Transimpedance amplifier
A transconductance amplifier and amplifying circuit technology, applied in the field of transconductance amplifiers, can solve problems such as waveform distortion, reduction of transconductance gain, small distortion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0118] Attach the reference figure 1 and 2 The configuration of the transconductance amplifier according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
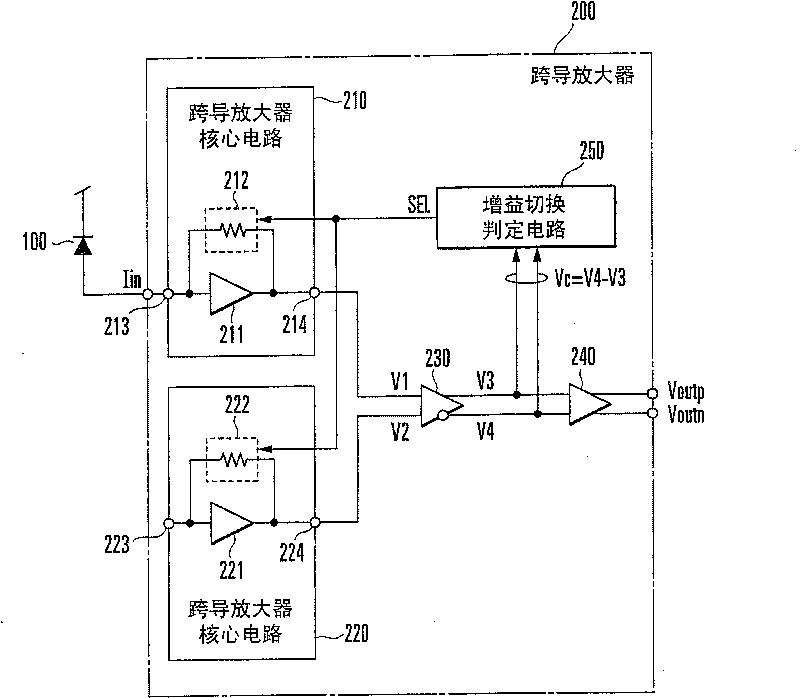
[0119] In an optical transmission circuit such as an optical transmission system, an optical interconnection, or a passive optical network (OPN) system capable of performing high-speed data transmission, an optical signal that is received by the light receiving element 100 and transmitted through an optical fiber is converted into an electrical signal. The receiving circuit adopts figure 1 The transconductance amplifier 200 is shown.
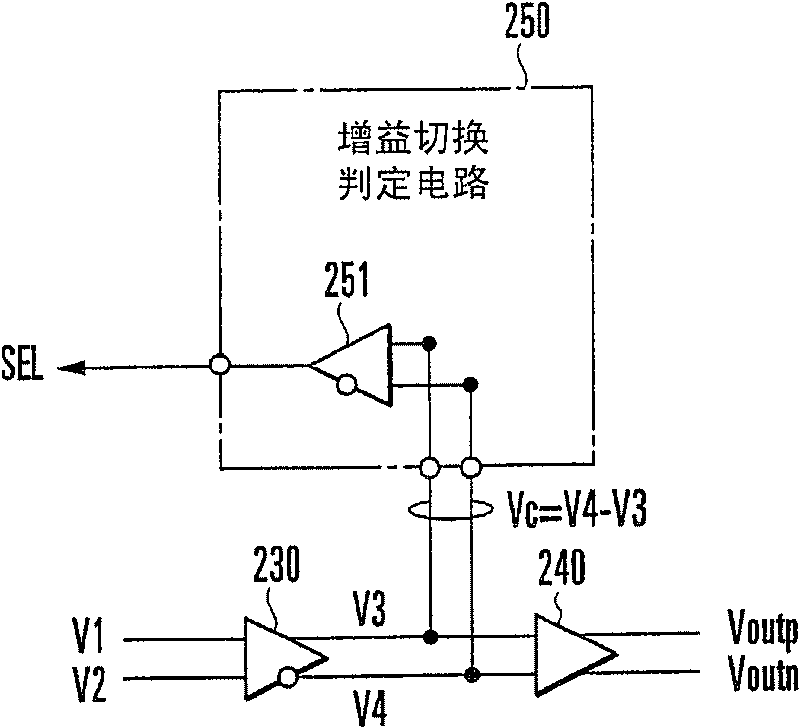
[0120] like figure 1 As shown, the transconductance amplifier 200 mainly includes a first transconductance amplifier core circuit 210 , a second transconductance amplifier core circuit 220 , an interstage buffer circuit 230 , an output buffer circuit 240 and a gain switching determination circuit 250 .
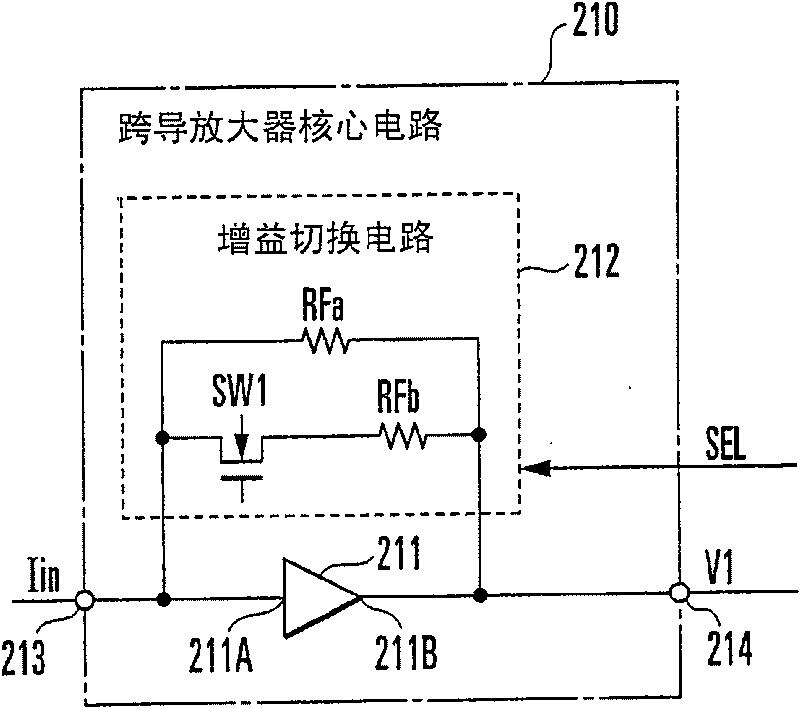
[0121] The first transconductance amplifier core circuit 210 in...
no. 2 example
[0156] Next will refer to Figures 9 to 11The configuration of a transconductance amplifier according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. exist Figures 9 to 11 in, with Figures 2 to 4 The same reference numerals denote the same components.
[0157] The case of switching the gain of the core circuits 210 and 220 of the transconductance amplifier between "high gain" and "low gain" by one step has been exemplified in the first embodiment. The second embodiment will exemplify the case of switching the gain through multiple steps, specifically, switching the core circuit 210 of the transconductance amplifier between "high gain", "intermediate gain" and "low gain" through two steps and a gain of 220 in the case. Note that the constituent elements of the transconductance amplifier according to this embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment except for the gain switching determination circuit and the first and second transconductance ...
no. 3 example
[0177] Next will refer to Figures 14 to 16 A transconductance amplifier core circuit employed in a transconductance amplifier according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0178] Figure 14 Each of the transconductance amplifier core circuits 210B and 220B includes a transconductance gain switching circuit 281 and an open-loop gain switching circuit 282 for switching the transconductance gain. Each gain switching circuit 212B and 222B switches the open-loop gain in the same manner as switching the gain between "medium gain" and "low gain".
[0179] The transconductance gain switching circuit 281 includes feedback resistors RF1, RF2, and RF3 that determine the transconductance gain, and NMOS transistors MN1 and MN2 that operate as switches. The open-loop gain switching circuit 282 includes load resistors RL1, RL2, and RL3 that determine an open-loop gain, and NMOS transistors MN3 and MN4 that operate as switches. The NMOS transistors MN1 to M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com