Double cross-linkage process to enhance post-implantation bioprosthetic tissue durablity
a bioprosthetic tissue and double cross-linking technology, applied in the field of bioprosthetic devices, can solve the problems of limited application, tissue calcification and collagen degeneration, and the amino groups of adjacent collagen molecules and residual amino groups of diamines were not cross-linked or further modified, and achieve the effect of eliminating phospholipids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Calcification Mitigation—Rat Model
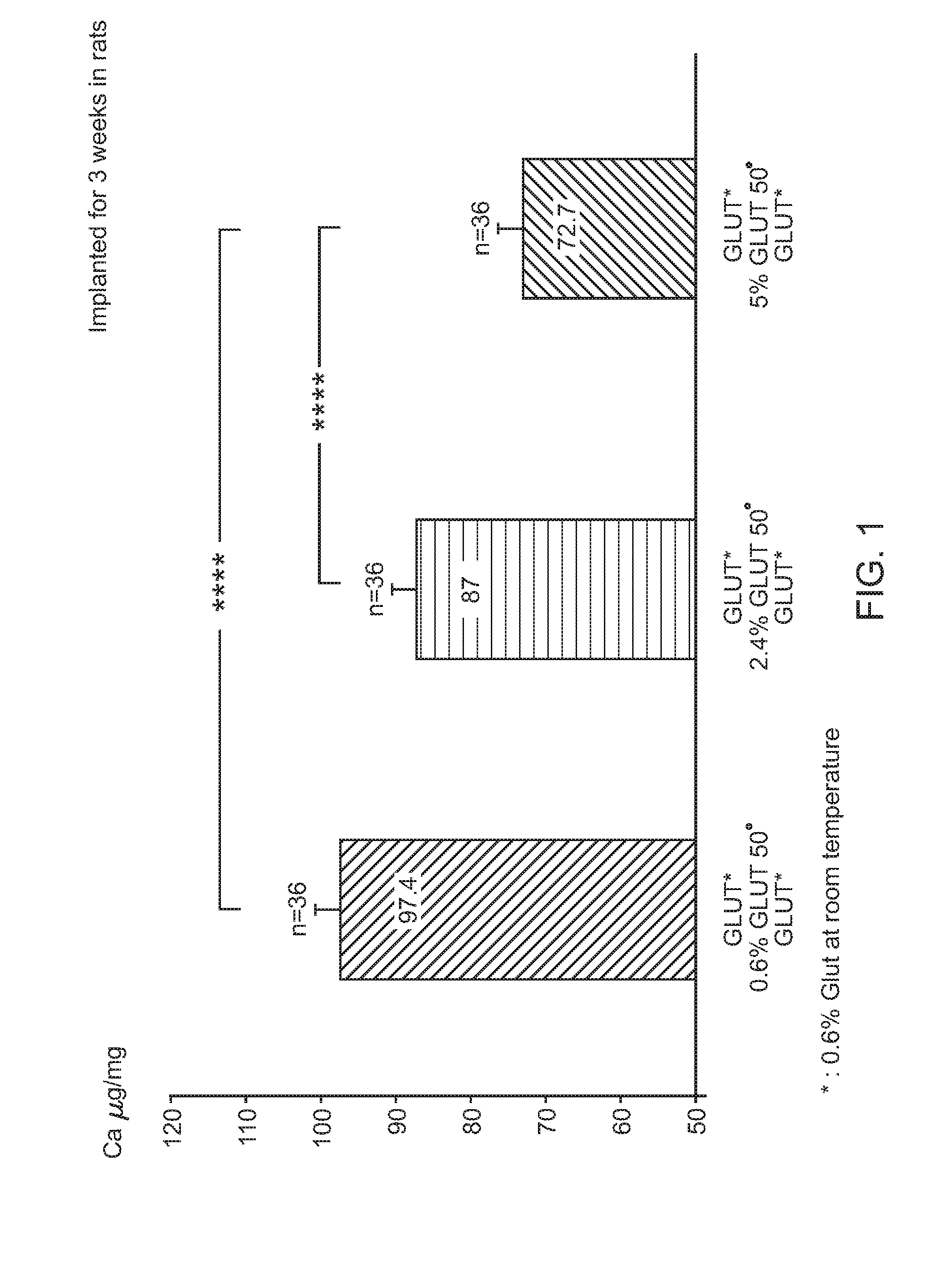
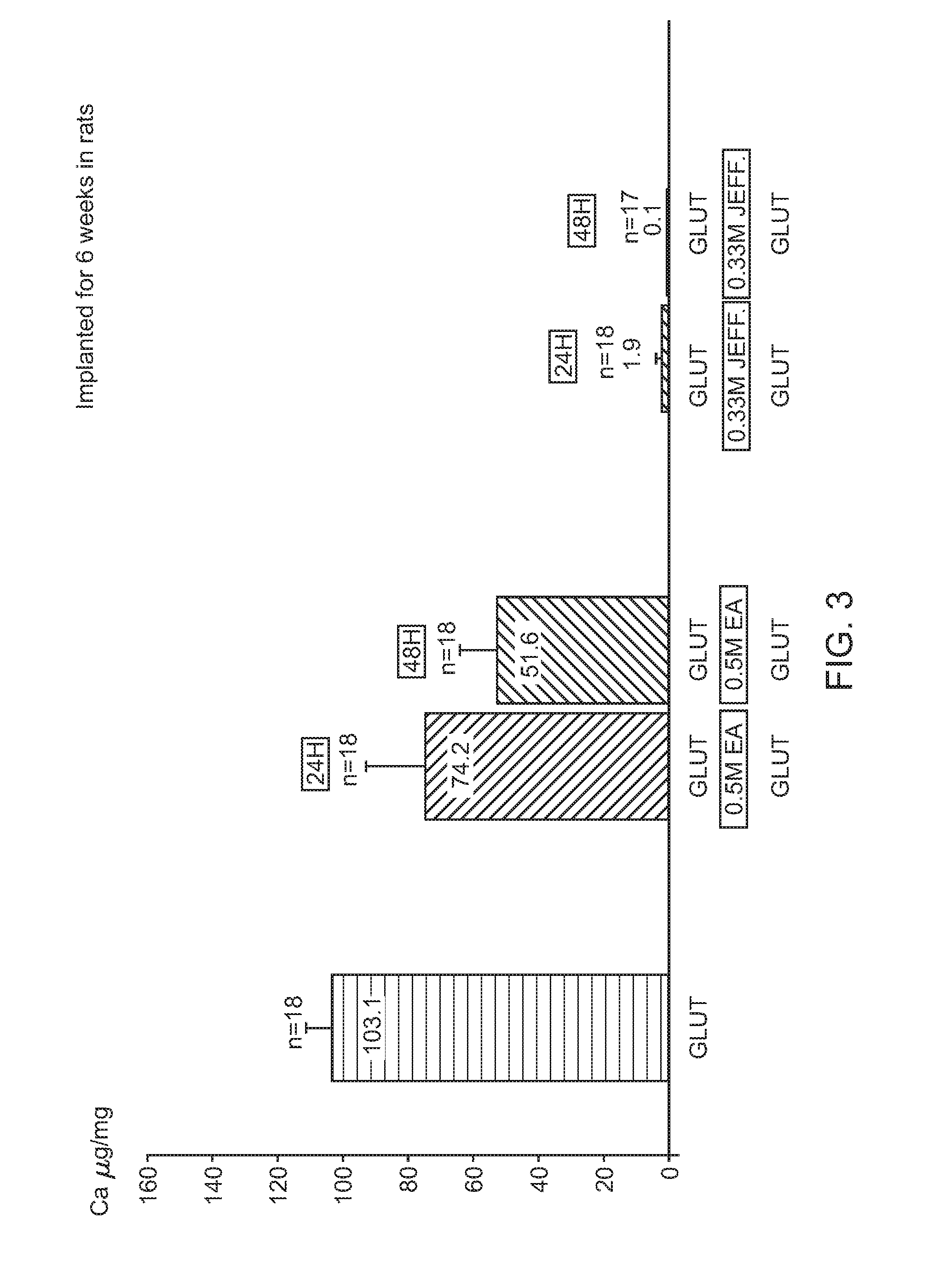
[0086]In order to evaluate the calcification mitigation properties of pericardial tissue treated in accordance with the method described herein (“SFX-treated”), animal feasibility studies were conducted. After rinsing of the samples in 0.9% NaCl to eliminate excess Glut, 18 samples / treatment (n=4 / rat) were implanted subcutaneously on the back of 12 day old rats for 6 weeks (FIG. 3). These studies demonstrated that Jeffamine crosslinking / sodium borohydride treatment is superior to ethanolamine / sodium borohydride which is superior to the control group (Glut only) in mitigating the occurrence of calcification in tissue (0.1 vs 51.61 vs 103.1 μg / mg). In all studies in rats, SFX-treated tissue demonstrated reduced variability in calcification data when compared to control tissue. Data from intramuscular implantation in rabbits were discarded because they were associated with too many variations.
example 2
Aldehyde Crosslinking Using Jeffamine and Sodium Borohydride of Glutaraldehyde-Fixed Tissue
[0087]Bioprosthetic tissue was removed from 0.625% glutaraldehyde just after a heat treatment step, and stored in 0.6% Glut (pH 7.4) for 2 days. One litre of crosslinking solution was prepared containing 333 mM Jeffamine (Poly (propylene glycol) bis-(2-aminopropyl ether), average M 230 (Aldrich ref. 406651) and 0.25% sodium borohydride in DW. The capping solution was placed on an orbital shaker, then tissues (leaflets, pericardium) were placed in the solution with a ratio of 3 leaflets per 100 mL. The container was not completely sealed because hydrogen gas liberated by the chemical reaction with water could cause the container to explode. The orbital shaker was operated at between 60-80 rpm for 24 hours at 37° C. The tissue was removed and stored in 0.6% Glut solution for 2-3 days and then treated in the FET solution (formaldehyde, ethanol, Tween-80) for 9 hours at 32° C. before being stored ...
example 3
Amino Group Crosslinking Using a High Concentration of Dialdehydes at High Temperature
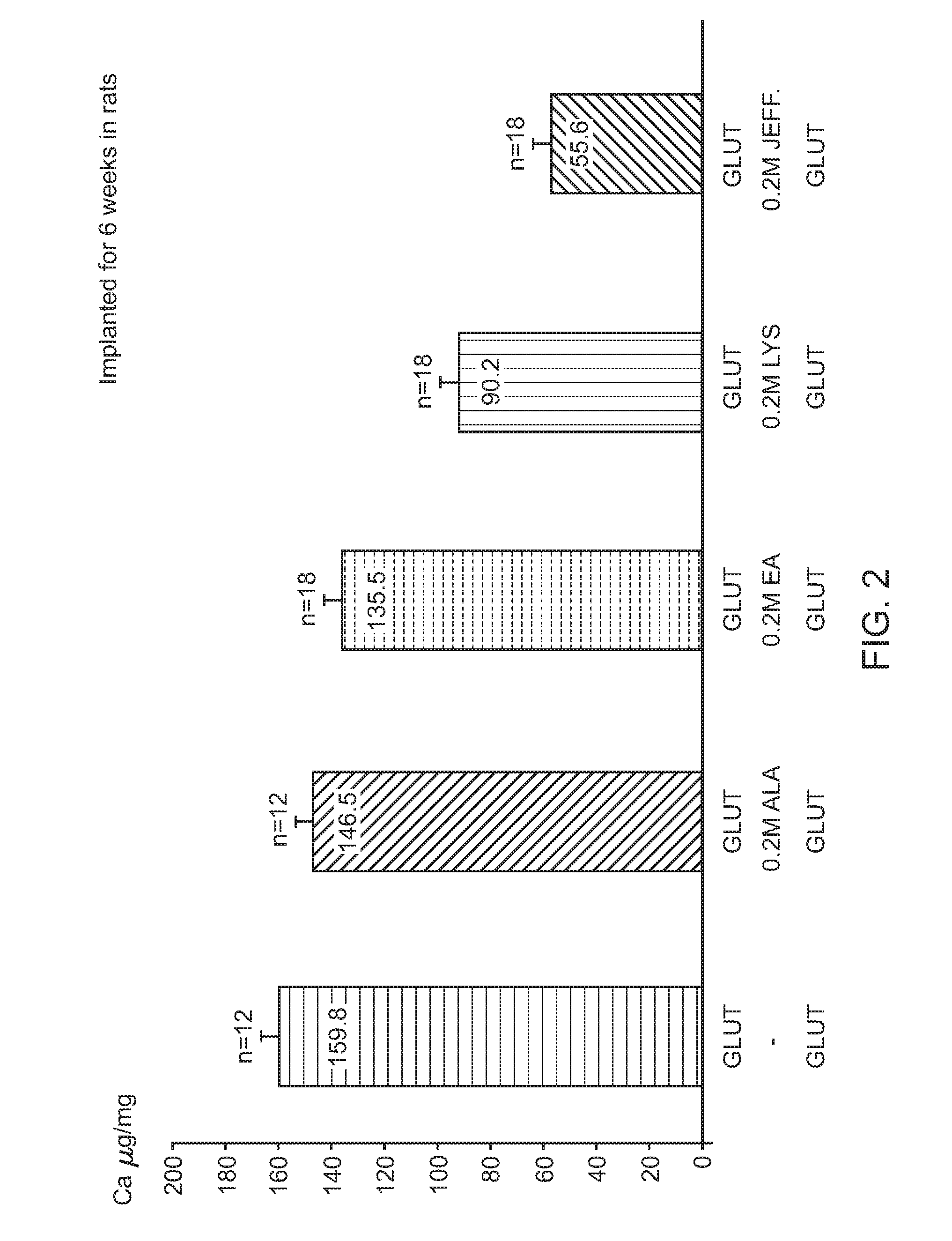
[0088]As shown in FIG. 6, tissues were treated first at 50° for 6 days, then in 0.5 M lysine for 24 hours at 37° C. with agitation. The FET treatment was applied either before or after lysine treatment.
[0089]The effect of lysine treatment is cumulative to the heat treatment, and FET further improves results. The place of FET could play a role with a preference when FET is after lysine treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com