User Interface for Patient Risk Analysis System
a risk analysis and user interface technology, applied in the field of system and method of risk-based patient monitoring, can solve the problems of increasing complexity of medicine, increasing information avalanche, and clinicians being confronted with an avalanche of patient data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
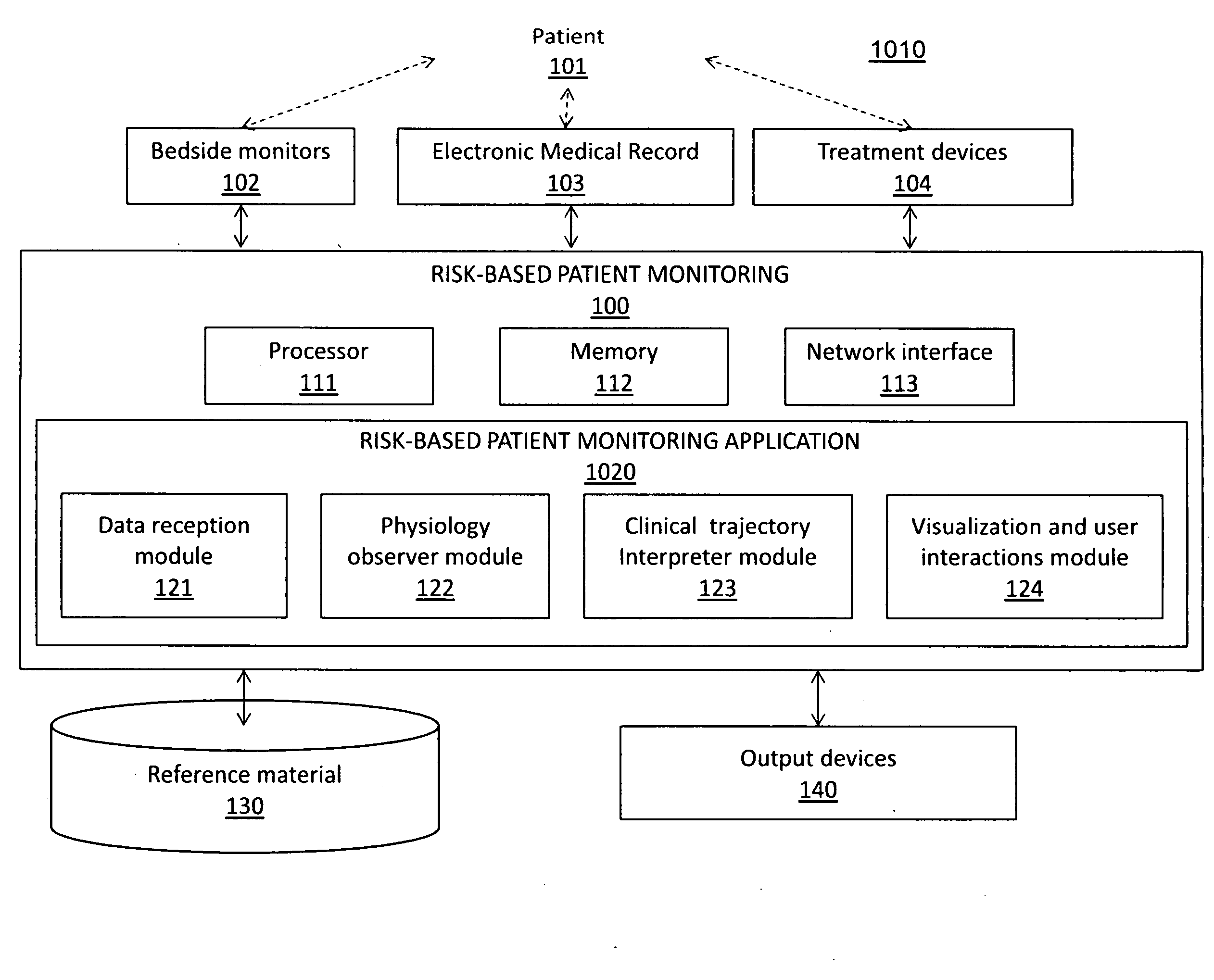
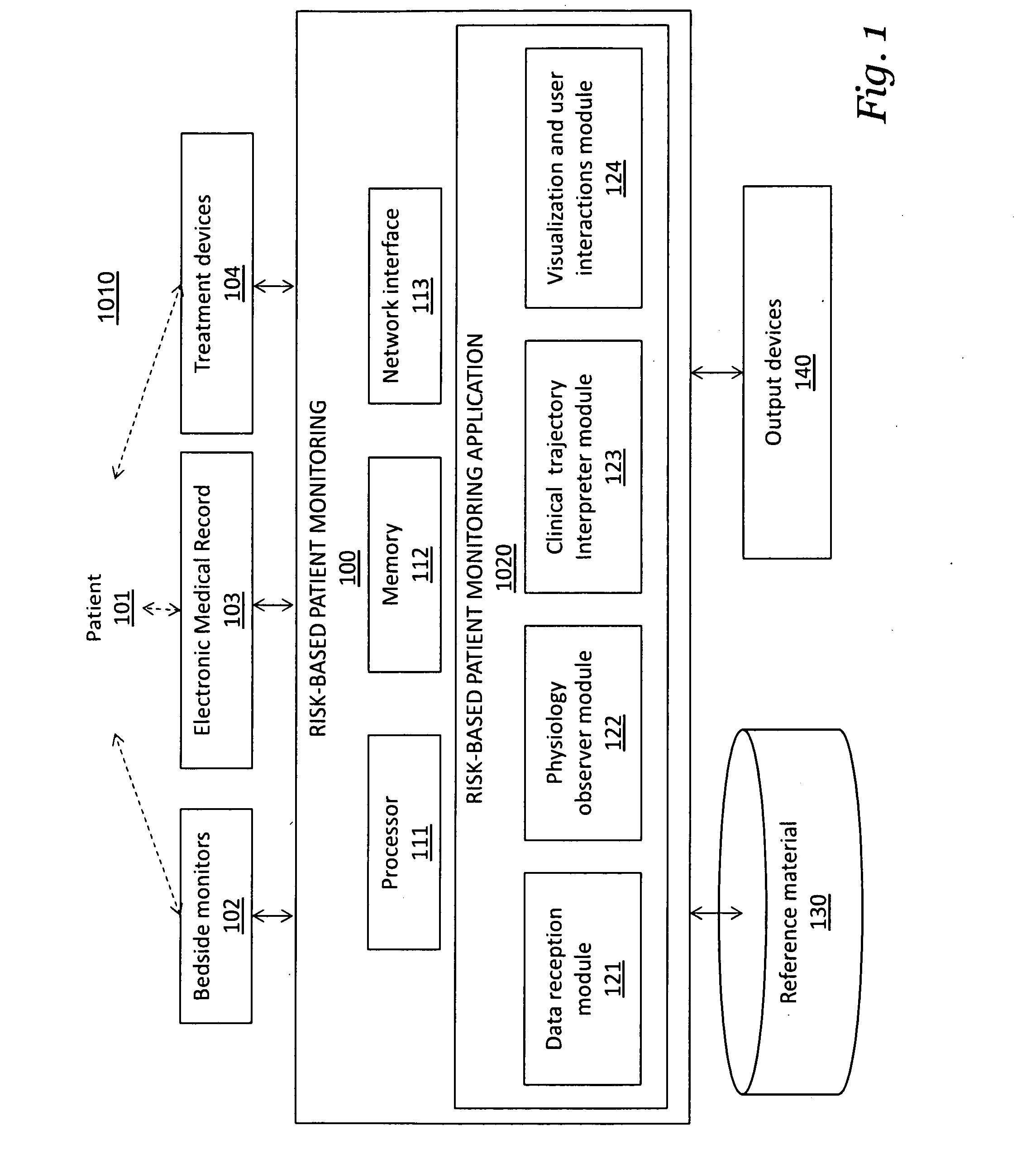
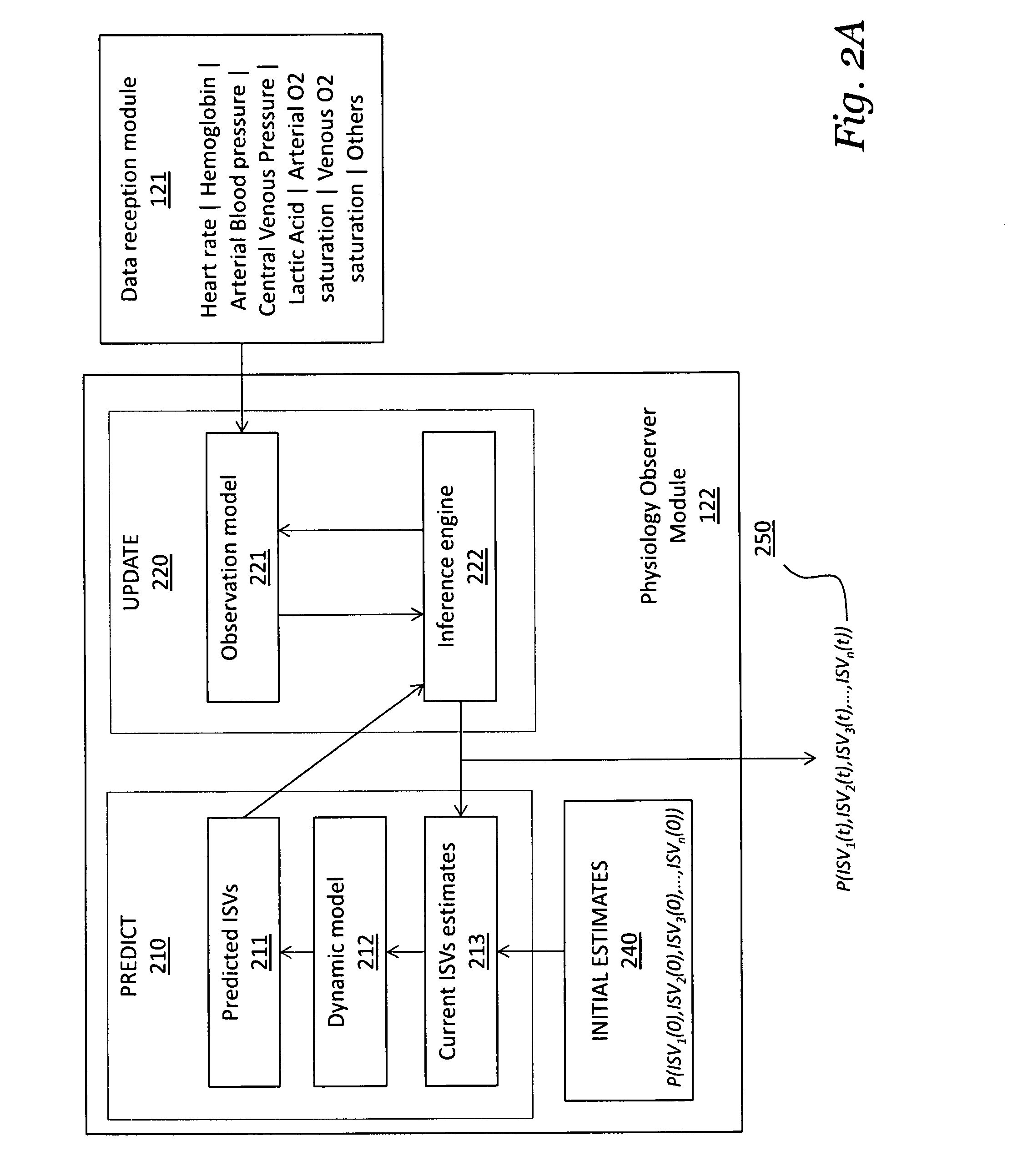
[0016]A first embodiment teaches a computer-implemented method of graphically communicating, to a user, patient risks for an individual patient, and includes the steps of receiving, from a device, data relating to a plurality of possible clinical patient states in which the patient may be classified; causing the display, on a display device, of a plurality of graphical indicators, each of the plurality of graphical indicators corresponding to one of the plurality of possible clinical patient states, each of the plurality of graphical indicators graphically identifying the probability that the patient is in a corresponding clinical patient state at a given point in a range of time, the plurality of graphical indicators configured to indicate a hazard level; and causing the display, on the display device, of a timeline controller configured to allow a user to dynamically select a plurality of points in time over the range of time, the graphical indicators changing dynamically in respo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com