Magnet sensor arrangement
A technology of magnetic sensors and sensor elements, applied in the direction of converting sensor output, measuring devices, and adopting electrical devices, etc., which can solve problems such as eliminating deviations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
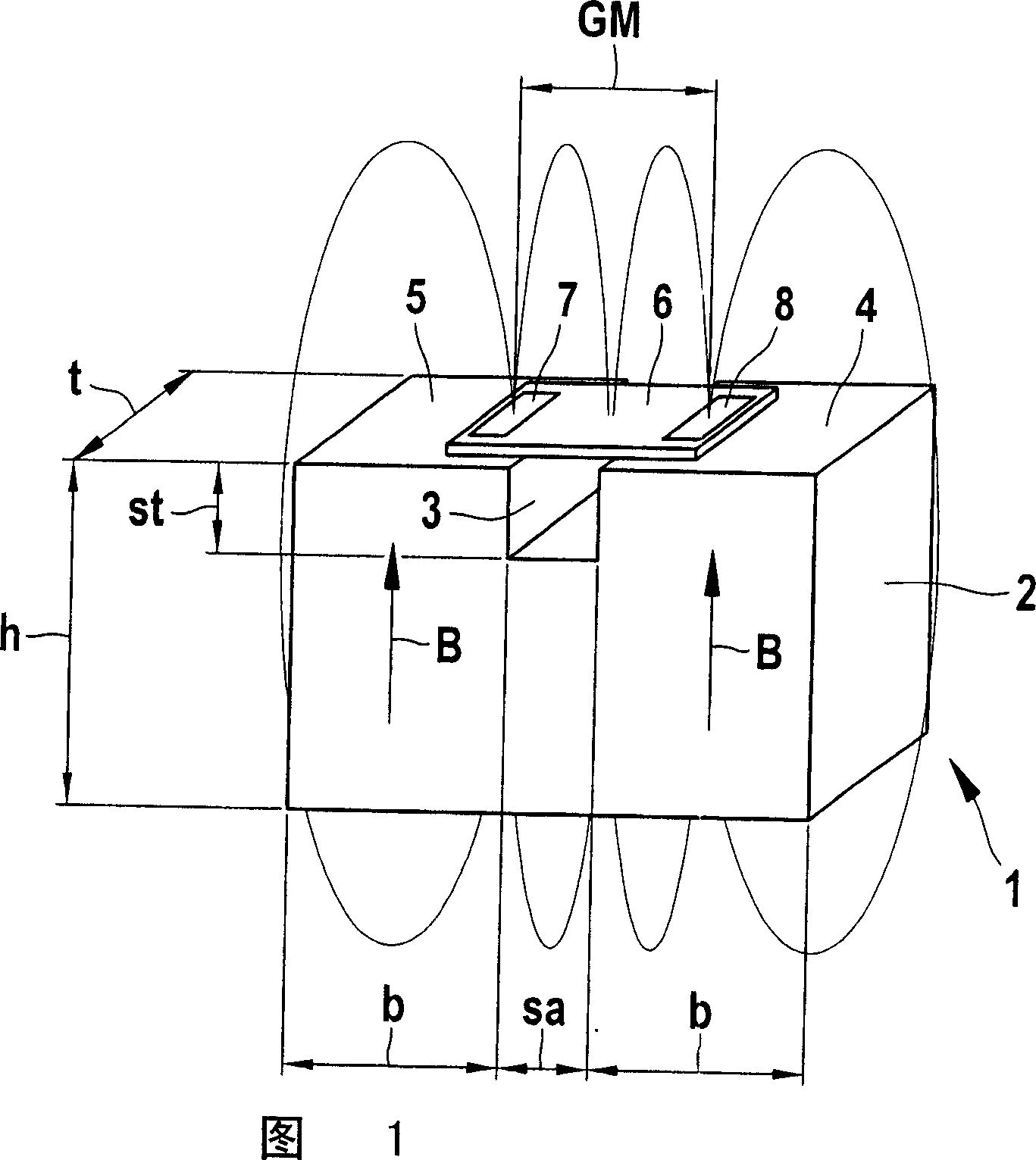
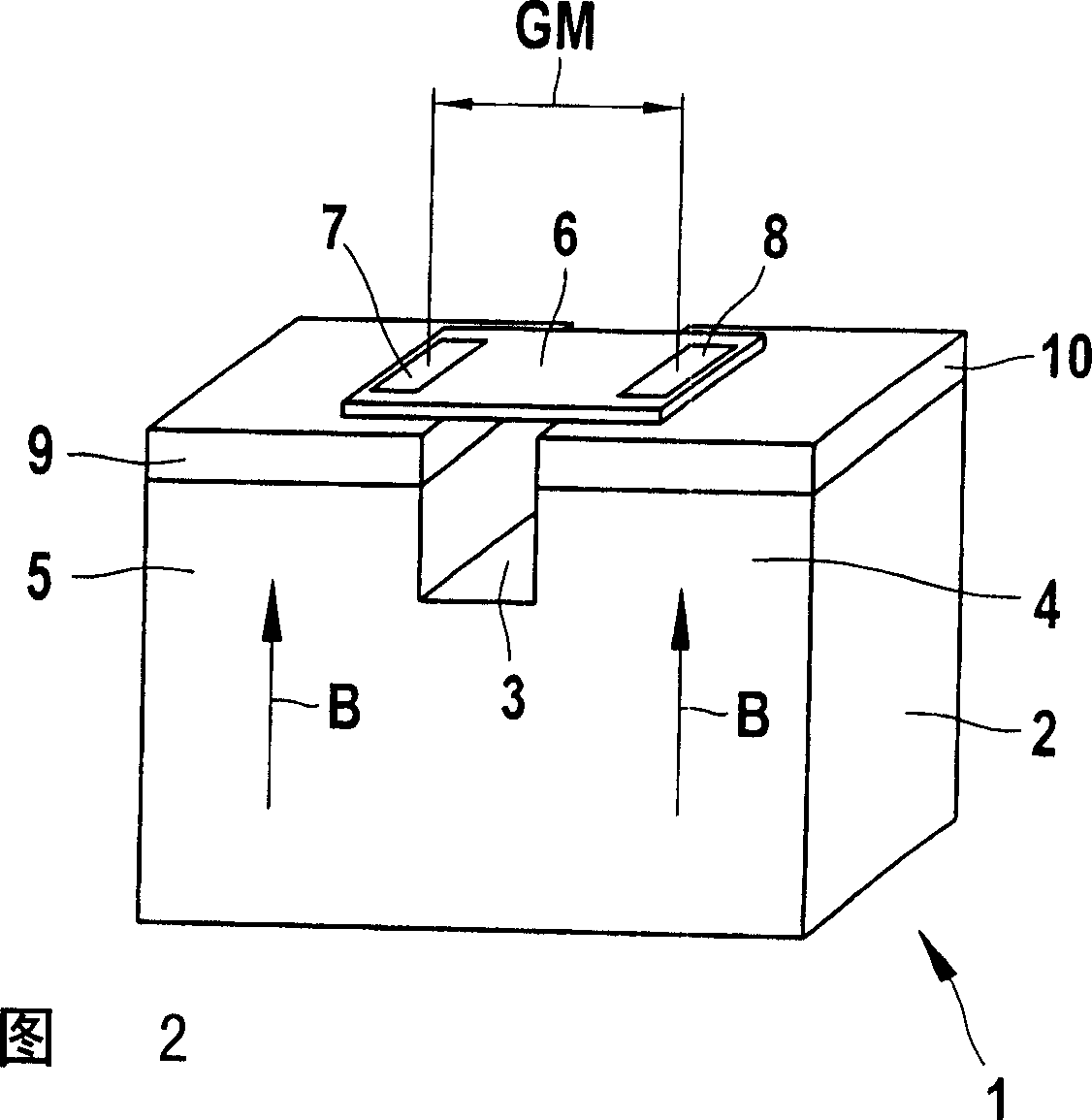
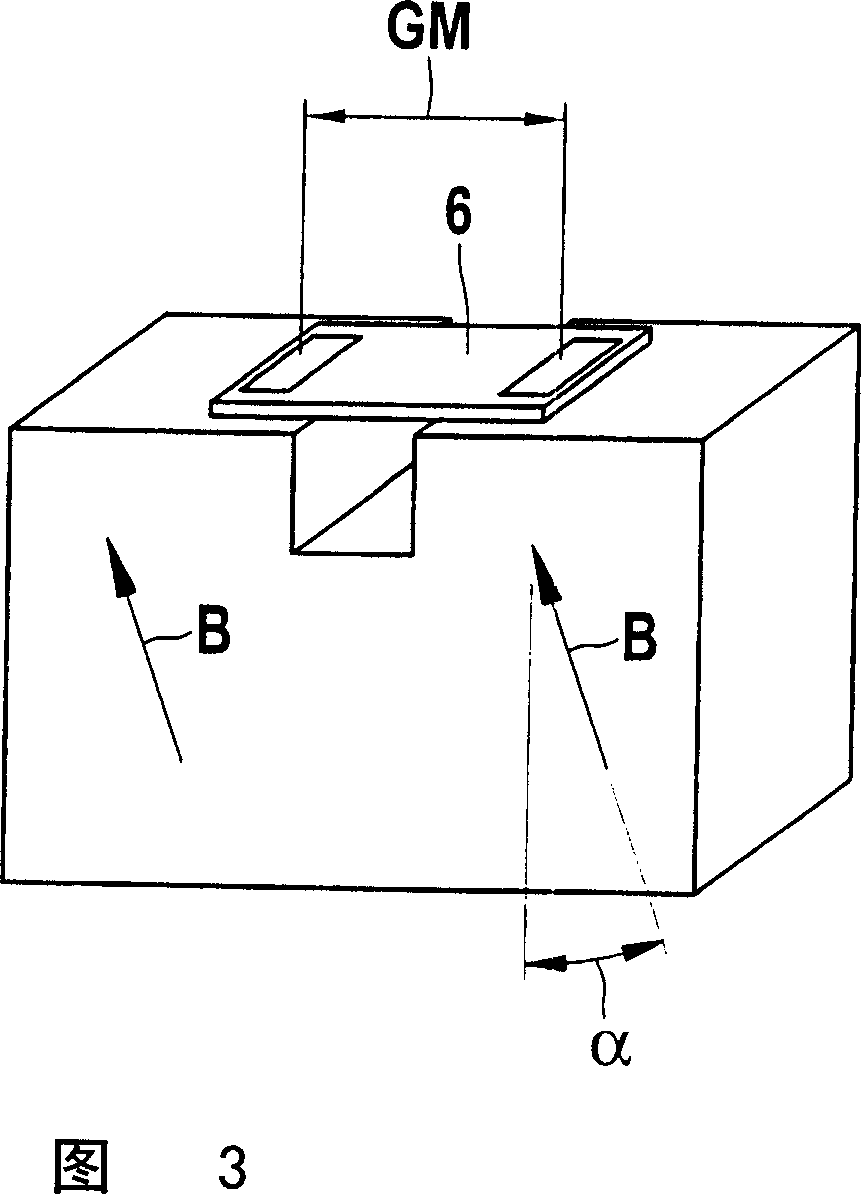
[0031] FIG. 1 shows a schematic illustration of a magnetic sensor device 1 with a permanent magnet embodied as a split magnet 2 . The open magnet 2 has regions 4 and 5 magnetized in the same direction on both sides of the opening 3 , whose corresponding magnetic field B with the field lines depicted here is aligned in the direction of the sensor 6 . The sensor 6 is here embodied as an XMR sensor and has two magnetoresistive sensor elements 7 and 8 . The sensor elements 7 and 8 are shown positioned in the gradiometer arrangement at a gradiometer interval GM and detect changes in the respective field gradients, for example by a metallic transmitter element guided past the magnetic sensor arrangement 1 , for example FIG. 5 caused by the gear shown in .
[0032] The setting of the optimum operating point of the sensor 6 is achieved by the mutual spacing of the individual magnets 4 and 5 defined by the opening width sa and the opening depth st and can be matched to the gradiometer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com