Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for a solid-state imaging device and a manufacturing method, which can be applied to electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., and can solve the problems of rising absorptivity, difficulty in concentrating light, and burying of recesses by resins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
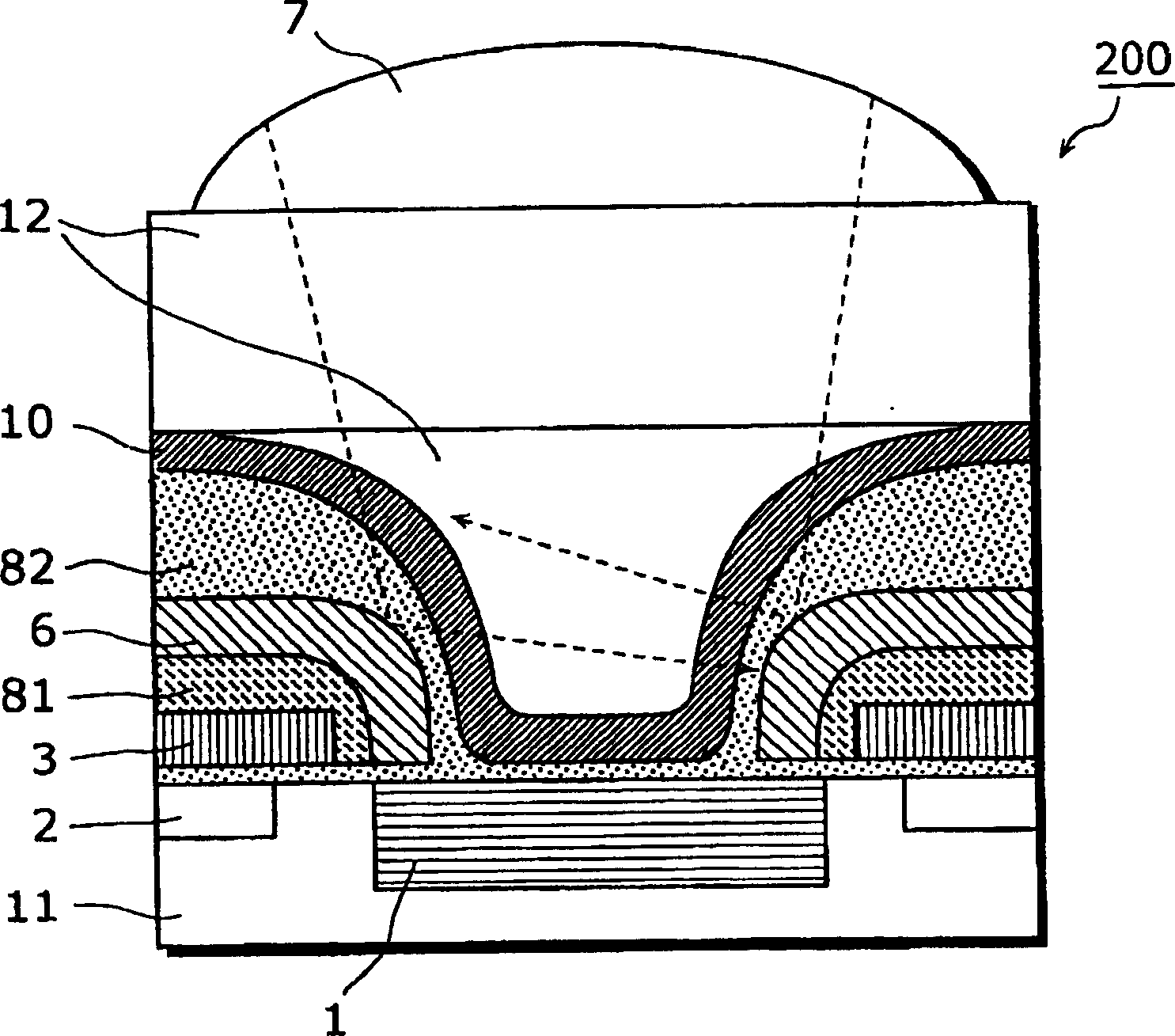
[0057] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram showing the cross-sectional structure of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0058] exist Figure 5 Among them, the solid-state imaging device 51 includes: a photodiode 1 having a photoelectric conversion function, a vertical transfer part 2 of an embedded channel structure that transfers signal charges to a vertical direction, a vertical transfer grid 3 that controls vertical transfer, and is used to make the incident Light is incident on the photodiode 1 and is not incident on the light-shielding film 6 of other areas such as the vertical transport section 2, and is made of SiO 2 The dielectric films 81, 82 and 83 as the main components, the dielectric film 21 with SiON as the main component, the protective film 10, and the organic dielectric film 12 with both planarization and color filtering functions are used to condense the incident light to the photoelectric A lens 7 fo...
no. 2 approach
[0077] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram showing the cross-sectional structure of the solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0078] In the solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment, the dielectric film 21 is also formed on the upper part of the photodiode 1. The difference from the first embodiment is that the dielectric film 21 and the photodiode 1 are formed on the upper part of the Si substrate 11 interface. SiO 2 Multilayer structure of film 82 .
[0079] like Figure 7 As shown, the solid-state imaging device 52 includes: a photodiode 1, a vertical transfer section 2, a vertical transfer grid 3, and a light-shielding film 6 for making incident light incident on the photodiode 1 and not incident on other areas such as the vertical transfer section 2. , with SiO 2 Dielectric films 81, 82, and 83 as main components, dielectric film 21 mainly composed of SiON, protective film 10, and organic dielectr...
no. 3 approach
[0100] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram showing the cross-sectional structure of the solid-state imaging device according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0101] like Figure 9 As shown, a unit pixel 201 includes: a photodiode 1 formed in a silicon substrate 11 with a photoelectric conversion function; a vertical transfer part 2 of an embedded channel structure that transfers signal charges to a vertical direction; a vertical transfer gate that controls vertical transfer pole 3; formed on the upper part of the vertical transfer gate 3, made of SiO 2 A dielectric film 81 as the main component; a light-shielding film 6 formed on the top of the dielectric film 81 and used to prevent incident light from entering areas such as the vertical transport portion 2 and the vertical grid 3; of SiO 2 The dielectric film 82 that is the main component; only the portion of the dielectric film 82 that is opposed to the opening of the photodiode 1 is connected, and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com