Automated Diagnosis-Assisting Medical Devices Utilizing Pattern Localization Of Quasi-Periodic Signals
a technology applied in the field of automatic diagnosis and medical devices utilizing pattern localization of quasi-period signals, can solve problems such as overlaid noise or other artifacts, and achieve the effects of enhancing existing electronic stethoscopes, not hindering devices from performing their tasks, and enhancing the accuracy of results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
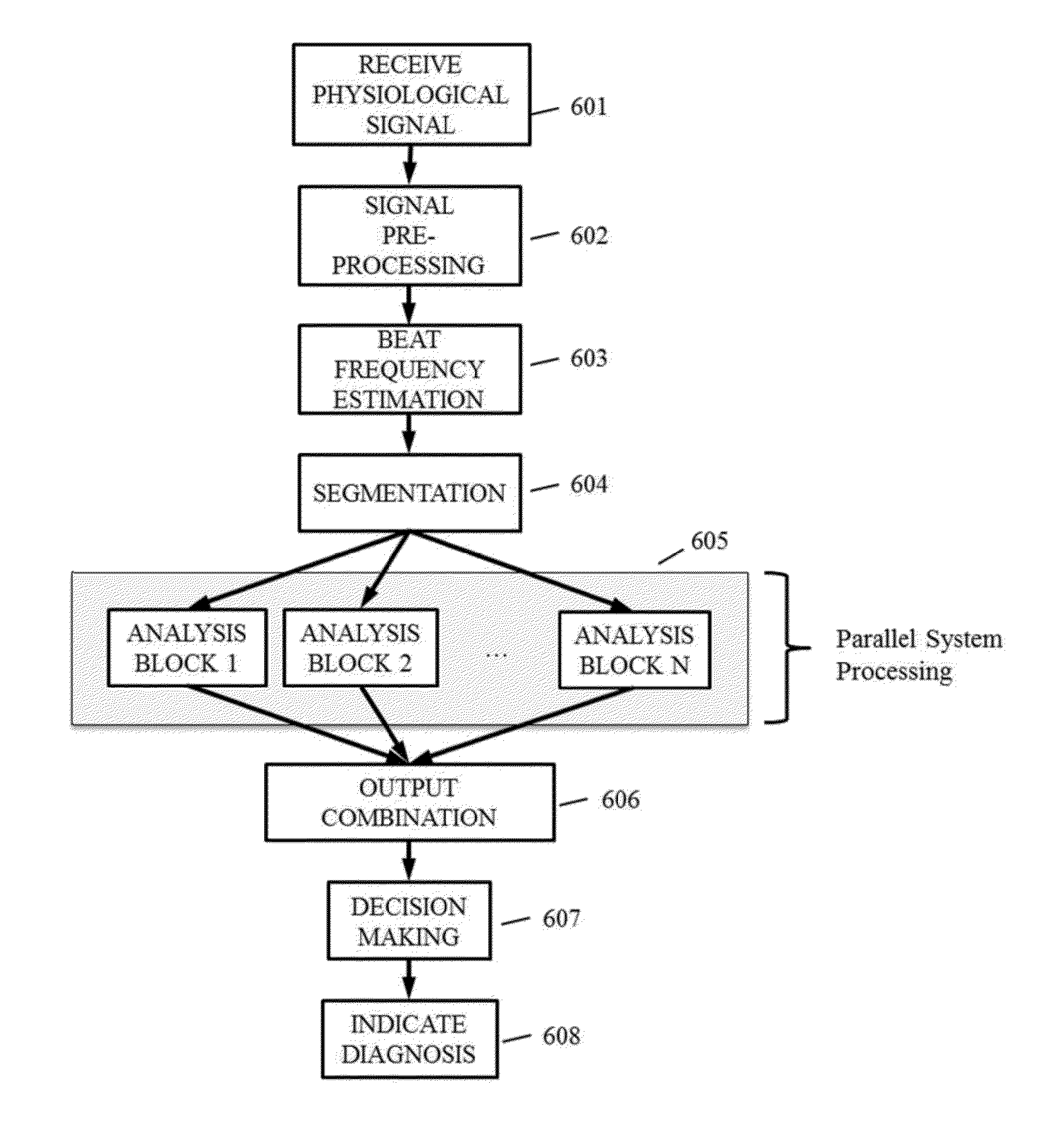
[0039]Referring to FIG. 1, a diagrammatic illustrates a rate / frequency estimation algorithm in accordance with one aspect of the present disclosure. At 101, a quasi-periodic input signal, such as an acoustical signal indicative of a physiological rhythm (e.g., heartbeat, respiration), is loaded. At 102, a DC component is removed from the input signal, s, according to sDCrem=s−mean(s), where
mean(x)=1N∑n=1Nx(n)
where is the mean operator, sDCram, is the input signal having its DC component removed, and N is the length of x.
[0040]At 103, filtering of the input signal is applied to produce a pre-processed signal that emphasizes the quasi-periodic patterns of the signal for rate estimation (e.g., the heart sound S1 and S2 in a phonocardiogram). The filtering is performed with a standard band-pass filter (high-pass filtering and / or low-pass filtering) or with wavelet filtering. In accordance with wavelet filtering, the signal is decomposed into detail and approximation coefficients, and, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com