Electronic circuit and data storage system
a technology of electronic circuits and data storage systems, applied in the field of electronic circuits, can solve the problems of not being able to modify individual components, not being able to modify the resistance value after manufacture, etc., and achieve the effect of fine control of the tuning or modification of the resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
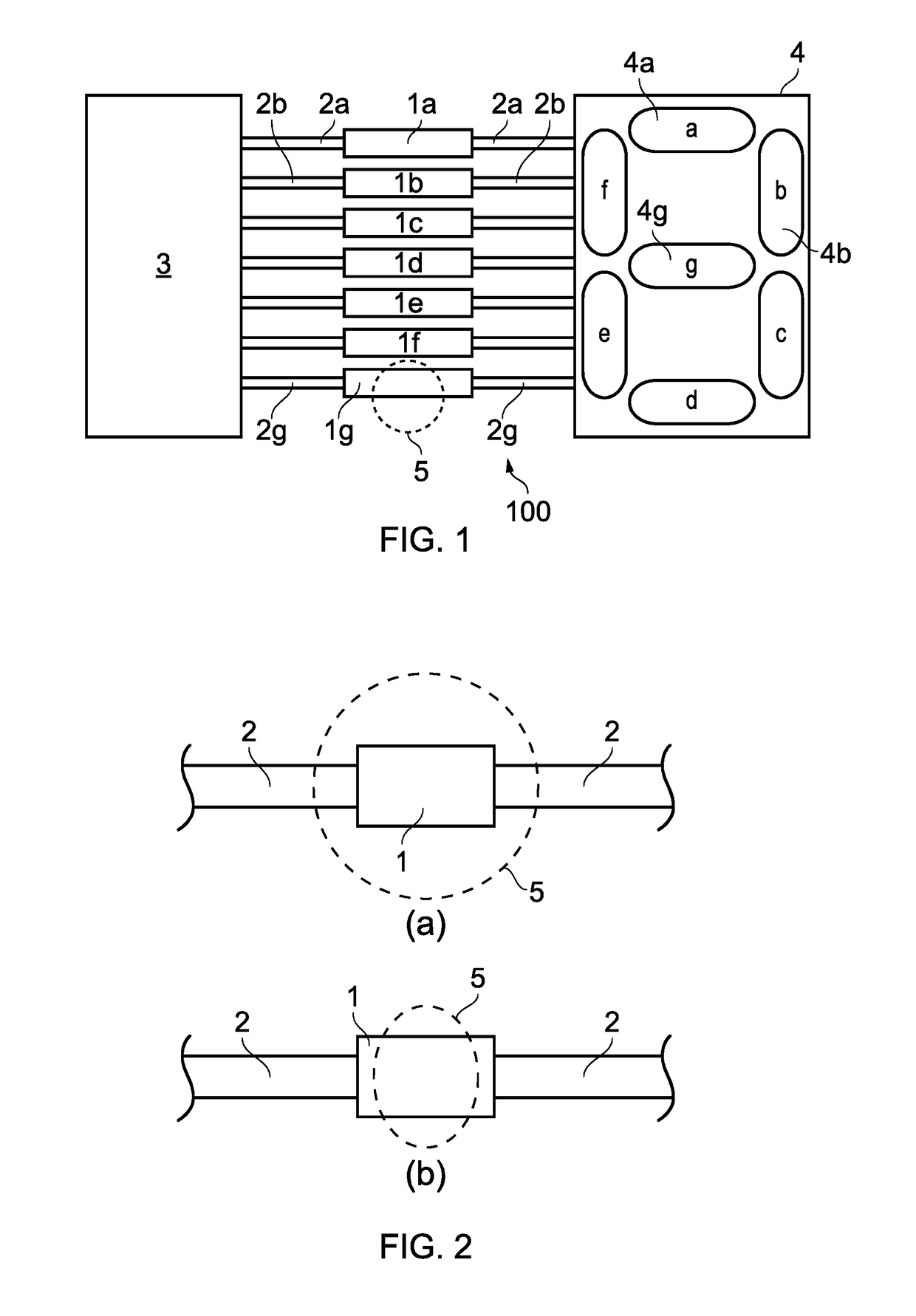
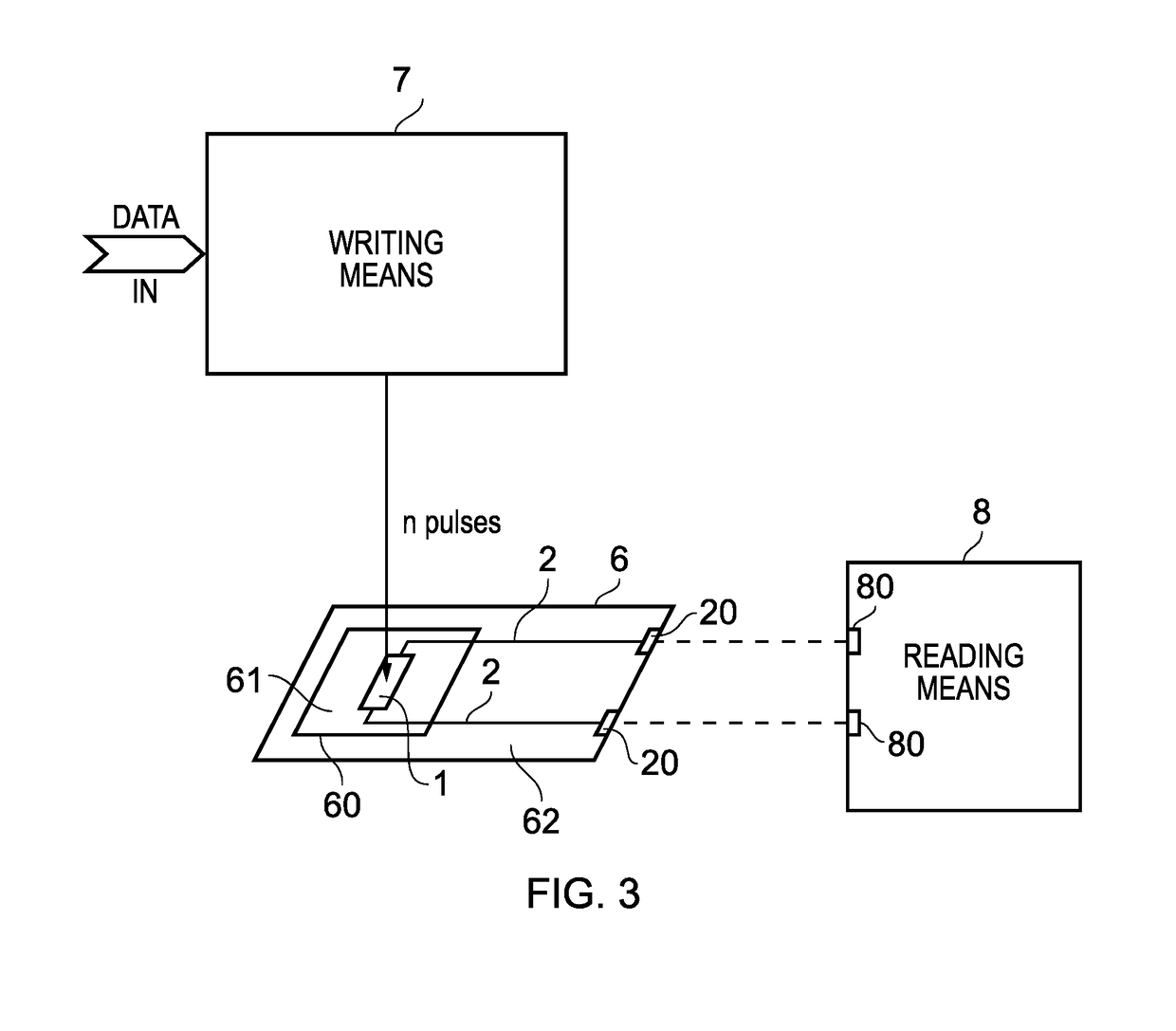
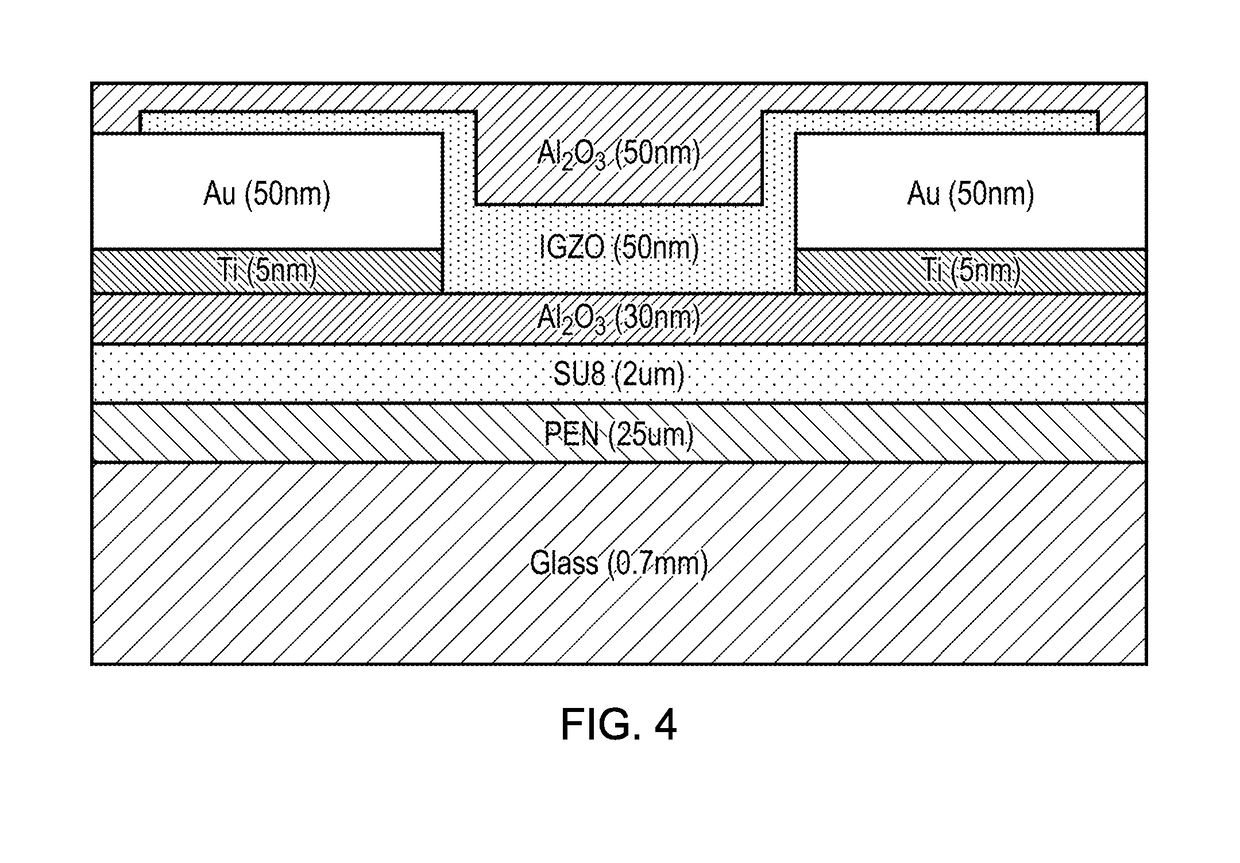
[0061]Referring now to FIG. 1, this is a schematic representation of an electronic circuit embodying the invention. The circuit 100 comprises a plurality of resistive elements 1a-1g, with each resistive element consisting of a thin, substantially planar rectangular layer of semiconductive / semiconductor material. The circuit further comprises drive circuitry 3 and a 7-segment display 4, comprising 7 individually controllable display segments 4a-4g. Each resistive element 1a-1g is coupled / connected to a respective one of the display segments 4a-4g by a conductive track 2a (which in this example is provided by a thin layer of metallic material, for example gold, silver, aluminium, copper, and each resistive element 1a-1g is also coupled to the drive circuitry 3 by means of a respective further conductive track 2a-2g. Each resistive element 1a-1g is arranged such that, before irradiation, its resistance is sufficiently high that, during operation of the circuit, its respective display s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com