Optical packet exchanger
一种光分组、交换器的技术,应用在数据交换网络、电磁发射器、电磁接收器等方向,能够解决容量降低数量、传输效率降低、难以读取地址信号等问题,达到阻止吞吐量的减少的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
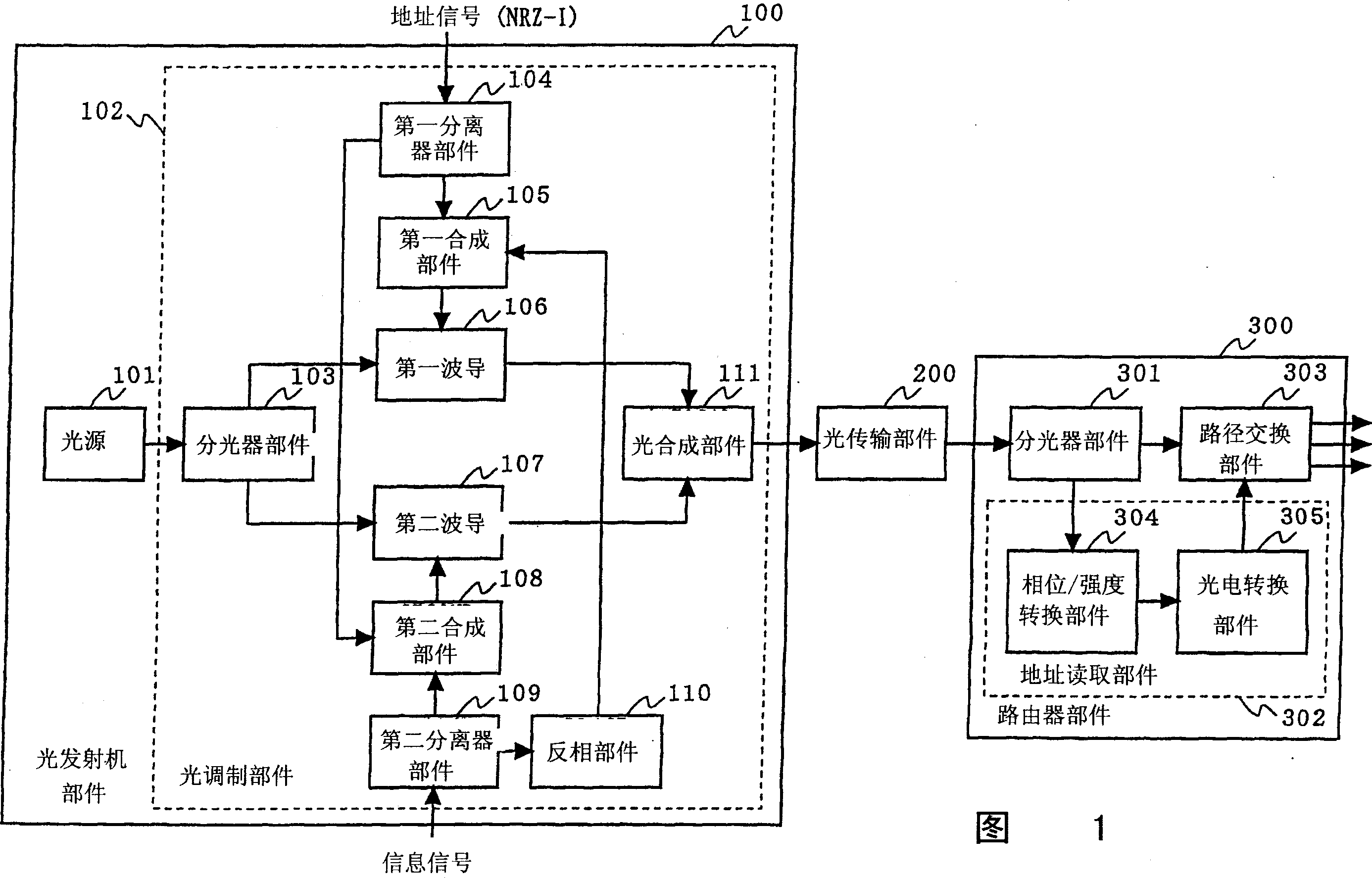
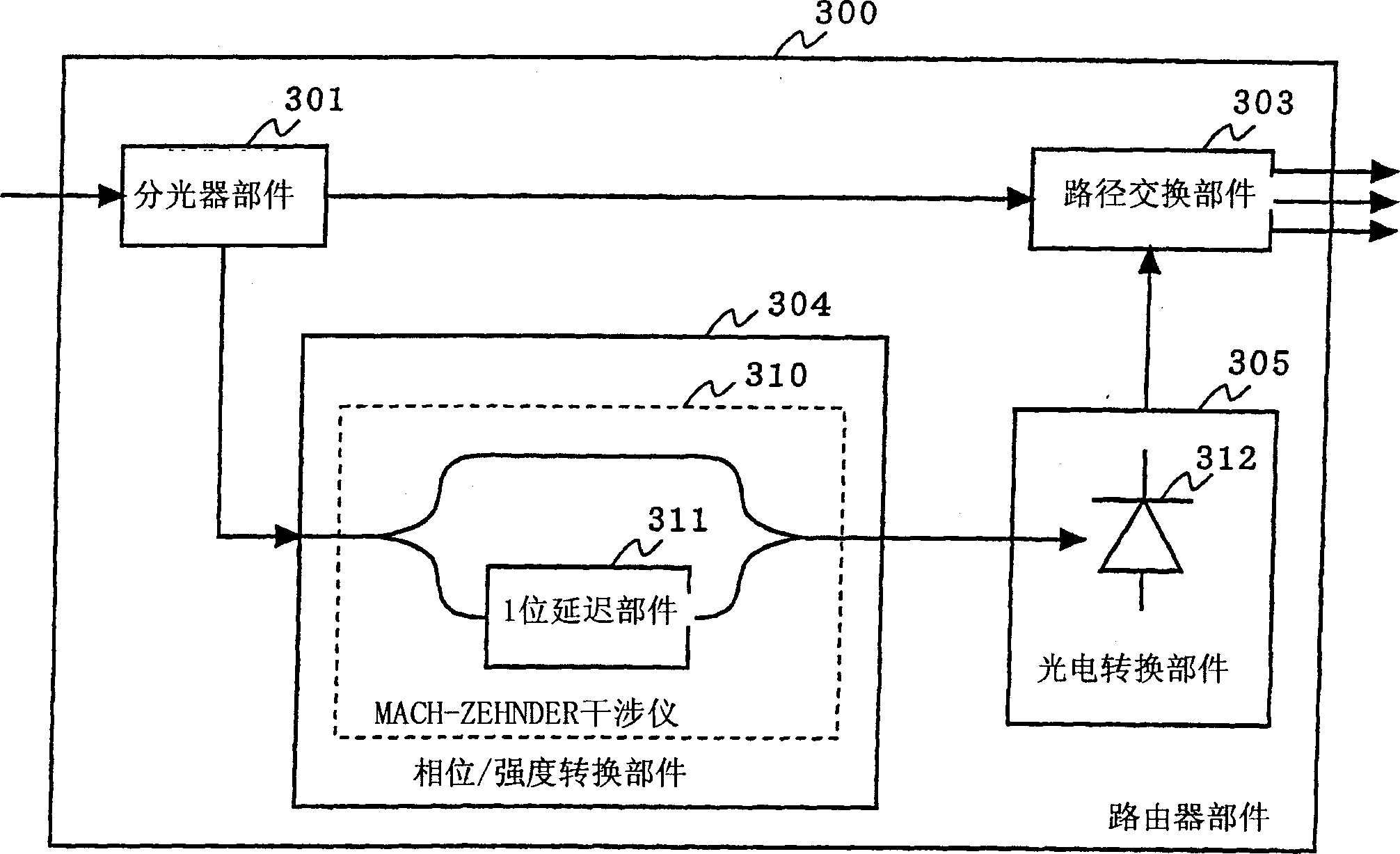
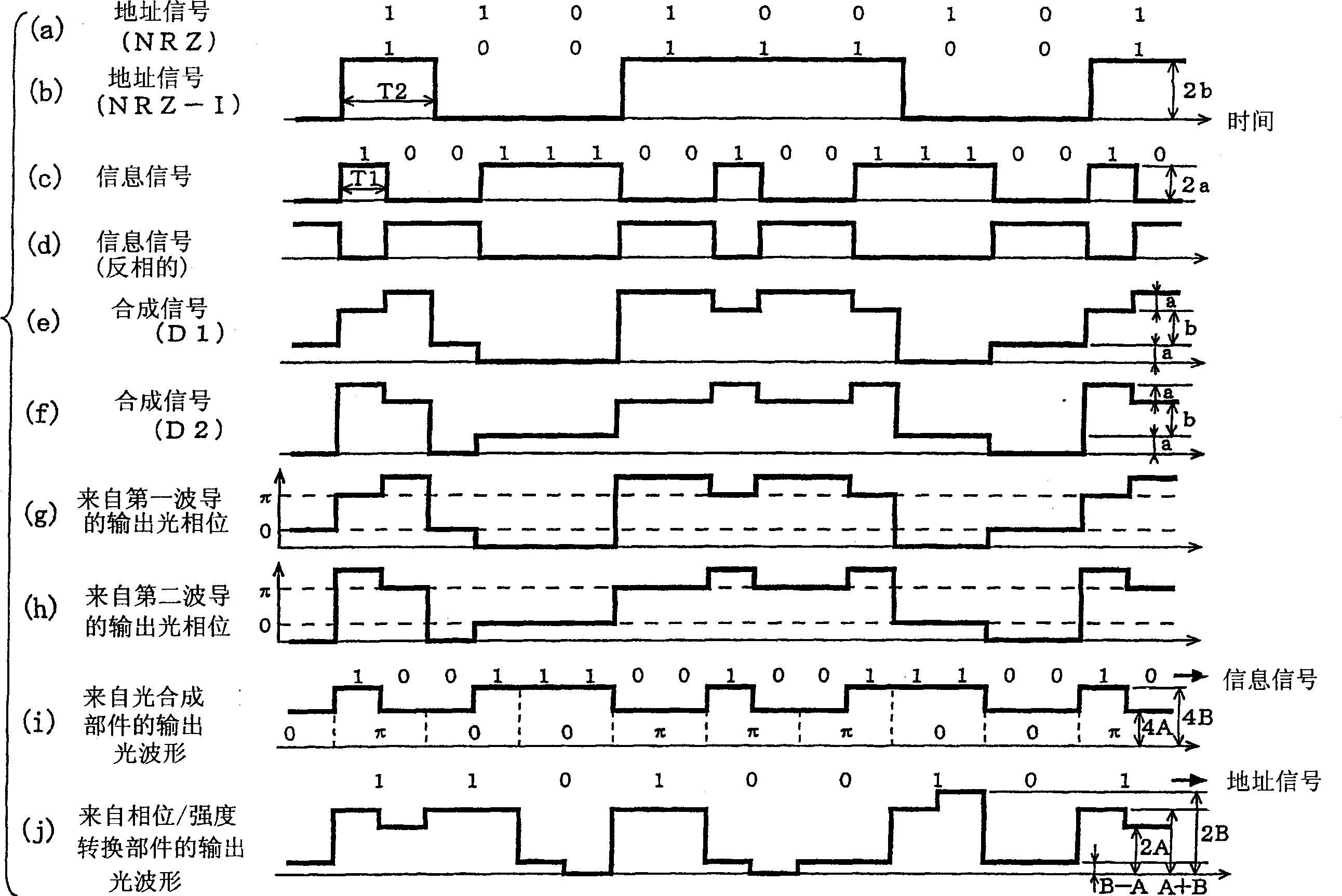
[0027]Fig. 1 is a block diagram illustrating the structure of an optical packet switch according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1 , an optical packet switch according to a first embodiment of the present invention includes an optical transmitter section 100 , an optical transmission section 200 and a router section 300 . The optical transmitter component 100 includes a light source 101 and a light modulation component 102 . The light modulation unit 102 includes a splitter unit 103, a first splitter unit 104, a first synthesis unit 105, a first waveguide 106, a second waveguide 107, a second synthesis unit 108, a second splitter unit 109, and an inverting unit 110 And light synthesis component 111. The router part 300 includes an optical splitter part 301 , an address reading part 302 and a routing switching part 303 . The address reading section 302 includes a phase / intensity conversion section 304 and a photoelectric conversion section 305 .
[00...
no. 2 example
[0051] Figure 7 is a block diagram illustrating the structure of an optical packet switch according to a second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 7 , an optical packet switch according to the second embodiment includes an optical transmitter section 120 , an optical transmission section 200 and a router section 300 . The optical transmitter part 120 includes an optical signal source 121 and a light modulation part 122 . The optical signal source 121 includes a light source 101 , a first splitter part 104 , a first combining part 105 and a first waveguide 106 . The light modulation section 122 includes the second waveguide 107 , the second synthesis section 108 , the second splitter section 109 and the inversion section 110 . The router section 300 has the same structure as the router section 300 in the first embodiment.
[0052] Such as Figure 7 It can be seen that in the optical packet switcher according to the second embodiment, the phase modulation function...
no. 3 example
[0054] Figure 8 is a block diagram illustrating the structure of an optical packet switch according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 8 , an optical packet switch according to the third embodiment includes an optical transmitter section 130 , an optical transmission section 200 and a router section 300 . The optical transmitter part 130 includes an optical signal source 131 and a light modulation part 132 . The optical signal source 131 includes a light source 101 , a second waveguide 107 , a second combining part 108 , a second splitter part 109 and an inverting part 110 . The light modulation part 132 includes the first splitter part 104 , the first combining part 105 and the first waveguide 106 . The router section 300 has the same structure as the router section 300 in the first embodiment.
[0055] Such as Figure 8 It can be seen that in the optical packet switcher according to the third embodiment, the phase modulation function using the addre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com