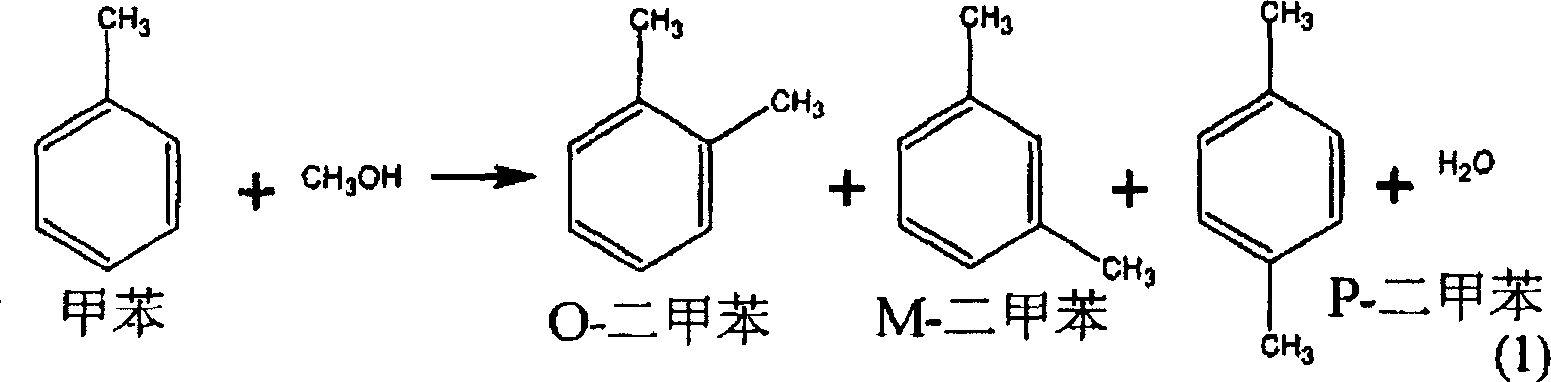
Toluene methylation process
A technology of toluene methyl and toluene, applied in chemical instruments and methods, catalysts, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as activity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 2.70 ml of catalyst was loaded into the reactor. The catalyst was dried at a temperature of 200° C. under a flow of hydrogen for at least 1 hour before feeding. Reactor pressure was maintained at 20 psig. at about 32hr -1 A premixed toluene / methanol feed with a molar ratio of 1 / 1 was added at a rate of about 1.445 ml / min at a LHSV of . co-feed hydrogen at a rate of 50cc / min to give H 2 The / HC molar ratio is about 0.1. The catalyst bed inlet temperature was slowly increased (10°C / min) and adjusted to about 600°C. After 1 hour from initial airflow, adjust operating conditions to run conditions. Feed rate reduced to about 0.089ml / min to give LHSV about 2hr -1 . Also, the rate of hydrogen as a co-feed was increased from 50cc / min to 223cc / min to reduce the H 2 The / HC molar ratio was kept at about 7. The reaction start-up conditions and operating conditions, as well as toluene conversion and p-xylene selectivity are listed in Tables 1A and 1B.
[0032] ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 2.70 ml of catalyst was loaded into the reactor and the catalyst was dried at 200°C under hydrogen flow for at least 1 hour before feeding, and the reactor pressure was maintained at 20 psig. Introduce molar ratio 2 / 1 pair premixed toluene / methanol feed at about 0.101ml / min, LHSV about 2hr -1 . Hydrogen as a co-feed in H 2 The / HC molar ratio is about 1.6 and is introduced at a speed of 51cc / min. The catalyst bed inlet temperature is slowly increased (10°C / min) and adjusted to 600°C. 2 A / HC molar ratio of 7.8 increases the co-feed hydrogen rate from 51 cc / min to 223 cc / min. After 99 hours of stream, in H 2 The hydrogen co-feed rate was further reduced from 223 cc / min to 51 cc / min at a / HC molar ratio of about 1.7. By adding H 2 The conversion of toluene was improved when the / HC molar ratio was decreased from about 7.8 to 1.7. The start-up and normal operating conditions of the reactor, as well as toluene conversion and p-xylene selectivity are described in Table...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1.40 ml of catalyst was loaded into the reactor and the catalyst was dried at a temperature of 200° C. in a stream of hydrogen for at least 1 hour prior to feeding, and the reactor pressure was maintained at about 20 psig. A feed of toluene / methanol premixed at a molar ratio of 2 / 1 was introduced at a rate of about 0.182ml / min with a LHSV of about 8hr -1 . Co-feed hydrogen at 471 cc / min to give H 2 The / HC molar ratio is about 8.0. The catalyst bed inlet temperature was slowly increased (10°C / min) and adjusted to about 500°C. The operating conditions of the reactor, as well as toluene conversion and p-xylene selectivity are described in Tables 3A and 3B.
[0042] Initial conditions
[0043] Flow time, hours
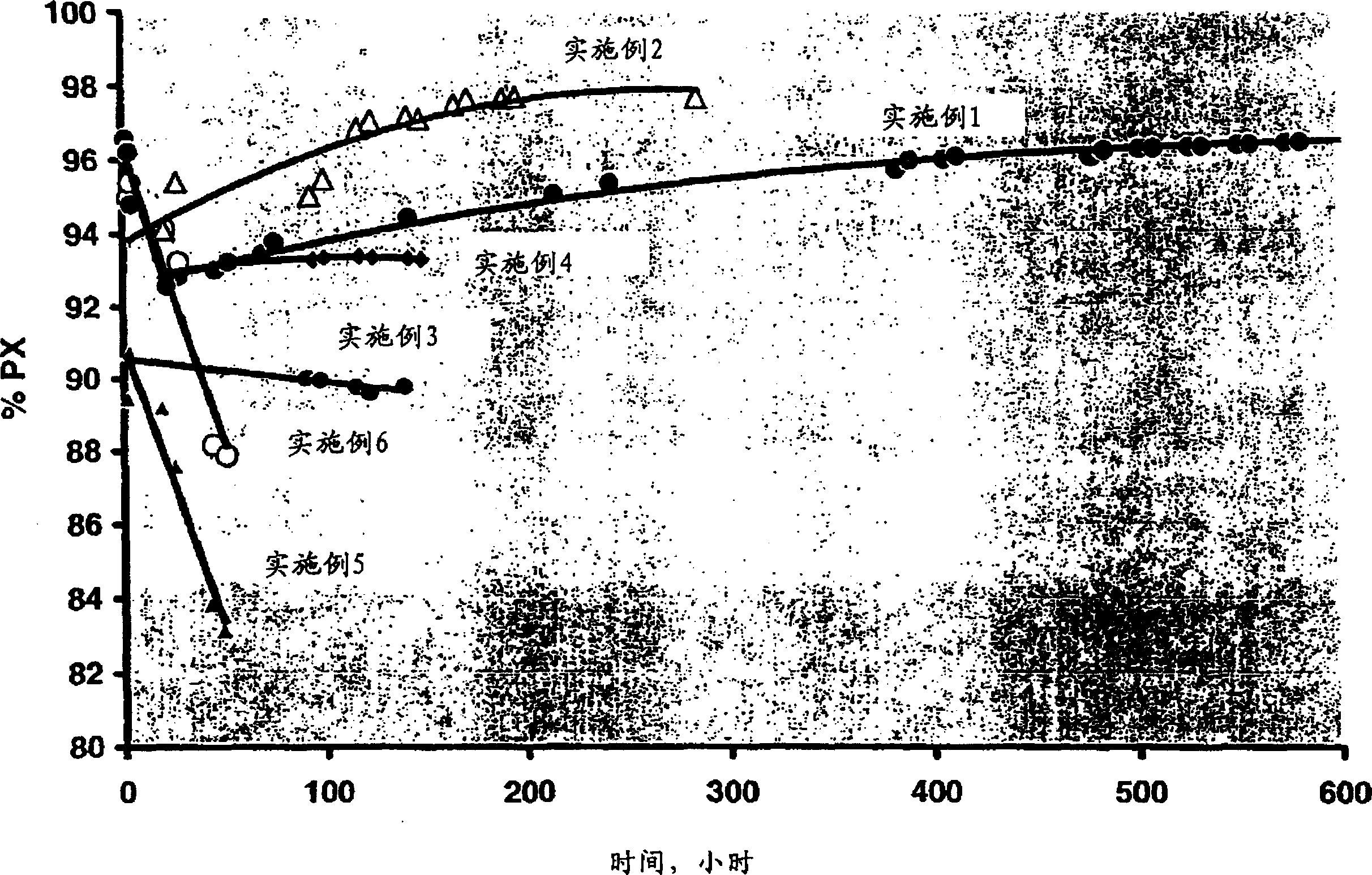
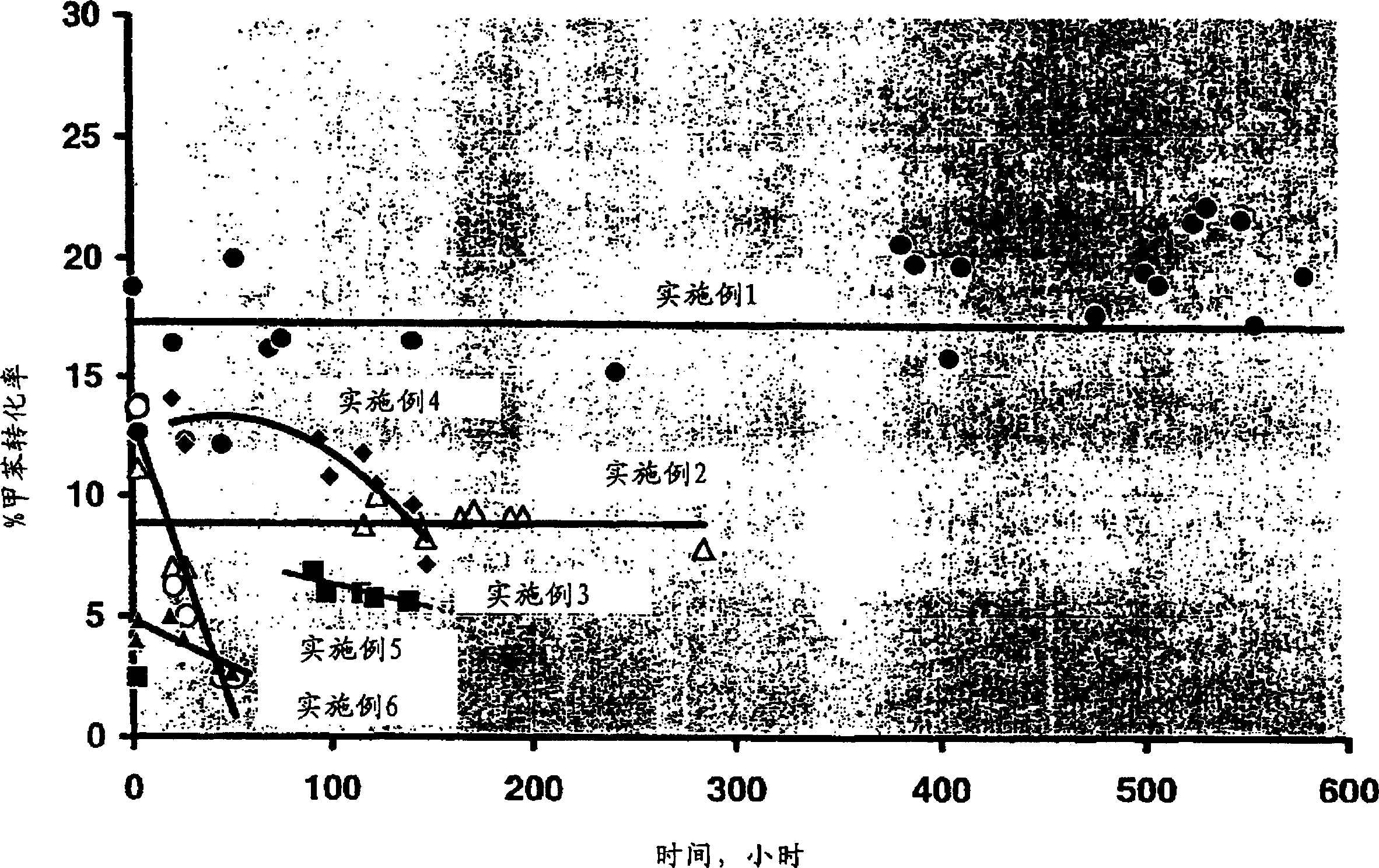
[0044] from figure 1 with 2 It can also be seen in Example 3 that the selectivity to p-xylene in Example 3 was approximately 90% during the 139 hour reaction run, while the initial conversion was approximately 2%. Data recorded during s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com