Ompa and asp14 in vaccine compositions and as diagnostic targets
a technology of anaplasmosis and vaccine composition, which is applied in the field of anaplasma phagocytophilum outer surface protein a (ompa) epitopes, can solve the problems of insufficient tools for rapid and definitive diagnosis in any species other than dogs, high probability of actual cases, and inability to detect anaplasmosis in humans and animals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Neutravidin Affinity Purification of Biotinylated Aph DC Surface Proteins snd Two-Dimensional-Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (2D-LC / MS-MS) Proteome Analysis Identifies Novel Outer Membrane Protein Candidates
[0071]DC bacteria were purified to remove the majority of contaminating host cellular debris. DC surface proteins labeled by Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin were recovered by neutravidin affinity chromatography (data not shown). Aliquots of input host cell-free DC lysate, affinity-captured DC surface proteins, neutravidin beads plus unlabeled DC whole cell lysate (lane 3), and neutravidin beads alone were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining.
[0072]Because the Aph DC is the adherent and infectious form and the complement of DC surface proteins is unknown, we set out to identify DC surface proteins. Aph infected HL-60 cells were sonicated to liberate the bacteria from host cells and destroy fragile RC organisms. Electron microscopic examination of sonicated samples ...
example 2
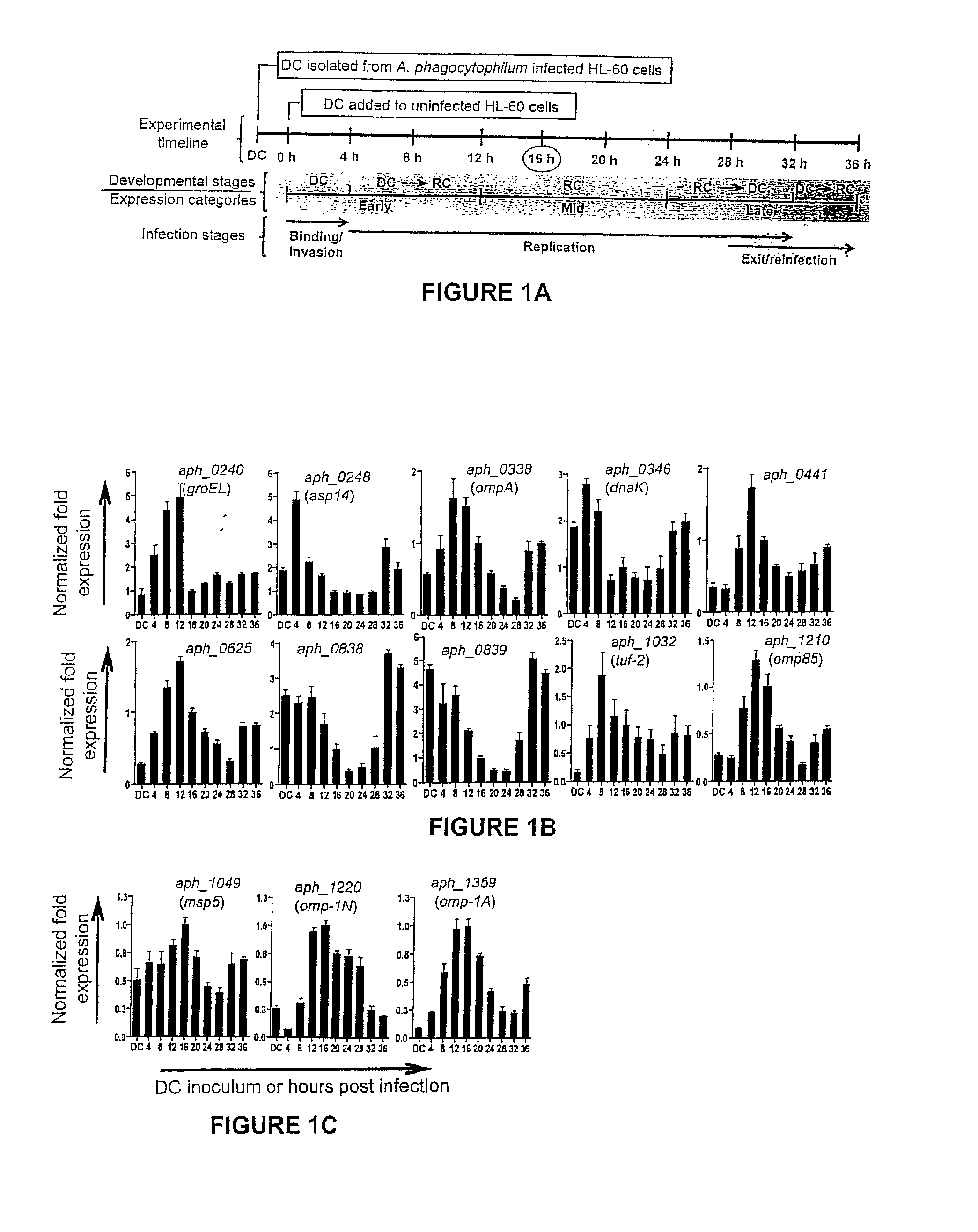
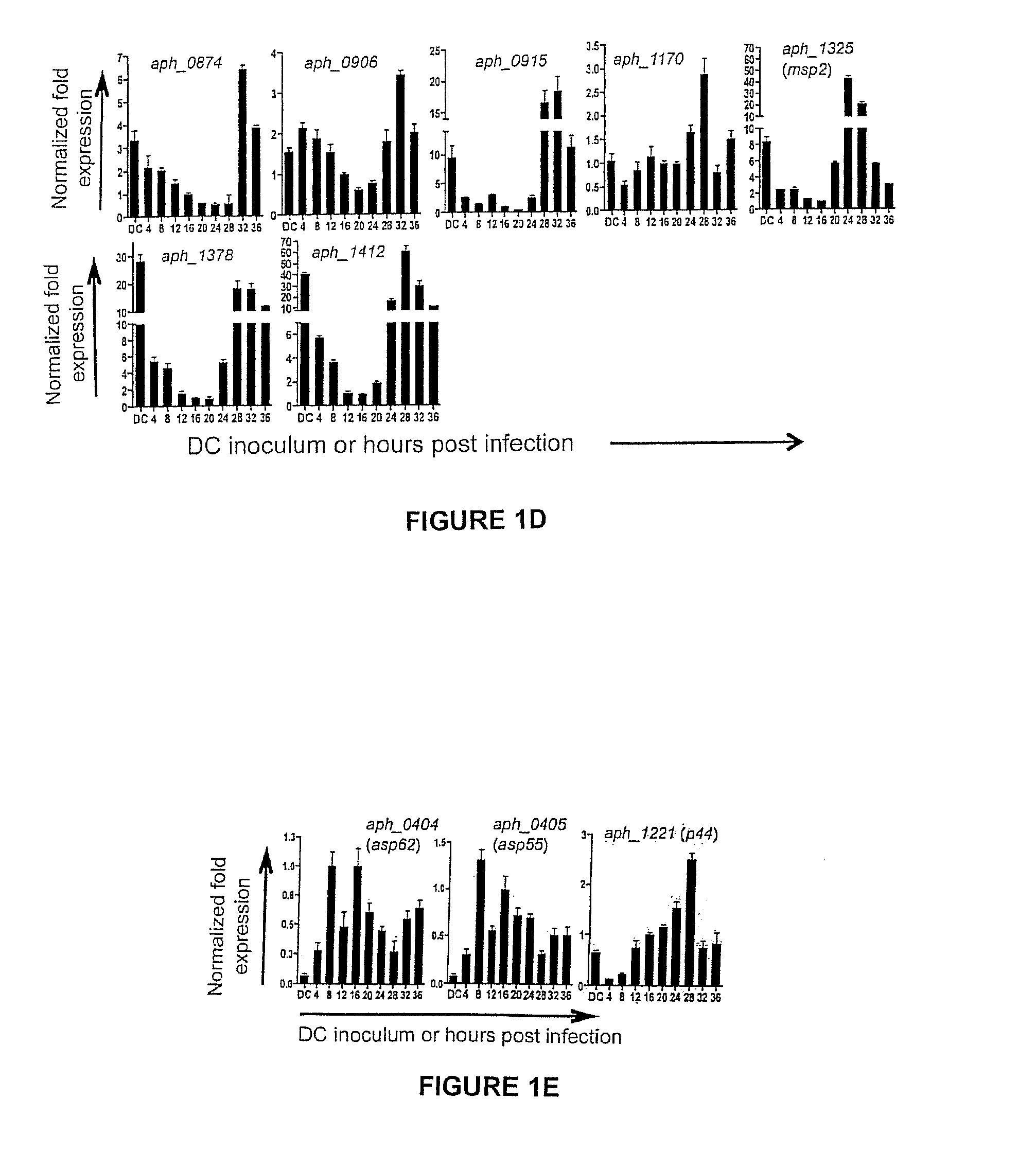
Selection of Aph OMP Candidates for Further Study. FIG. 1A Illustrates the Experimental Timeline Relative to the the Infection Cycle and Stages of Aph Organisms during Infection of a host
[0075]DC organisms were used to synchronously infect HL-60 cells and the infection proceeded for 36 h, a time period that allows for the bacteria to complete their biphasic developmental cycle and reinitiate infection. Total RNA was isolated from the DC inoculum and from infected host cells at several postinfection time points. RT-qPCR was performed using gene-specific primers. Relative transcript levels for each target were normalized to Aph 16S rRNA gene transcript levels using the 2−ΔΔCT method. To determine the relative transcription of OMP candidate genes between RC and DC organisms, normalized transcript levels of each gene per time point (shown in FIG. 1B-D) were calculated as the fold-change in expression relative to expression at 16 h (encircled in the experimental timeline in FIG. 1A), a t...
example 3
Differential Transcription Profiling of Omp Candidate Genes Throughout the Aph Infection Cycle
[0078]To gain insight into the transcription of the 20 genes of interest during the Aph infection cycle, we synchronously infected HL-60 cells with DC organisms and allowed the infection to proceed in order for the bacteria to complete their biphasic developmental cycle and initiate a second round of infection. We isolated total RNA from DC organisms used as the inoculum and from bacteria recovered at several post-infection time points. RT-qPCR was performed on total RNA using gene-specific primers. Relative transcript levels for each target were normalized to Aph 16S rRNA gene (aph_1000) transcript levels using the 2−ΔΔCT method. To facilitate identification of genes that are up-regulated in the infectious DC form compared to the non-infectious RC form, normalized transcript levels for each gene per time point were calculated as the fold-change in expression relative to expression at 16 h,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com