Moving blade for a turbomachine, the blade having a common cooling air feed cavity
a turbomachine and moving blade technology, which is applied in the direction of blade accessories, machines/engines, mechanical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the life of the blade, difficult to provide a robust ceramic core, and significant risk of a core breaking, so as to facilitate air flow and simplify fabrication.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
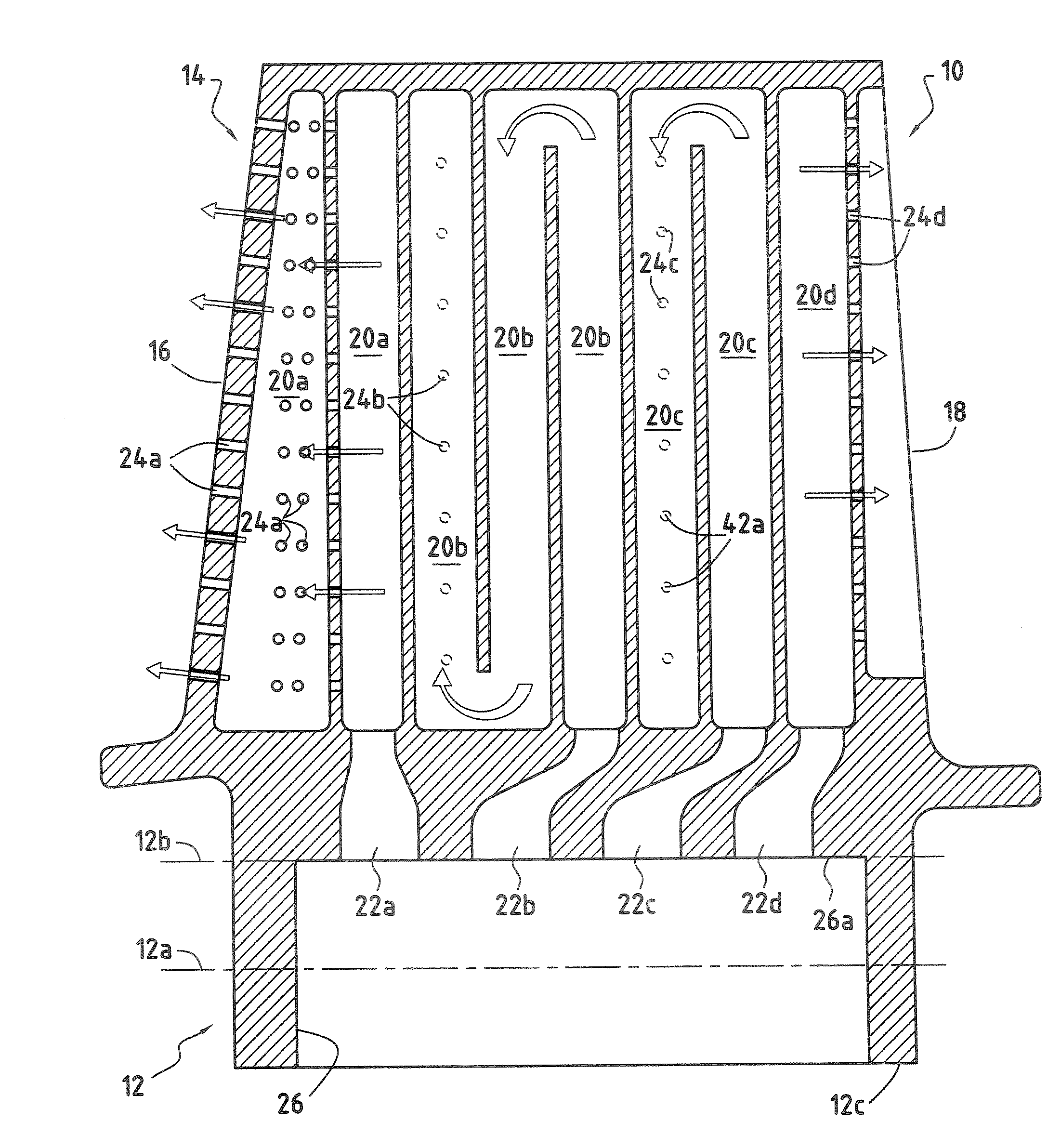
[0018]FIGS. 1, 2A, and 2B show a moving blade 10 for a turbomachine, such as a moving blade of a high-pressure turbine. Naturally, the invention can also be applied to other moving blades of the turbomachine, for example to the low-pressure turbine blades thereof.
[0019]The blade 10 has an aerodynamic surface that extends radially between the blade root 12 and a blade tip 14. This aerodynamic surface comprises a leading edge 16 placed facing the flow of hot gas coming from the combustion chamber of the turbomachine, a trailing edge 18 opposite to the leading edge 16, a pressure side face, and a suction side face, the side faces (not shown in the figures) interconnecting the leading edge 16 and the trailing edge 18.
[0020]The blade 10 also has two lower swellings (or teeth) 12a disposed laterally on either side of the blade root 12 and two upper swellings 12b also disposed laterally on either side of the root, these swellings 12a, 12b defining bearing surfaces for fastening the root in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com