Method and apparatus for determining coolant temperature rationality in a motor vehicle
a technology for motor vehicles and coolant temperature, applied in the direction of thermometer testing/calibration, machines/engines, registering/indicating the working of vehicles, etc., can solve the problems of complex monitoring of the performance of the ect sensor, the difficulty of starting combustion engines, and the inability to detect the temperature rationality of the coolant, so as to improve the performance of the vehicle and reduce the iat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The following detailed description is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the invention or the application and uses of the invention. Furthermore, there is no intention to be bound by any expressed or implied theory presented in the preceding technical field, background, brief summary or the following detailed description.
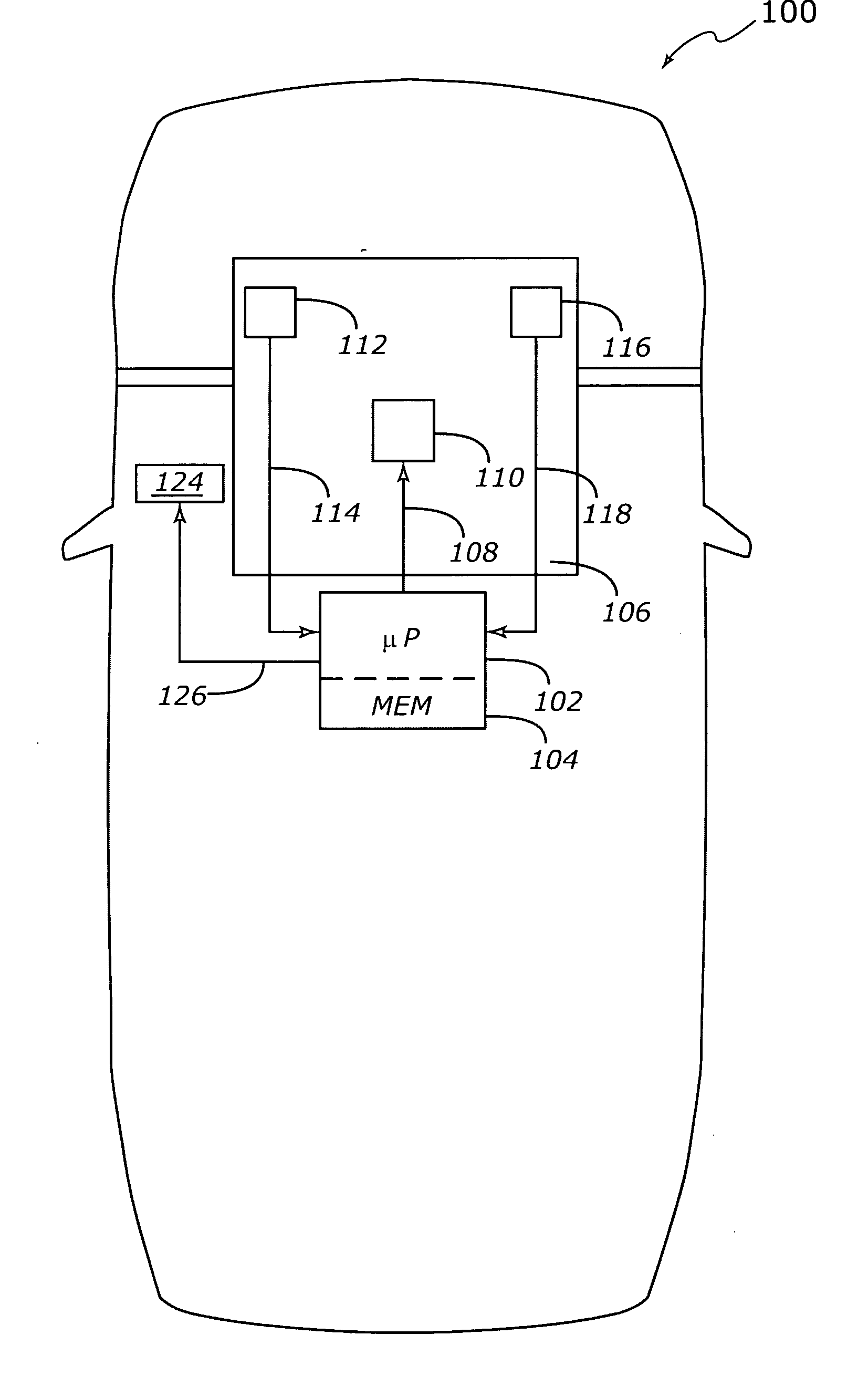
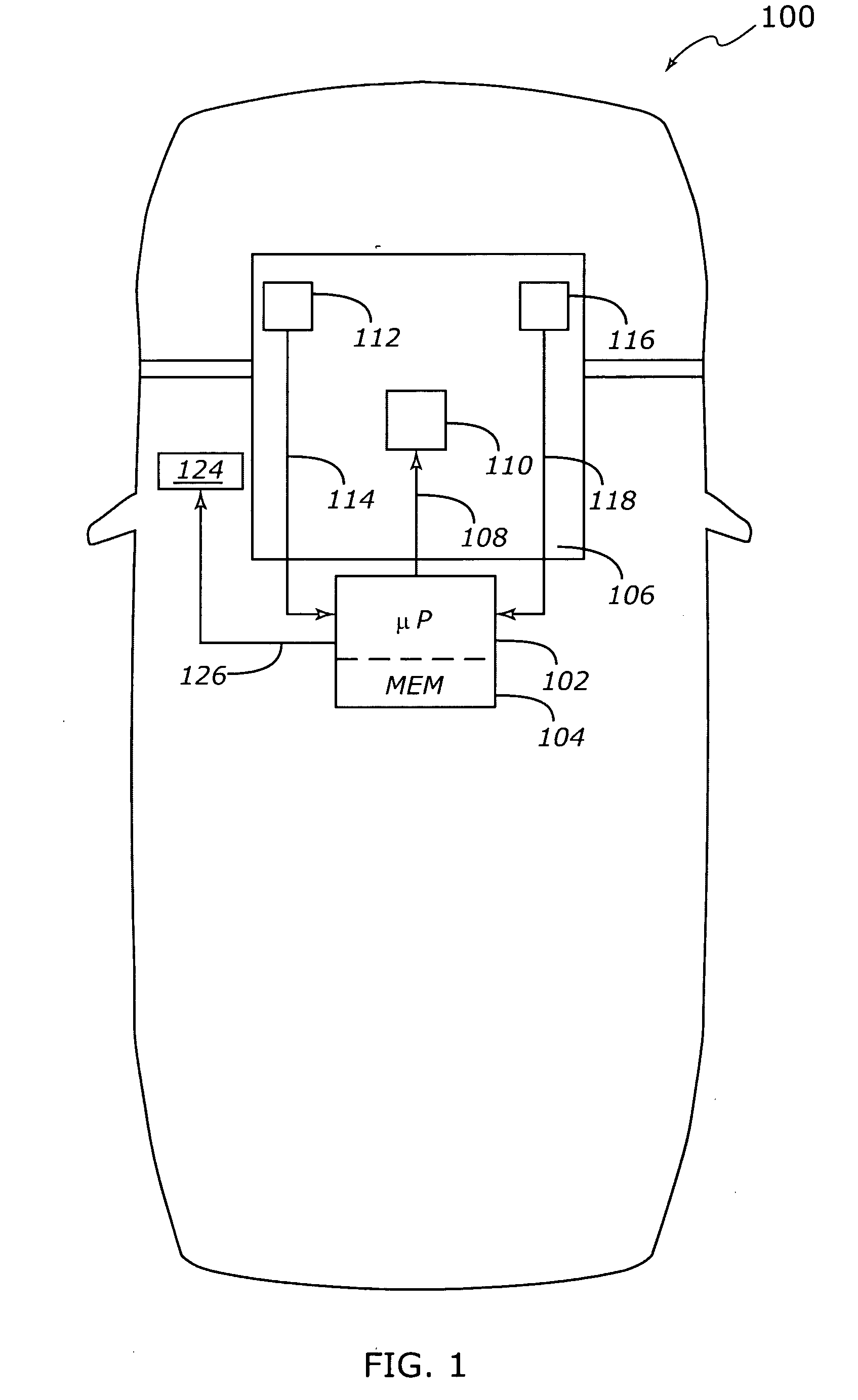
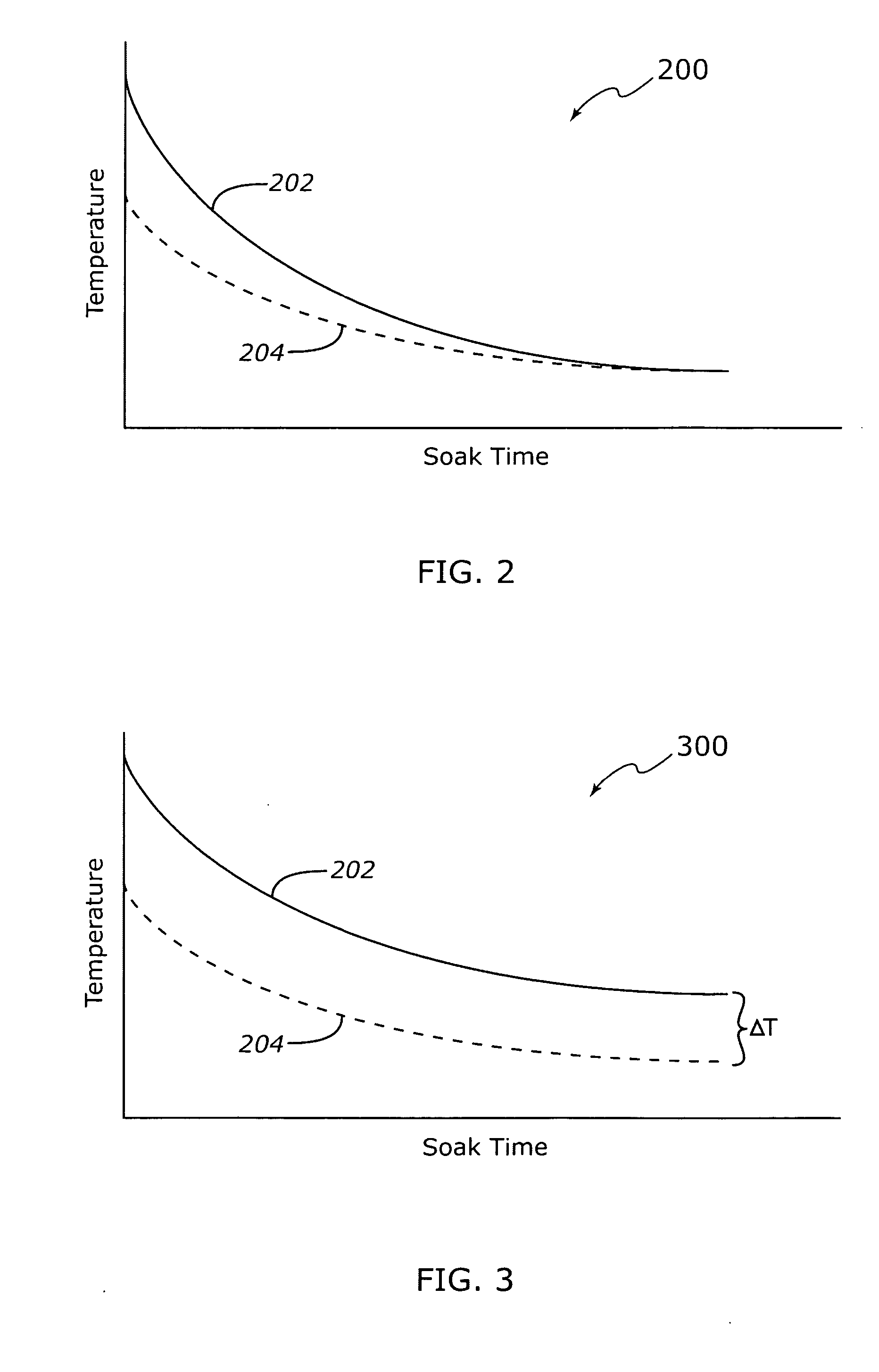
[0015] According to various exemplary embodiments, irrational results from an engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor are identified by observing differences between observed values of the coolant temperature and the temperature of intake air (IAT) after the vehicle has been inactive (e.g. ignition turned off) for an appropriate period of time. If the vehicle has been inactive (“soaking” in ambient air) for sufficient time, the coolant temperature will typically be approximately equal to the air temperature. If the controller identifies large differences between the coolant temperature and the air temperature after a prolonged soak, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com