Orthopedic device and method for correcting angular bone deformity
a technology of orthopedic devices and angular bones, applied in the field of orthopedic devices and methods for correcting angular deformation, can solve the problems of increased joint arthritis, reduced bone density, and pain in the knee, and achieve the effects of correcting angular deformation, and promoting asymmetric growth of growth plates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
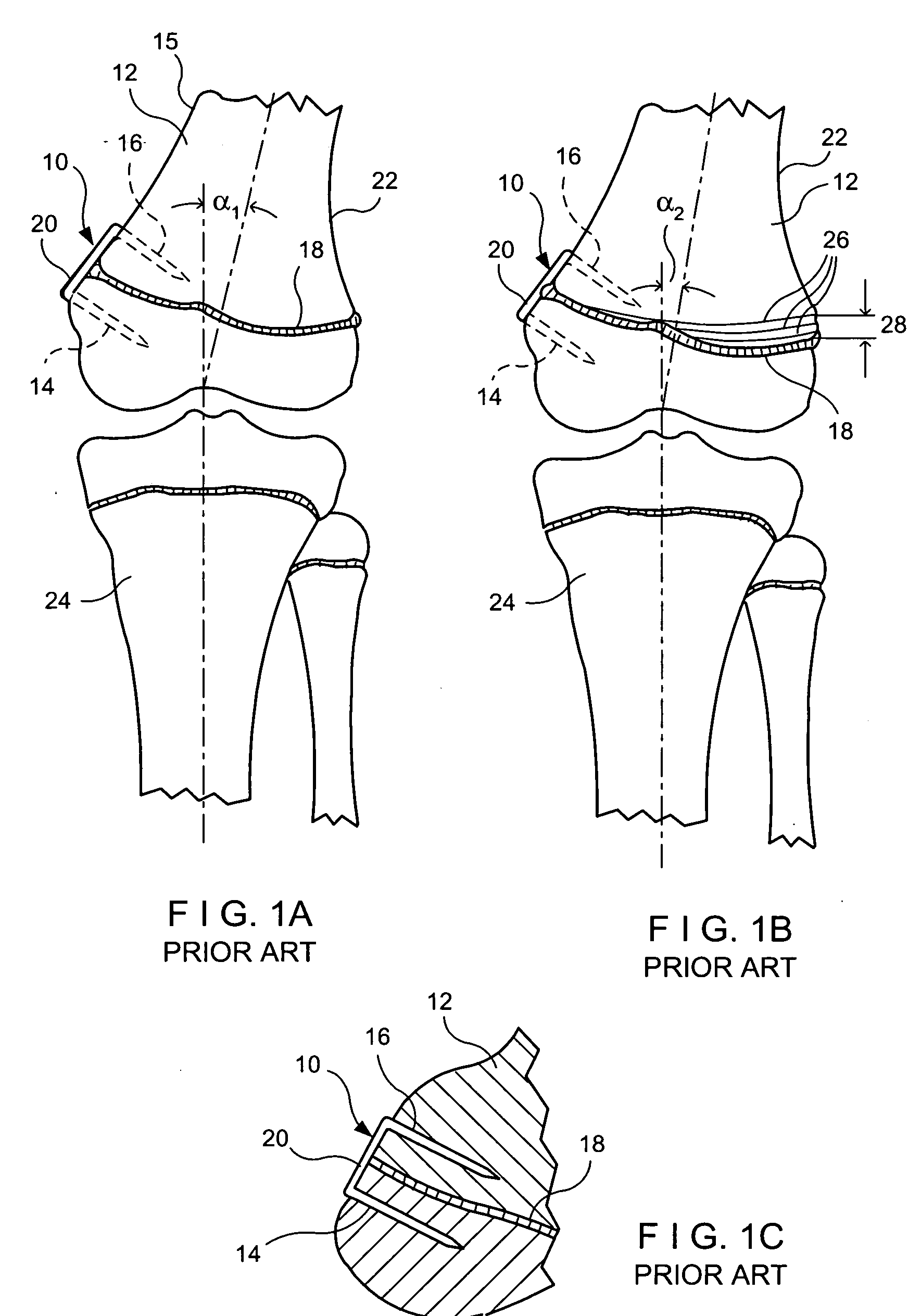
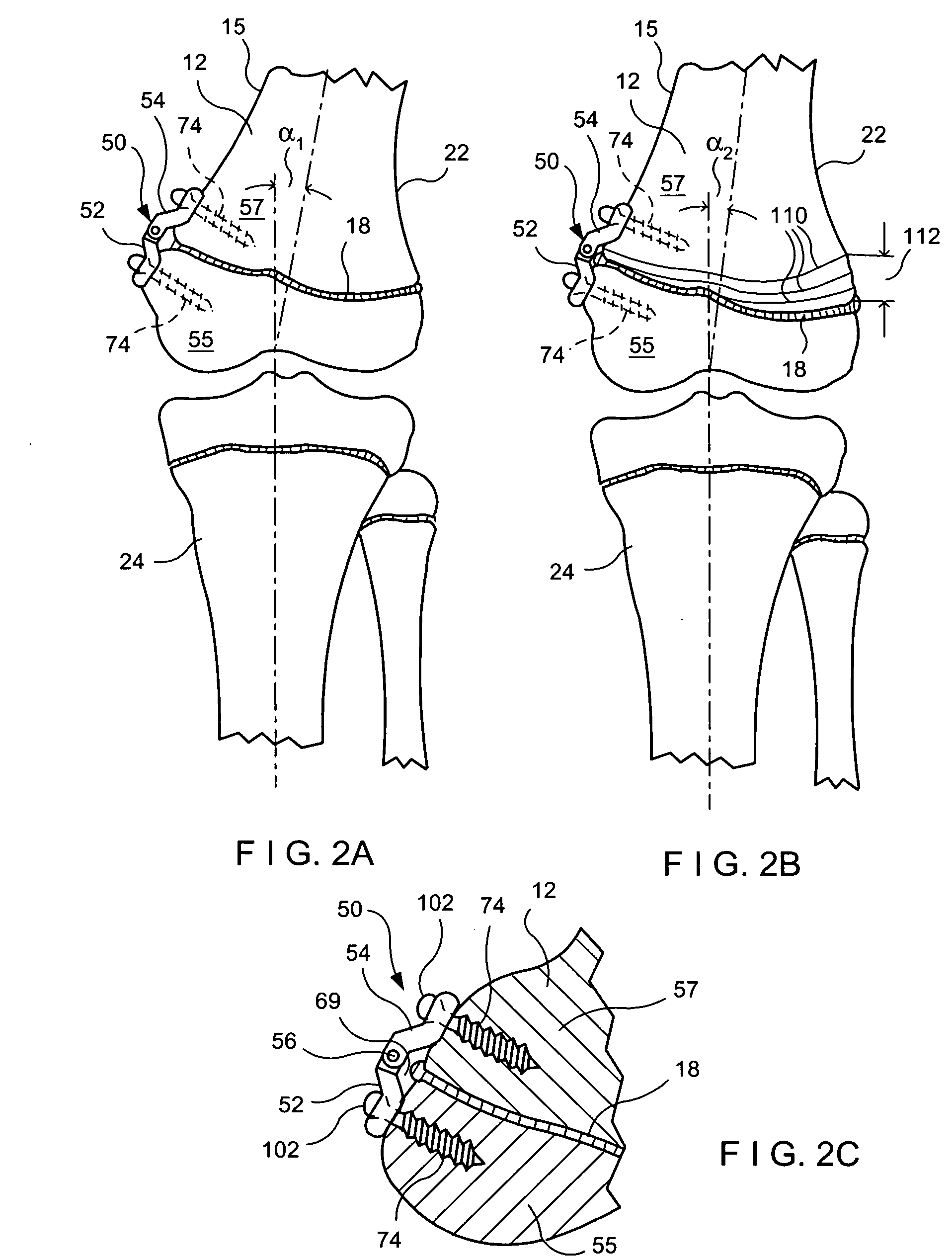
[0032] Referring to the drawings and to FIGS. 2A-2C in particular, wherein a procedure for correcting a genu valgus condition in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is illustrated. The procedure includes installing a unique orthopedic device 50 onto the lateral side 15 of the distal femur 12 about the distal femur physis or growth plate 18. For a genu varus condition, the orthopedic device 50 would alternatively be mounted onto the medial side 22 of the distal femur 12 about the growth plate 18. Other locations that may be suitable for installing the orthopedic device 50 may include, without limitation, the growth plate region of proximal tibia, distal tibia, proximal femur, as well as locations on the humerous, ulna and / or radius and spinal formation.
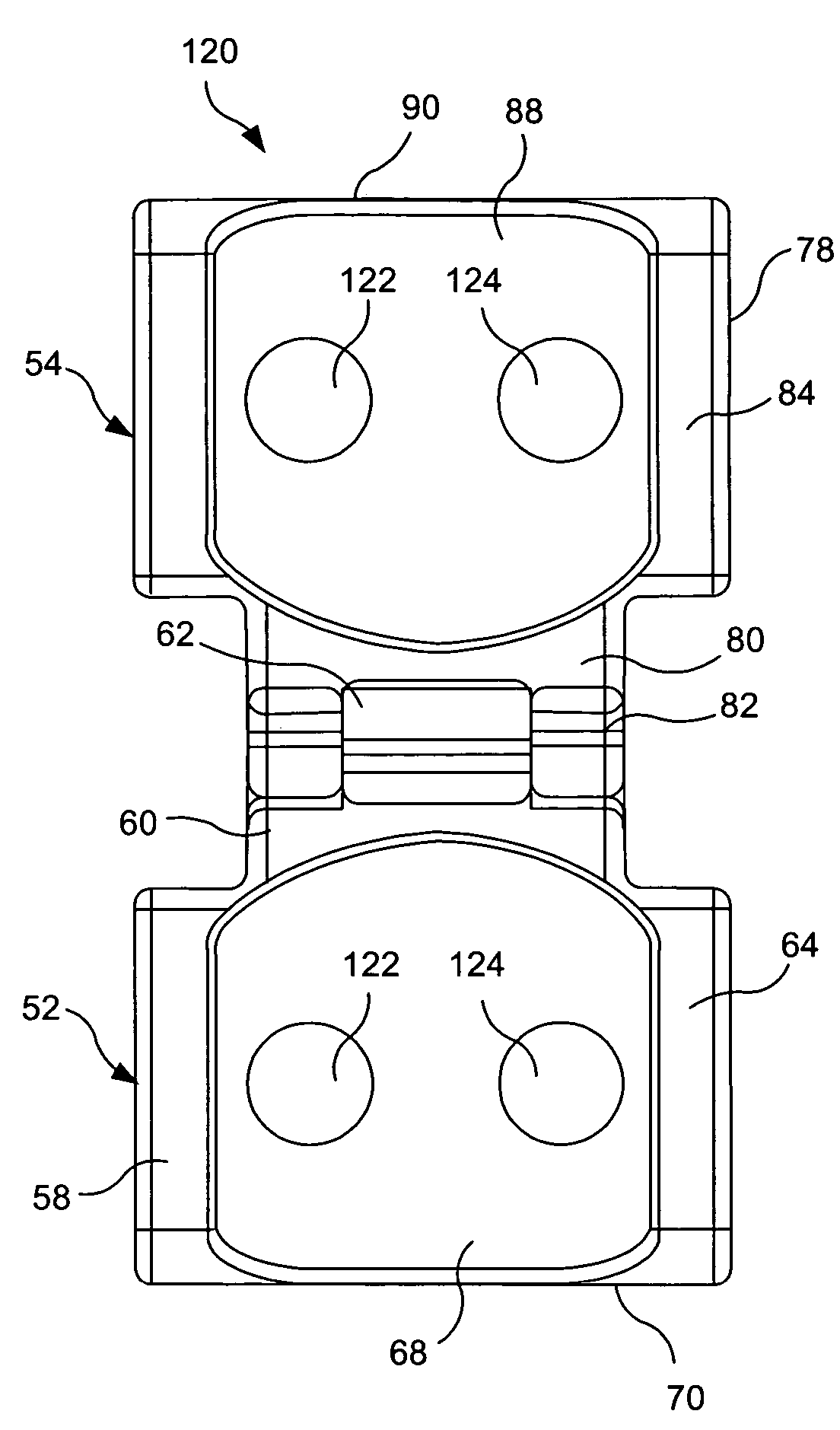
[0033] With further reference to FIGS. 4-10, the orthopedic device 50 includes a first substantially rigid hinge plate 52 pivotally connected to a second substantially rigid hinge plate 54 by means of a hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com