Intercooler
a technology of intercooler and cooling water, which is applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, machines/engines, light and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the boiling point reducing the efficiency of the cooling water, and reducing the cooling water pressure loss, so as to reduce the strength and breakage, prevent the boiling of the second cooling water, and reduce the effect of pressure loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0019]A first embodiment of the present disclosure will be described with reference to the drawings. In the first embodiment, an example in which an intercooler of the present disclosure is applied to a supercharged intake air cooling system for a vehicle will be described.
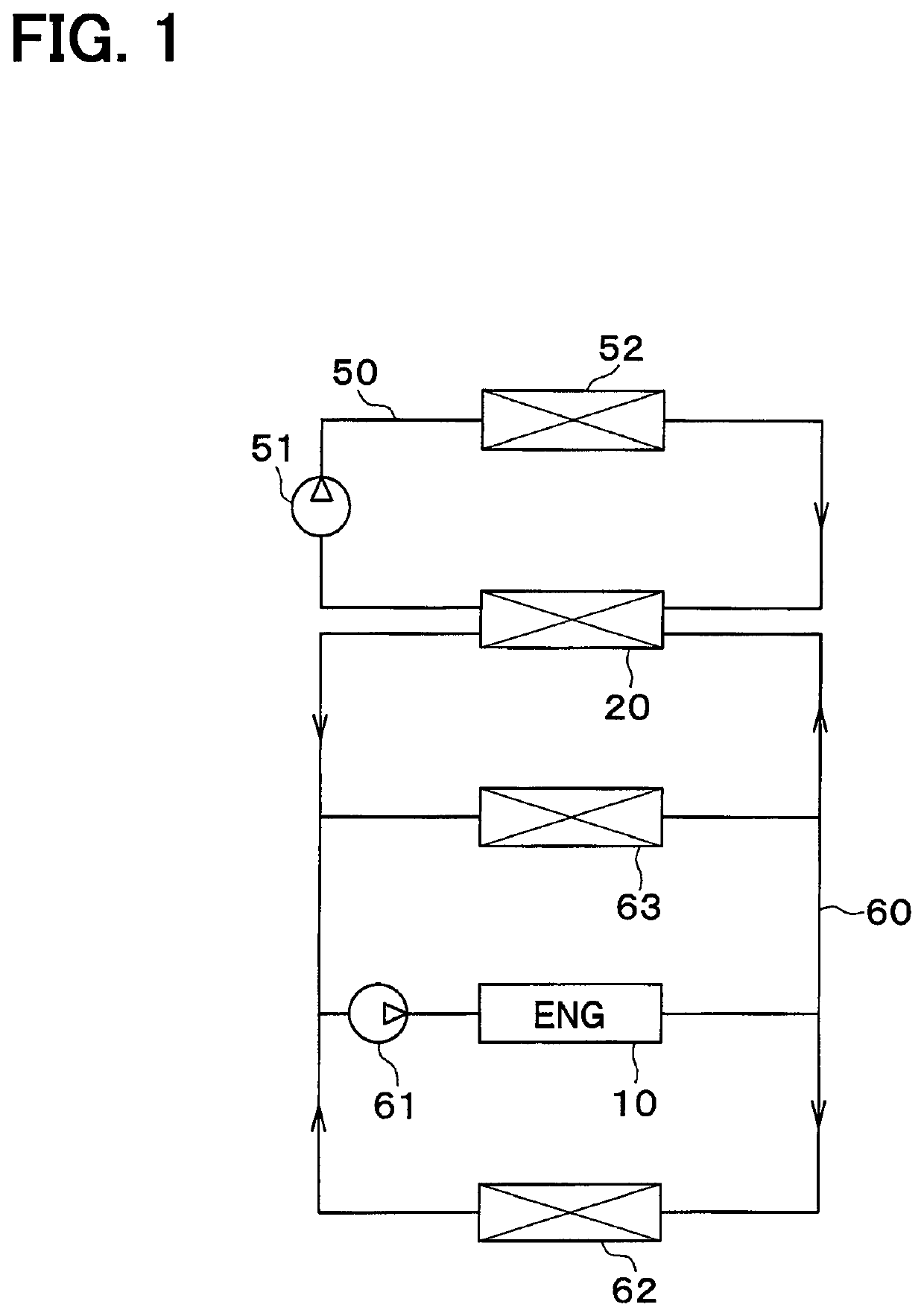
[0020]A supercharger (not shown) for supercharging intake air to an engine 10 is provided in an intake air system of the engine 10 of the vehicle (that is, an internal combustion engine). This supercharger is provided to compensate for the maximum output of the engine 10. That is, the vehicle of the present embodiment has the engine 10 made smaller for higher fuel efficiency and the supercharger is used to compensate for the maximum output reduced in exchange for making the engine 10 smaller.
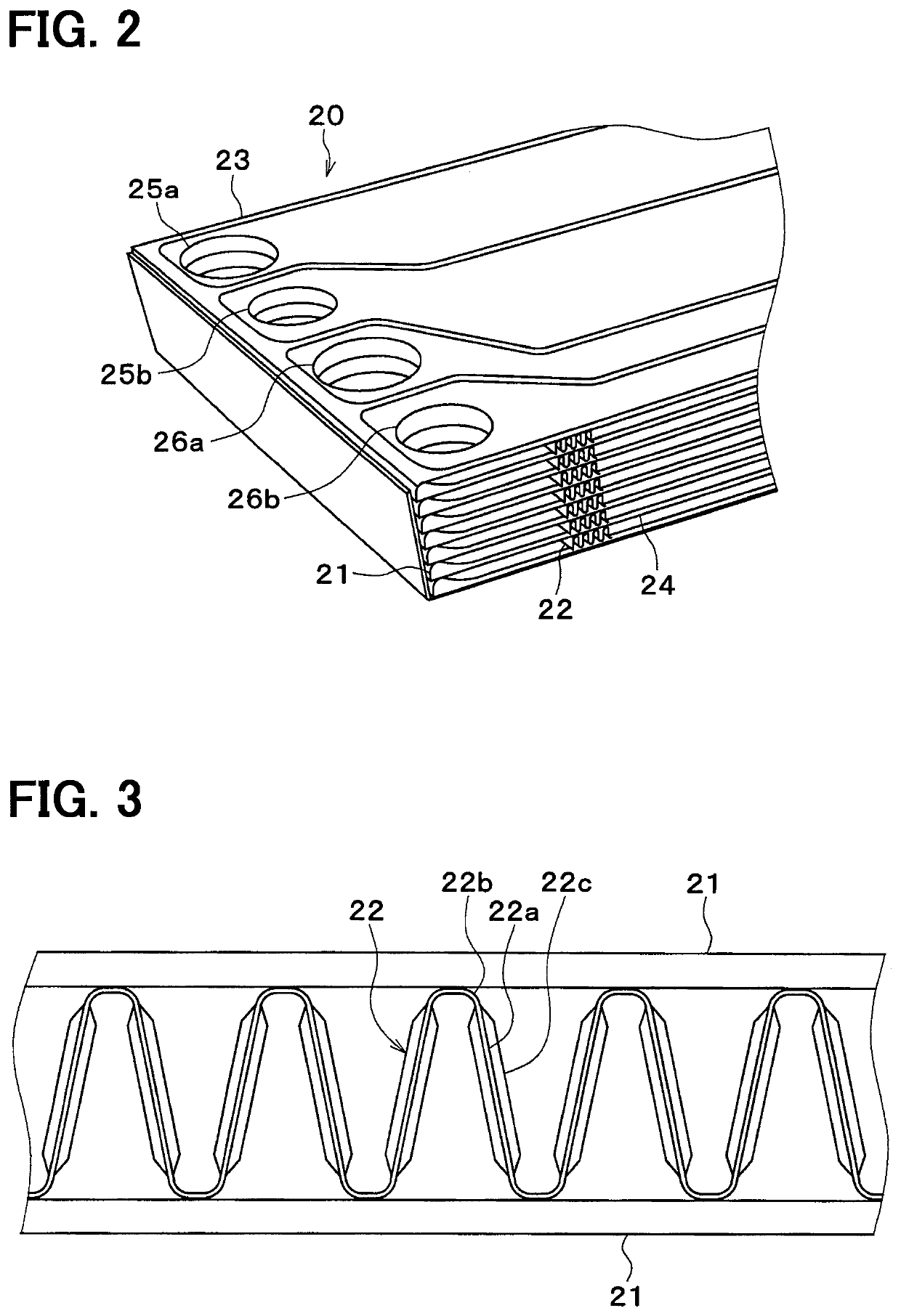
[0021]An intercooler 20 cooling engine intake air is located downstream of the supercharger in the intake air system with respect to a flow of the intake air. The intercooler 20 cools the supercharged intake air that has been ...
second embodiment
[0049]Next, a second embodiment of the present disclosure will be described. In the second embodiment, only parts different from the above-described first embodiment will be described. In the second embodiment, the configuration of the fin 22 is different from that of the first embodiment.
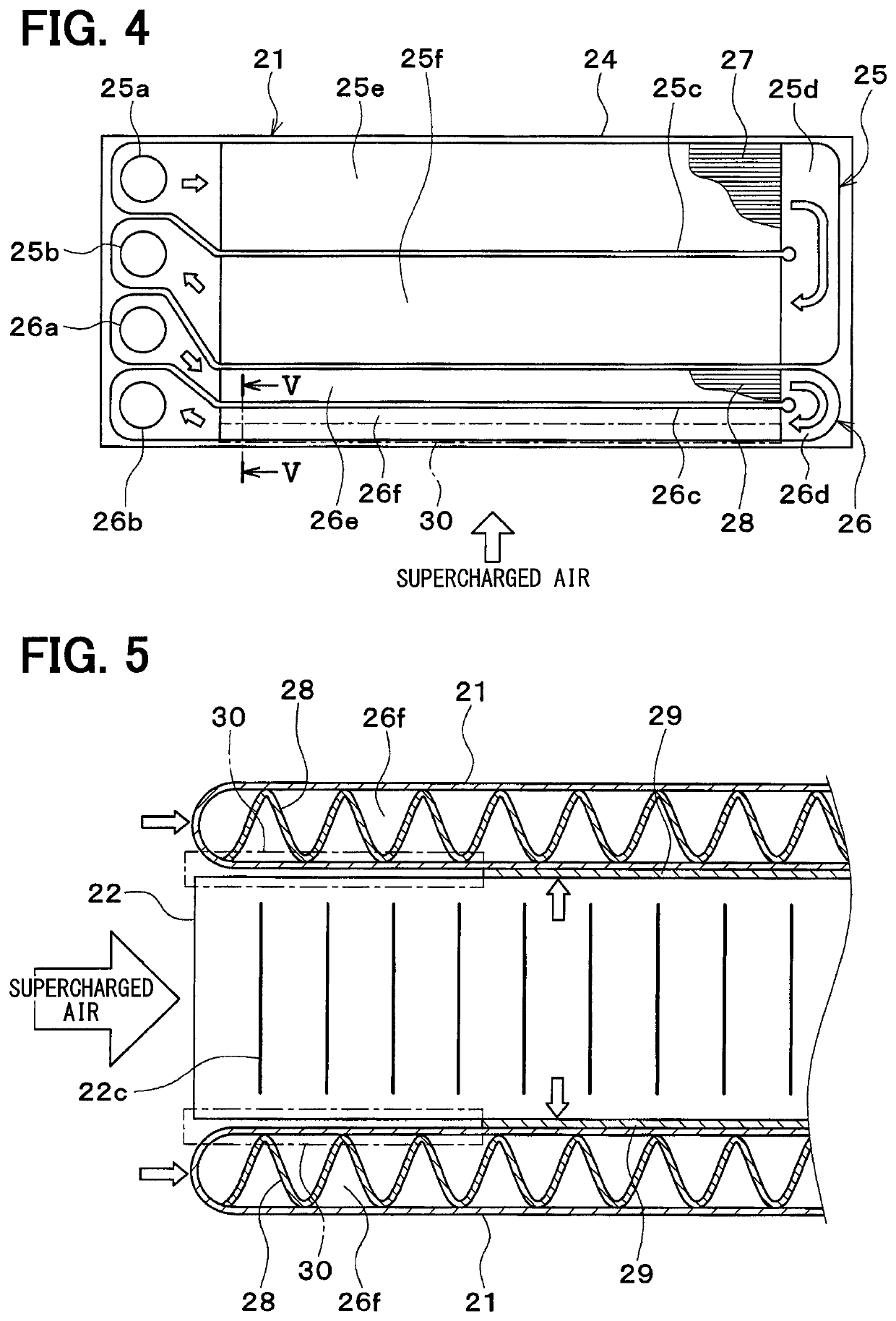
[0050]As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7, in the second embodiment, a step portion 22d is provided in the peak portion 22b of the fin 22 at a portion corresponding to the non-bonded portion 30. The height of the step portion 22d is lower than the other portion of the peak portion 22. Therefore, in the non-bonded portion 30, a gap is formed between the flow path tube 21 and the fin 22. The step portion 22d can be provided by means such as pressing a portion corresponding to the non-bonded portion 30 of the peak portion 22b.
[0051]According to the second embodiment, since a gap is formed between the flow path tube 21 and the fin 22 in the non-bonded portion 30, the heat of the supercharged intake air can be s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com