Organic polymer and novel polymerizable compound
A technique for polymerizing compounds and polymer compositions, applied in the fields of organic chemistry, other chemical processes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., which can solve the problems of inefficiency, high cost, clumsy production methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
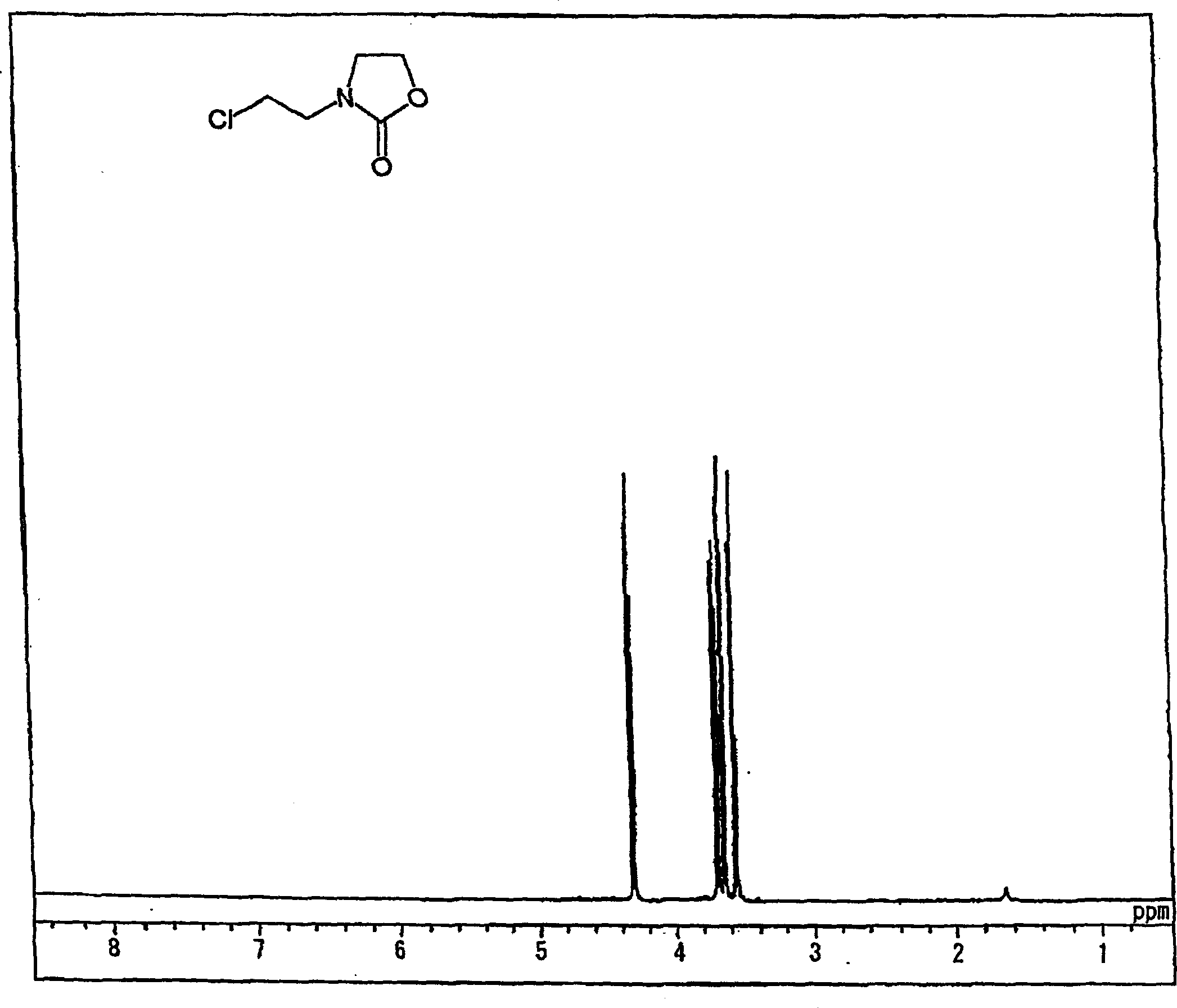
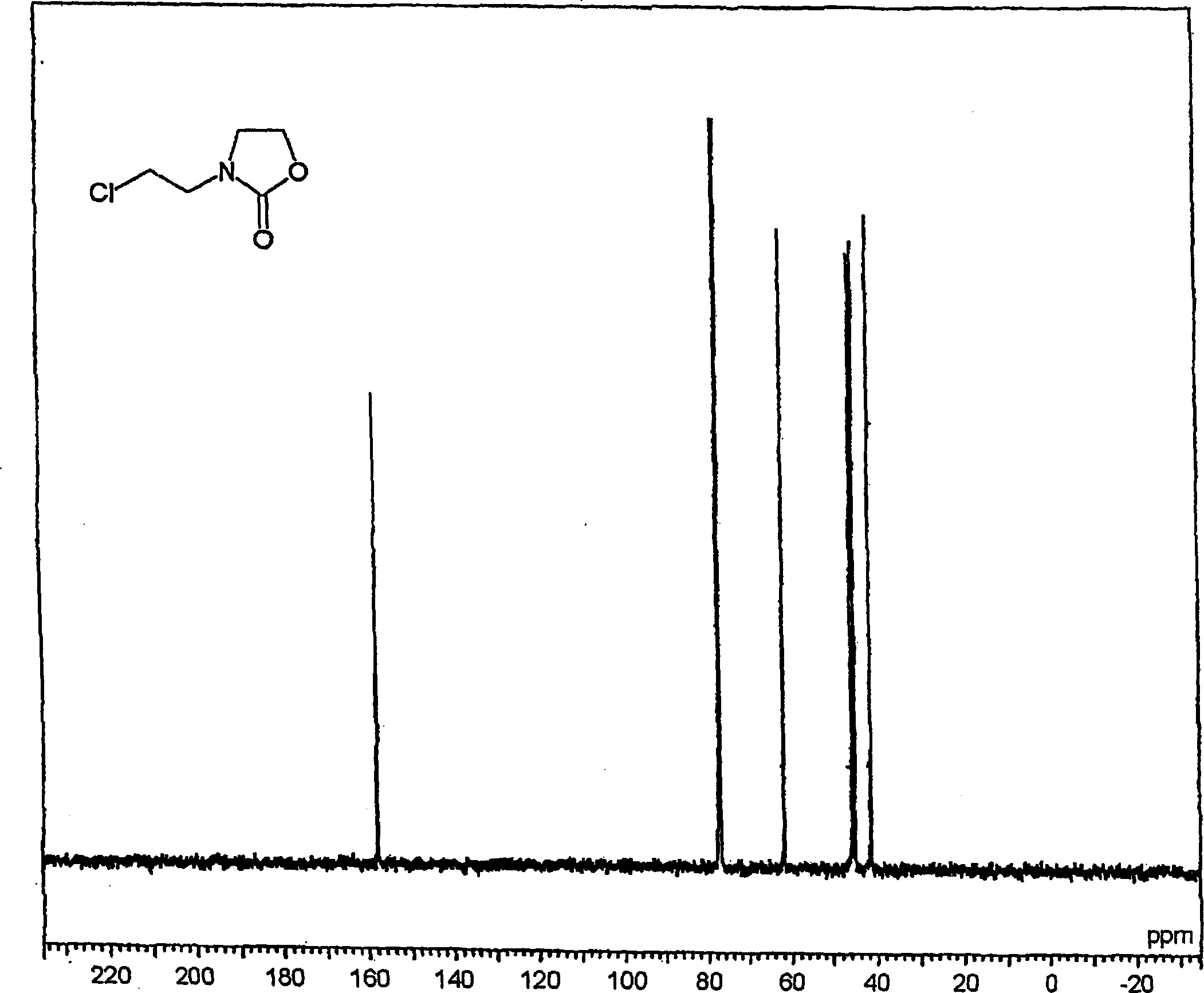
[0268] Synthesis of chloroethyloxazolidinone (referred to as "CEOZ") and N-methoxyethyl-N'-hydroxy-ethyl-ethyleneurea (abbreviated as "MHEU").
[0269] 97% sodium hydroxide (173.2 g, 4.20 mol), sodium bicarbonate (378.0 g, 4.50 mol) and water (1500 ml) were mixed to form a homogeneous solution.
[0270] Bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride (750.0 g, 4.20 mol) was gradually added to the solution at an internal temperature of 30-50°C over 0.5 hours and aged at 40°C for 4 hours. Chloroform (0.5 L) was added to the reactant with stirring, and allowed to stand, and the lower organic layer was collected. The upper aqueous layer was extracted with 3 portions of 0.5 L of chloroform (total amount: 1.5 L) to collect organic components. These chloroform layers were combined, and the solvent was distilled off to obtain CEOZ (569.8 g, 3.55 mol, pure yield: 84.5%) with a purity of 93.2%.
[0271] The resulting CEOZ structure is characterized as follows:
[0272] 1 H-NMR → see figure 1...
Embodiment 2
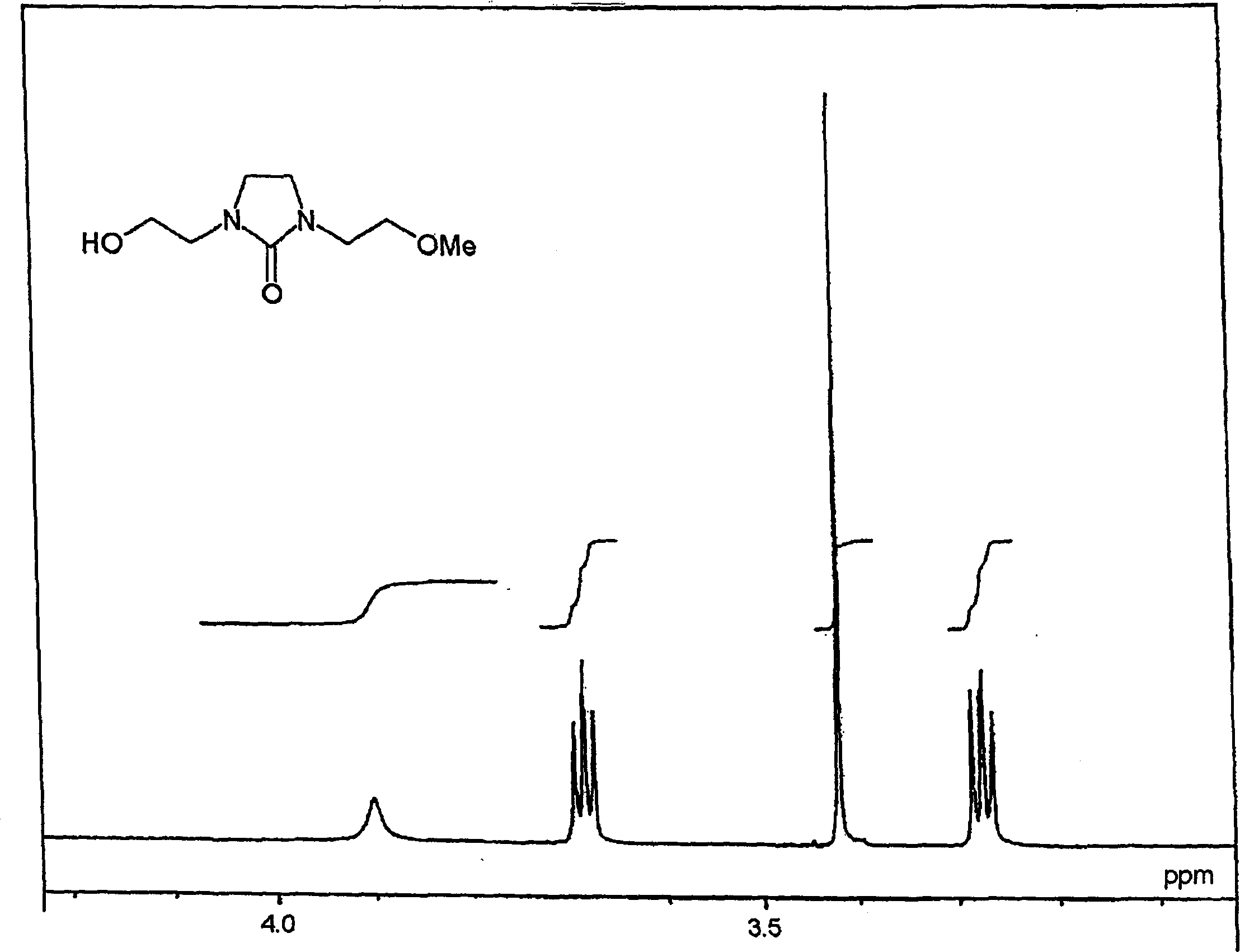
[0280] Synthesis of N-methoxyethyl-N'-mercaptoethyl-ethyleneurea ("THEU" for short).
[0281] Phosphorus tribromide (58.0 g, 0.214 mol) was added dropwise to N-methoxyethyl-N'-hydroxyethyl-ethyleneurea (MHEU ) (110.0 g, 0.579 mol). Then it was aged at 50° C. for 2 hours. Chloroform (200 mL) was added to the reaction mixture, and water (50 mL) was added dropwise at an internal temperature of 60°C. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and the layers were separated. The resulting organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain crude N-methoxyethyl-N'-bromoethyl-ethyleneurea (130.5 g, 0.520 mol, crude yield: 90%).
[0282] Add thiourea (69.6g, 0.914mol) and water (300mL) into crude N-methoxyethyl-N'-bromoethyl-ethyleneurea, then react at reflux (100-102°C) for 3 hours . Then the reactant was cooled to 40°C, 28% aqueous ammonia (148.0 g, 2.44 mol) was added dropwise at 40-46°C, and the resulting mixture was matured at 55°C for 3 hours.
[0283] After the...
Embodiment 3
[0288] Synthesis of N,N'-bis(hydroxyethyl)-ethyleneurea (abbreviated as "HEEU") and N,N'-bis(mercaptoethyl)-ethyleneurea (abbreviated as "DMEU").
[0289] CEOZ (568.0 g, 3.54 mol) with a purity of 93.2% was added dropwise to 2-aminoethanol (1180.0 g, 19.3 mol) at 105-110° C. over 1 hour. Then it was aged at 110° C. for 3 hours. It was then cooled and 97% aqueous sodium hydroxide (146.0 g, 3.54 mol) and water (220 ml) were added, followed by filtration. Anhydrous magnesium sulfate was added to the filtrate, and filtered again. The filtrate was passed through a silica gel column, and the silica gel column was rinsed with methanol. The silica gel column eluate and eluent (methanol solution) were combined, and the solvent, excess 2-aminoalcohol, etc. were distilled off under reduced pressure. The resulting concentrated residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain HEEU with a purity of 99% (469.4 g, 2.67 mol, pure yield: 75.4%).
[0290] The resulting stru...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com