Safety Switch Using Heat Shrinkage Tube and Secondary Battery Including The Same
a safety switch and heat shrinkage tube technology, applied in the field of safety switches, can solve the problems of shrinkage of the heat shrinkage tube to operate the safety switch of the battery, and achieve the effect of effectively discharging heat generated, reducing internal energy accumulated in the battery cell, and consuming charge energy of the battery cell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040]Now, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be noted, however, that the scope of the present invention is not limited by the illustrated embodiments.
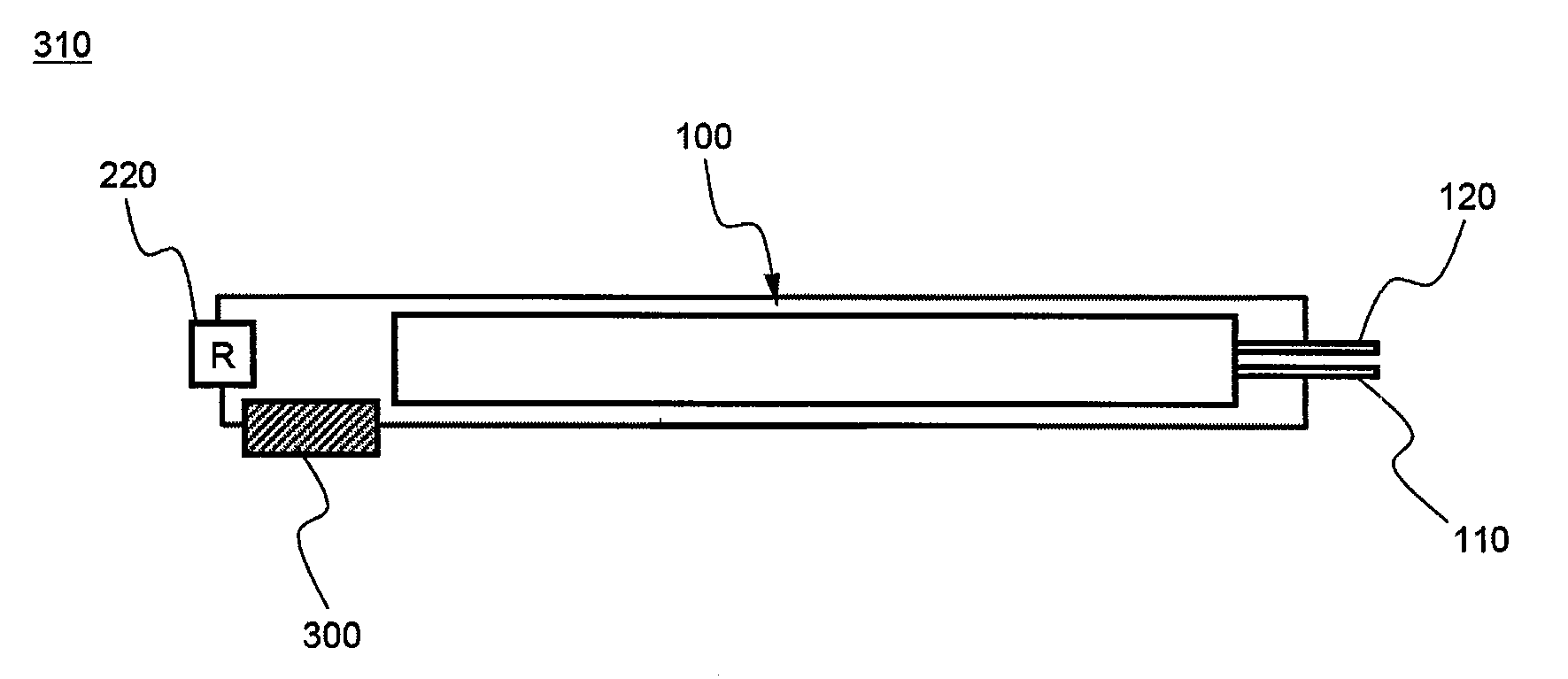
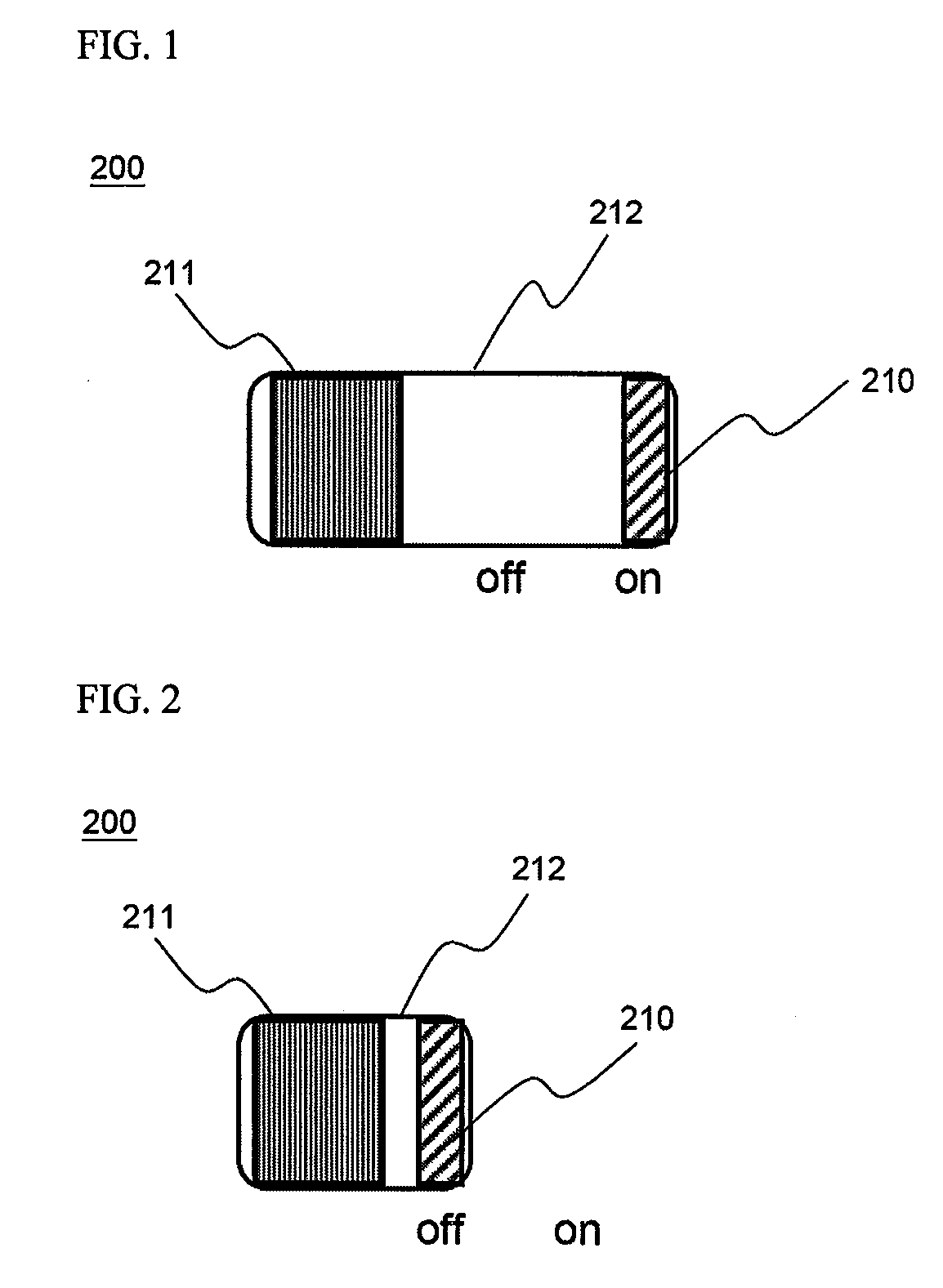
[0041]FIGS. 1 and 2 are typical views illustrating the operating principle of a safety switch according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, FIG. 1 illustrates the state of the safety switch, during the normal operation of the battery, before the operation of the safety switch is performed, and FIG. 2 illustrates the state of the safety switch, when the battery is abnormally operated, after the operation of the safety switch is performed. For convenience of description, the safety switch shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 will be hereinafter referred to as a charge switch.
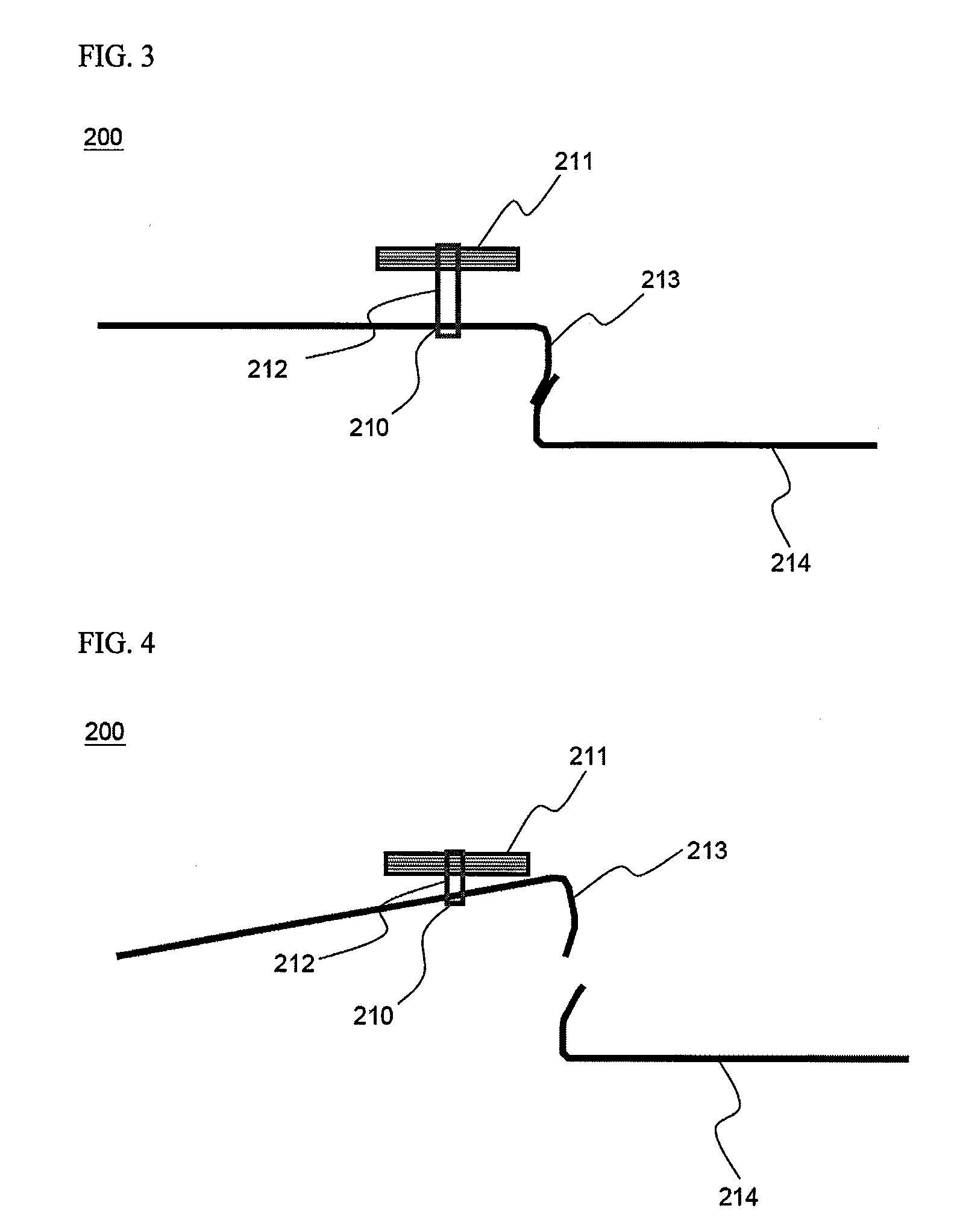
[0042]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the safety switch 200 is constructed in a structure in which one side of a heat shrinkage tube 212 is fixed by a support ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com