Determination of gain characteristics of a circularly-polarized antenna
a circularly polarized antenna and gain characteristic technology, applied in the direction of polarised antenna unit combination, non-resonant long antenna, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult measurement of circularly polarized antenna gain, difficult to meet the requirements of high frequency operation, and complicated set-up of conventional methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
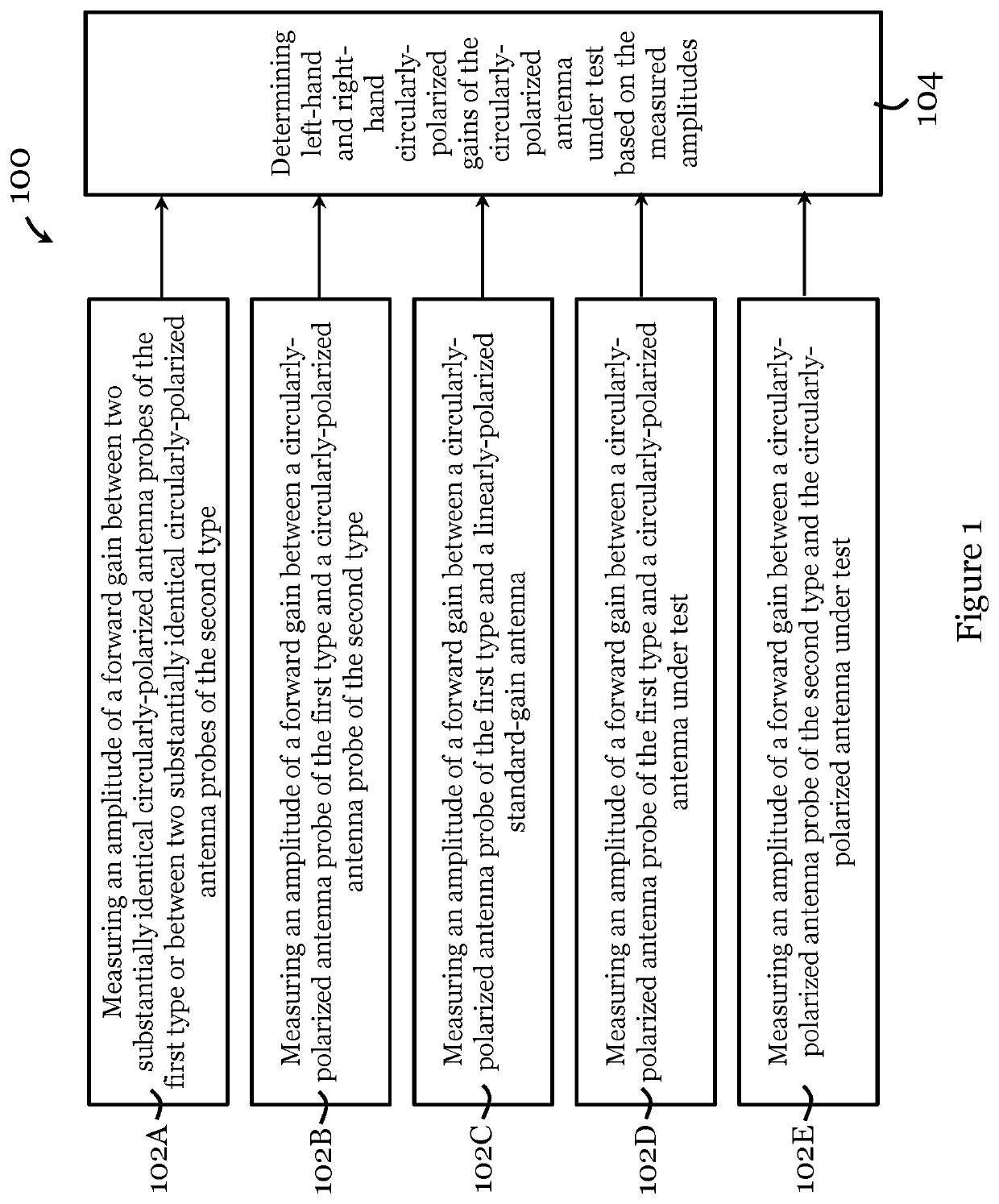
[0081]FIG. 1 illustrates a method 100 for determining gain characteristics of a circularly-polarized antenna in one embodiment of the invention. The circularly-polarized antenna under test in this method 100 is arranged for operation in millimeter-wave and terahertz ranges.
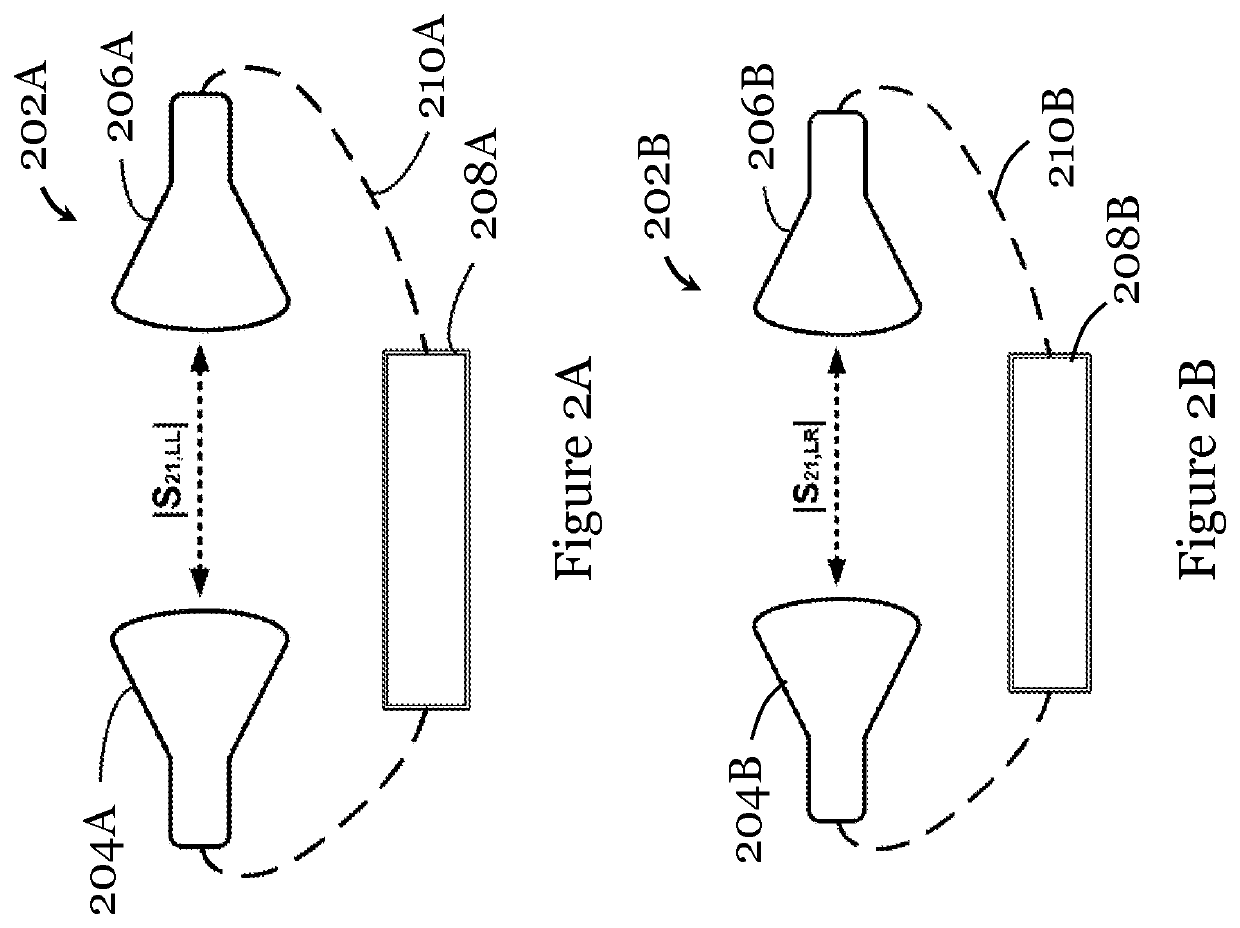
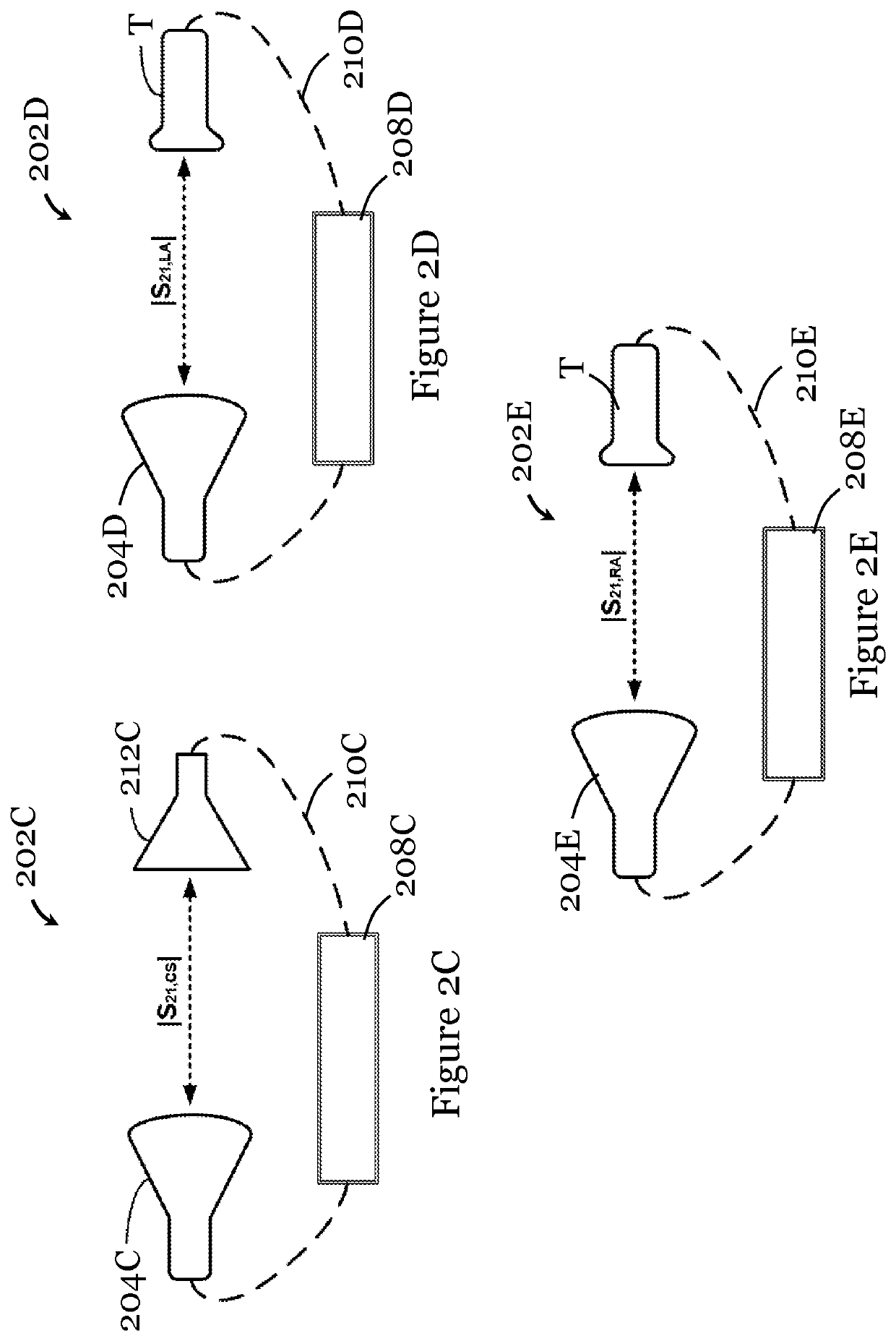
[0082]The method 100 includes, in step 102A, measuring an amplitude of a forward gain (e.g., forward voltage gain) between two substantially identical circularly-polarized antenna probes of the first type or between two substantially identical circularly-polarized antenna probes of the second type. In this example, the circularly-polarized antenna probe of the first type is a left-hand circularly-polarized antenna probe, and the circularly-polarized antenna probe of the second type is a right-hand circularly-polarized antenna probe. The measurement in step 102A includes connecting two substantially identical circularly-polarized antenna probes of the first type (or of the second type) to a measurement device, posi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com