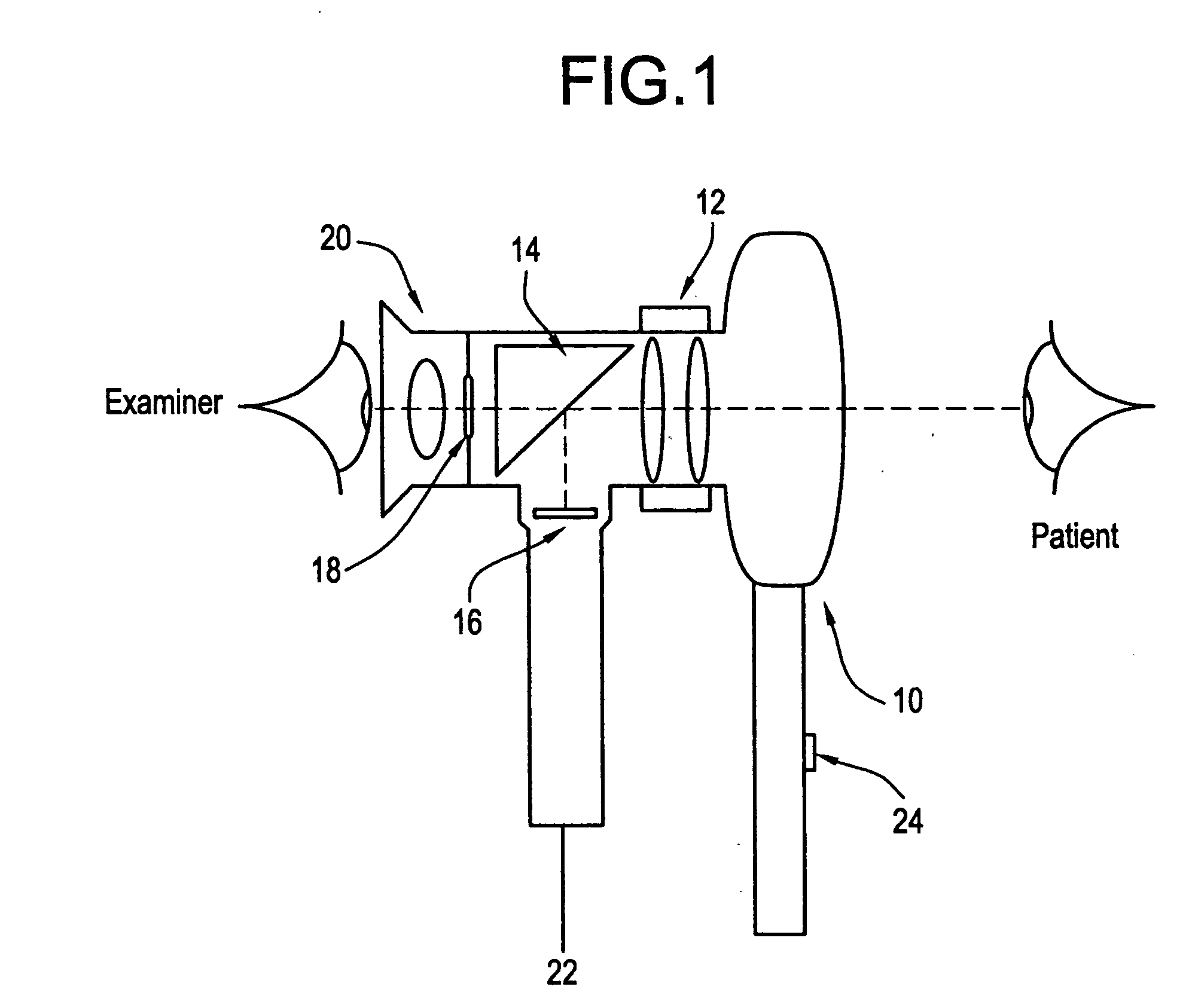
Video opto-diagnostic instrument with single-adjustment focus
a technology of opto-diagnostic instruments and focus, which is applied in the field of medical diagnostic instruments, can solve the problems of not having the above devices ensure that the image viewed by the examiner is in fine focus, and the focus of the image requires separate adjustments for the two different images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
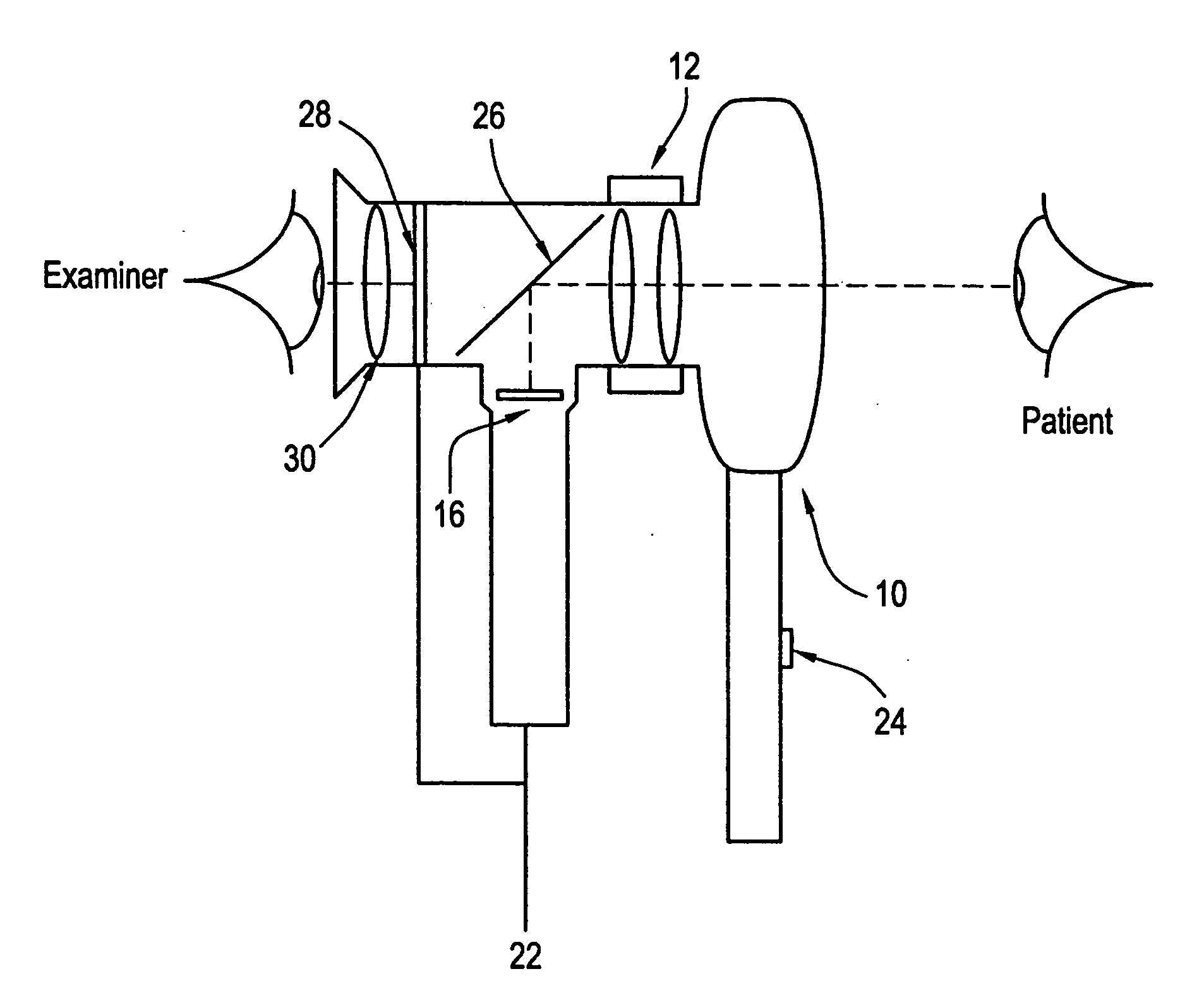
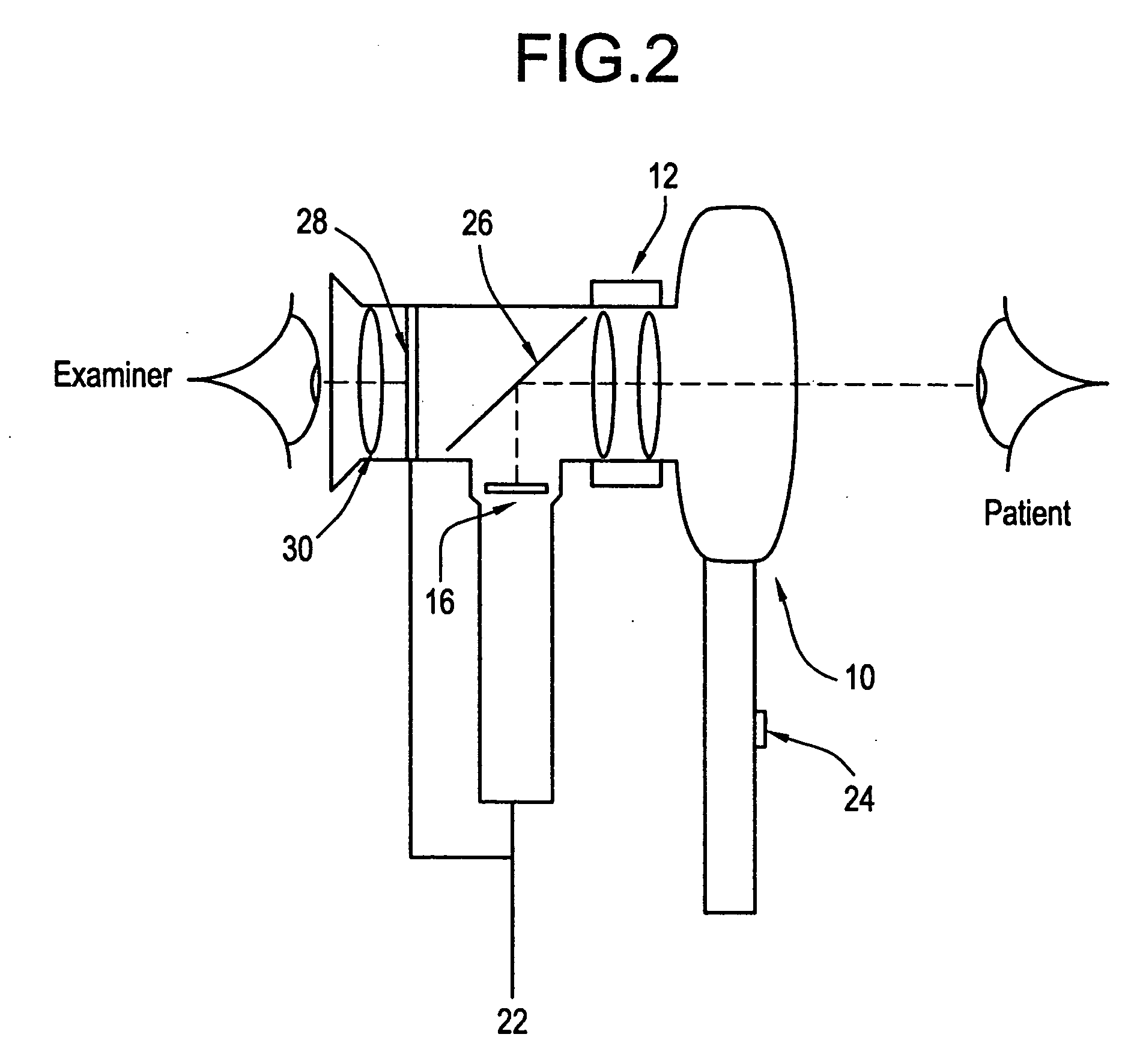
[0027] In a second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2, the examiner is able to view the output of the imager 16 directly. This is accomplished by replacing the beam-splitter assembly with a simple folding mirror 26 and mounting a miniature liquid crystal display (LCD) 28 and display viewing optics 30 where the physician would ordinarily place his eye on the ophthalmoscope. The light from the patient's eye is reflected by mirror 26 to form a first image on imager, 16, e.g., a CCD array. The output of the imager 16 is then sent to the LCD 28 to form a second image. Thus, the examiner by viewing the second image will be able to see the quality of the first image captured by the imager 16 and can compensate for poor image quality by adjusting the focus using lens system 12. Thus, the examiner is able to focus both first and second images simultaneously. The fine focus of lens system 12 can be automated.
third embodiment
[0028] In a third embodiment as shown in FIG. 3, an additional optics / detection system is incorporated to effect an automatic focusing thus relieving the physician of the focusing operation for the imager 16. The lens system 12, minus the focusing wheel (not shown separately) which remains in its original position, has been moved although it could be retained in its original position as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2. The beam splitter allows the examiner to view the patient's eye directly while also causing light to pass through the lens system 12 and a partial reflector 32 to form a first image on CCD 16. The partial reflector also sends light to mirror 34 which sends the light through lenslet array 36 to form a second image on a linear CCD array 38. The output from the linear CCD array is then sent through a difference amplifier 40 to form an error signal which is sent to lens system 12 through feedback loop 42. Such a system will judge if the image is sharp (in focus) based upon well-un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com