Failsafe differential amplifier circuit
A fail-safe and auxiliary amplifier technology, applied in the direction of differential amplifiers, amplifier combinations, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of input differential signal equipment not connected to the system, input differential signal attenuation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
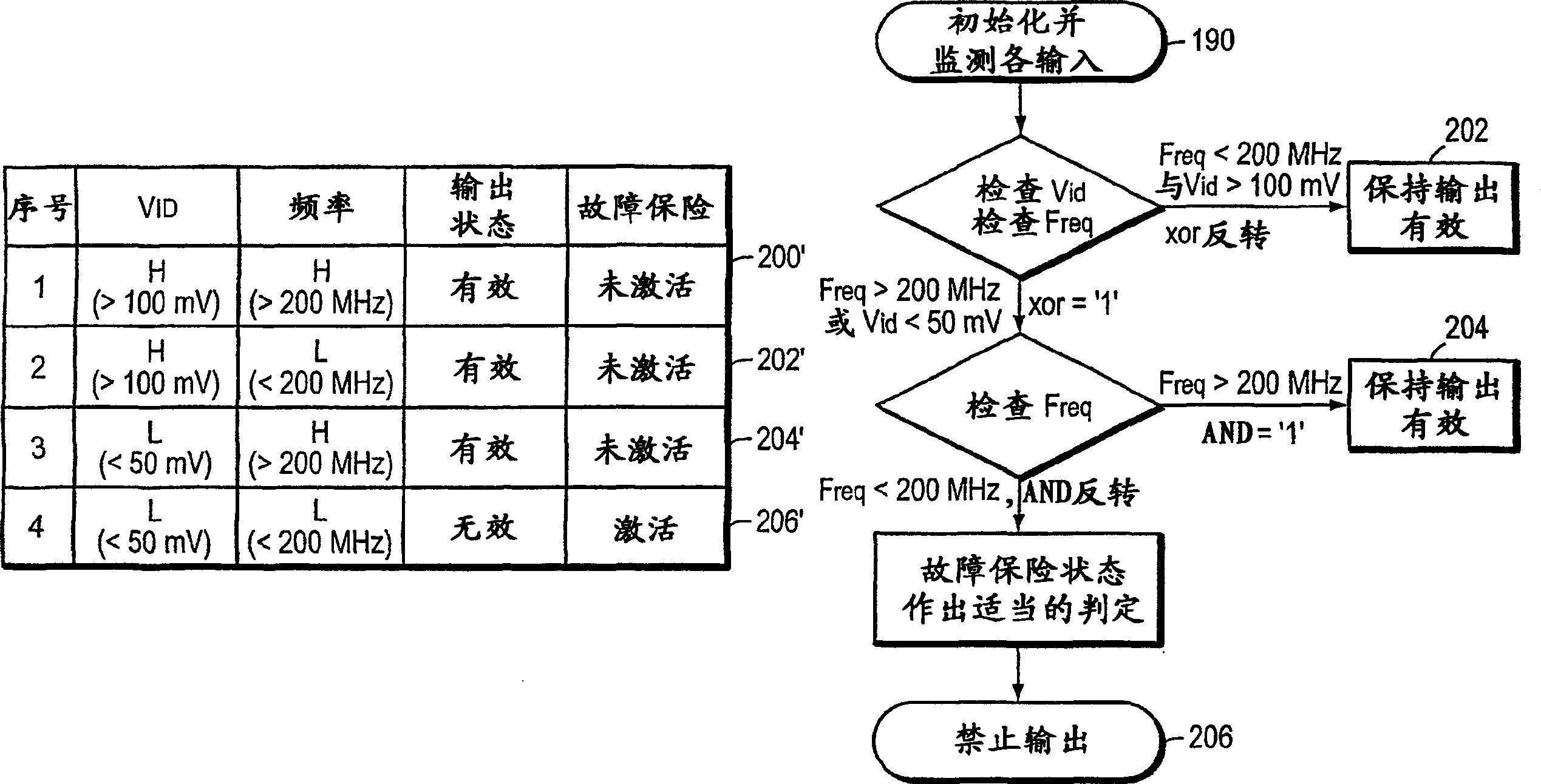
[0019] figure 1 shows the basic hysteresis curve found in virtually all differential signal receivers. The horizontal axis represents the positive differential signal Vid, and the vertical axis represents the output signal from 0 to +Vcc. A negative differential signal starting at 100 increases until the threshold Vid+ is reached, at which point the output goes high. Vid then travels in the negative direction 102 while the output remains high until the threshold Vid- is reached, at which point the output goes low. The difference between Vid+ and Vid- is the hysteresis 104 inherent in the circuit. The hysteresis is required due to the differential input sensitivity of the amplifier. Without hysteresis, if a signal falls within the input sensitivity region, the amplifier cannot accurately determine its state. If the signal stays in this undefined region, there is a possibility that the amplifier becomes unstable and oscillates. Additional hysteresis can be added by design t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com