Thermal signature target form
a technology of thermal signature and target form, which is applied in the direction of heat exchange equipment, metal-working equipment, weapons, etc., can solve the problems of not being competitive in the thermal target market, screen printed ink matrix technology lacks a sturdy, durable form, and is unsuitable for repeated projectile impact during live-fire training exercises
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
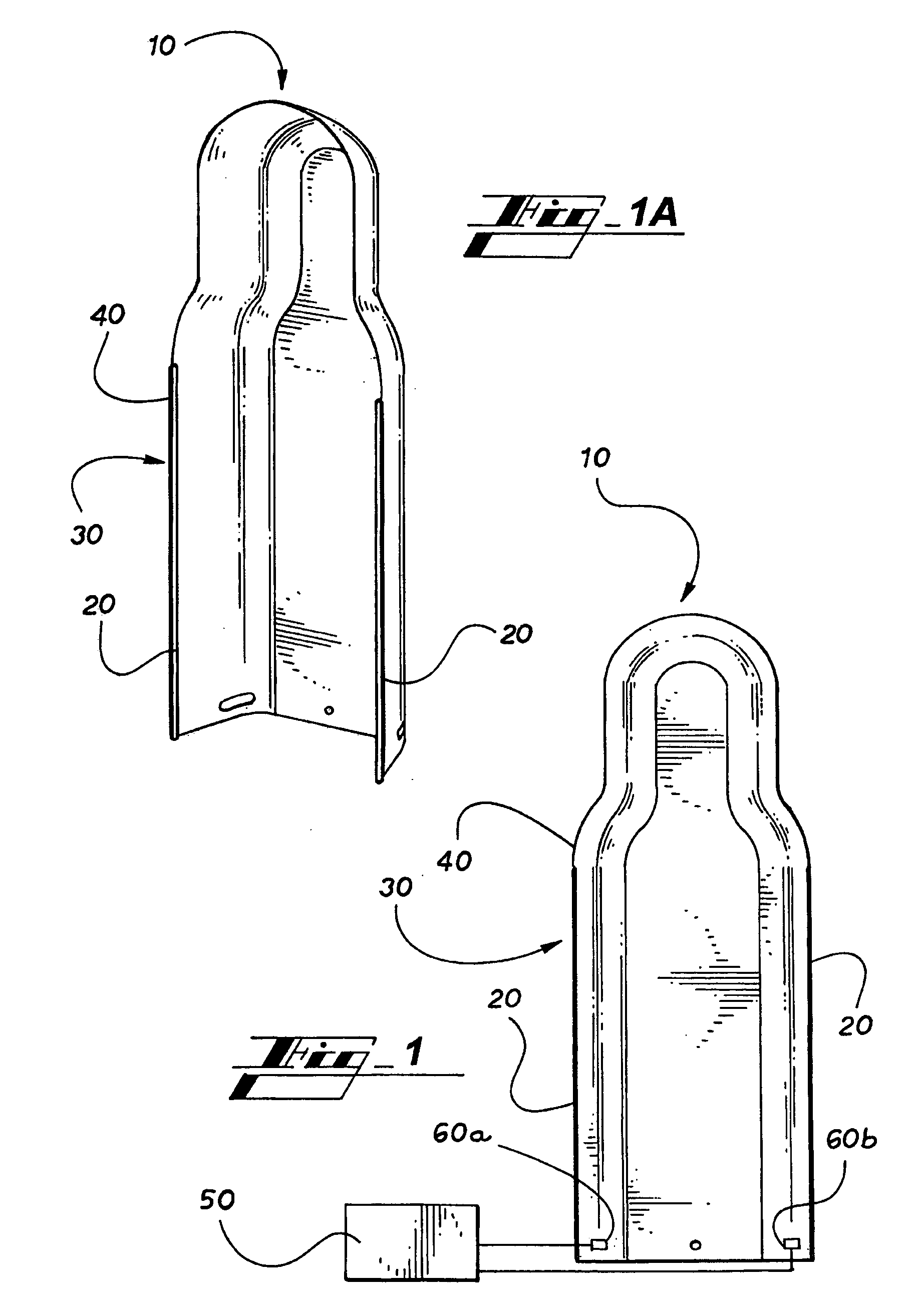
[0017]With reference to FIG. 1 and FIGS. 1a-1d, a molded thermal signature target form 10 in accordance with an embodiment of the invention is illustrated. A thermal signature target form 10 comprises a conductive polymer material suitable for conducting infrared (IR) radiation such that a thermal signature is created and viewable by any number of suitable IR imaging or viewing systems. A pair of busbars 20 are embedded or attached to the outside edge 30 of the thermal signature target form 10, and the busbars 20 direct electrical current throughout the entire target form 10. When the thermal signature target form 10 is electrically energized, the resistance of the conductive polymer material creates heat, causing the target form 10 to emit infrared (IR) radiation which can be detected using suitable IR imaging or viewing systems. The busbars 20 can be attached to the thermal signature target form 10 by pre-molding grooves 40 into the target form 10 and embedding the busbars 20 in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com