Baby sling
a baby sling and sling body technology, applied in the field of baby slings, can solve the problems of user safety, slippage during use, etc., and achieve the effects of low elastic fabric, high reliability of knitting, and stable quality control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
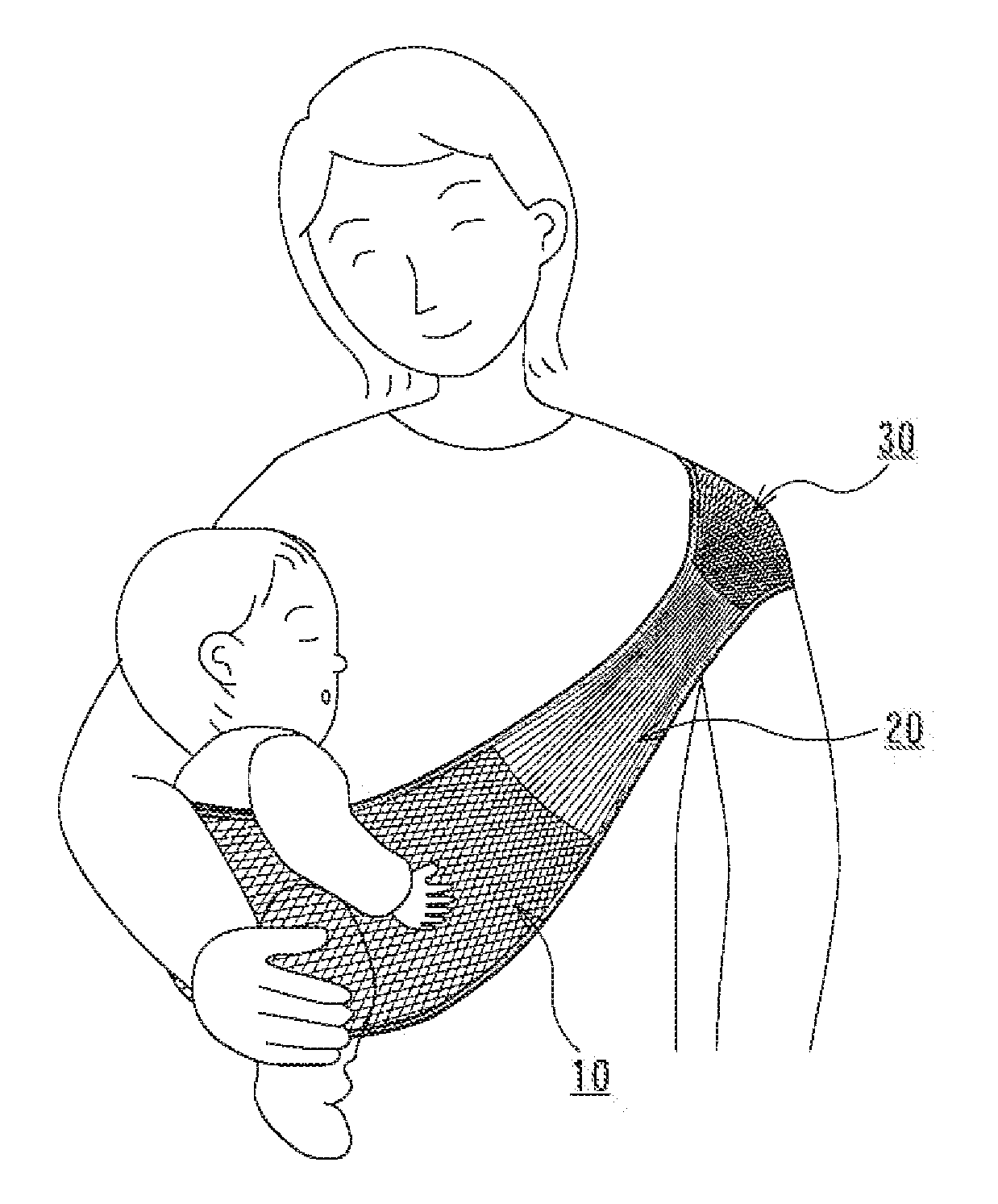
[0058]In FIG. 1, a baby sling according to an embodiment of the present invention includes an infant holding part 10, a belt part 20 and a shoulder pad part 30 integrally knitted together to form an annular shape.
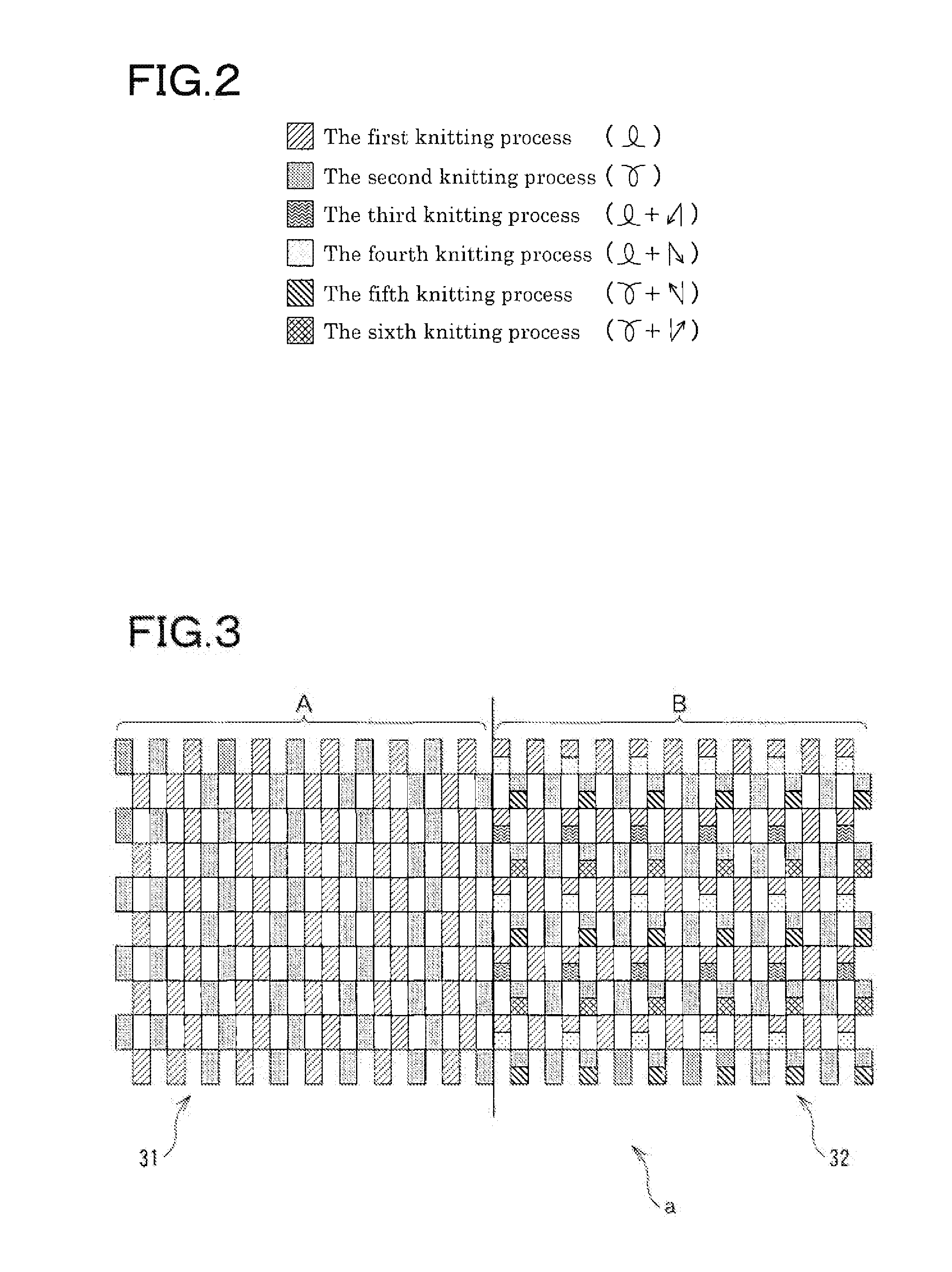
[0059]The infant holding part 10 has a maximum width that corresponds to a central part in a longitudinal direction of an annular body and a gradually decrease in width between both sides in the longitudinal direction of an annular body toward both ends in the longitudinal direction of the annular body. In addition, both sides in the longitudinal direction of the annular body are formed of a knitted fabric “A” that has a low elasticity in the longitudinal direction of the annular body and includes an outer part 11 which is knitted with a rib stitch, also known as Japanese “gomuami”. The rib stitch that is applied to the outer part 11 is referred to as the Japanese “gomuami” or a fraise stitch also. There is no distinction between opposite surfaces of a knitted fabric thereo...
second embodiment
[0087]FIG. 12 shows a baby sling according to a second embodiment of the invention in which a shoulder pad part 30 has some increase in part of width in a width direction which is at right angle to a longitudinal direction of an annular body. The shoulder pad part 30 has the increased width which is longer than a width of a belt part 20 by 10 to 30%. Thereby, a burden on a shoulder of a person who carries an infant with the baby sling can be shared and reduced. Especially in the second embodiment shown in FIG. 12, the shoulder pad part 30 is an extension of the same rib stitch as the belt part 20. Therefore, workability may be improved.
[0088]In the baby sling according to the second embodiment of the invention, the shoulder pad part 30 has some increase in part of width in the width direction which is at right angle to the longitudinal direction of the annular body by 10 to 30% compared to the width of the belt part 20. However, an infant's body weight is about 10 kg. Thereby, the s...
third embodiment
[0103]FIG. 13 shows a baby sling according to a third embodiment of the invention. As shown in FIG. 13, a shoulder pad part 30 has a center that is curved upward to form a convex shape when the baby sling is folded in two so as to be at right angles to each other in a longitudinal direction of an annular body. In this case, as shown in FIG. 11a, when the curved convex-shaped portion is placed on a shoulder, to be precise when a concave part that is inside the convex-shaped portion is placed on the shoulder which has a convex shape, an infant's body weight can be a composition of vectors going from an upper side and a lateral side of the shoulder. Thereby, even a person who is likely to have a stiff shoulder can use it so that he or she is not likely to have the stiff shoulder. Moreover, it does not put a burden on an adjacent part of a neck. Therefore, the user's burden such as fatigue can be reduced.
[0104]Thus, the baby sling allows a burden on shoulder of a person who carries an i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com