing ratios of the driven pulleys 309a 309b are controllably varied, the ratio of the driver pulley 311 varies in response, under the spring load, to maintain the belt 310 tension. This spring loaded 313 ratio-varying function of the driver pulley 311 in response to the controlled ratio-varying function of the driven pulleys 309a 309b also allows for the overall belt drive pulley system to deliver a wider range of gearing ratio compared to embodiment two, for similarly sized ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com