Optical semiconductor device
An encoder and optical technology, applied in the field of optical encoders, can solve the problems of reduced parallelism, narrowing of the distance between a light-emitting element 31 and a light-receiving element 32 and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0033] (1) The first embodiment
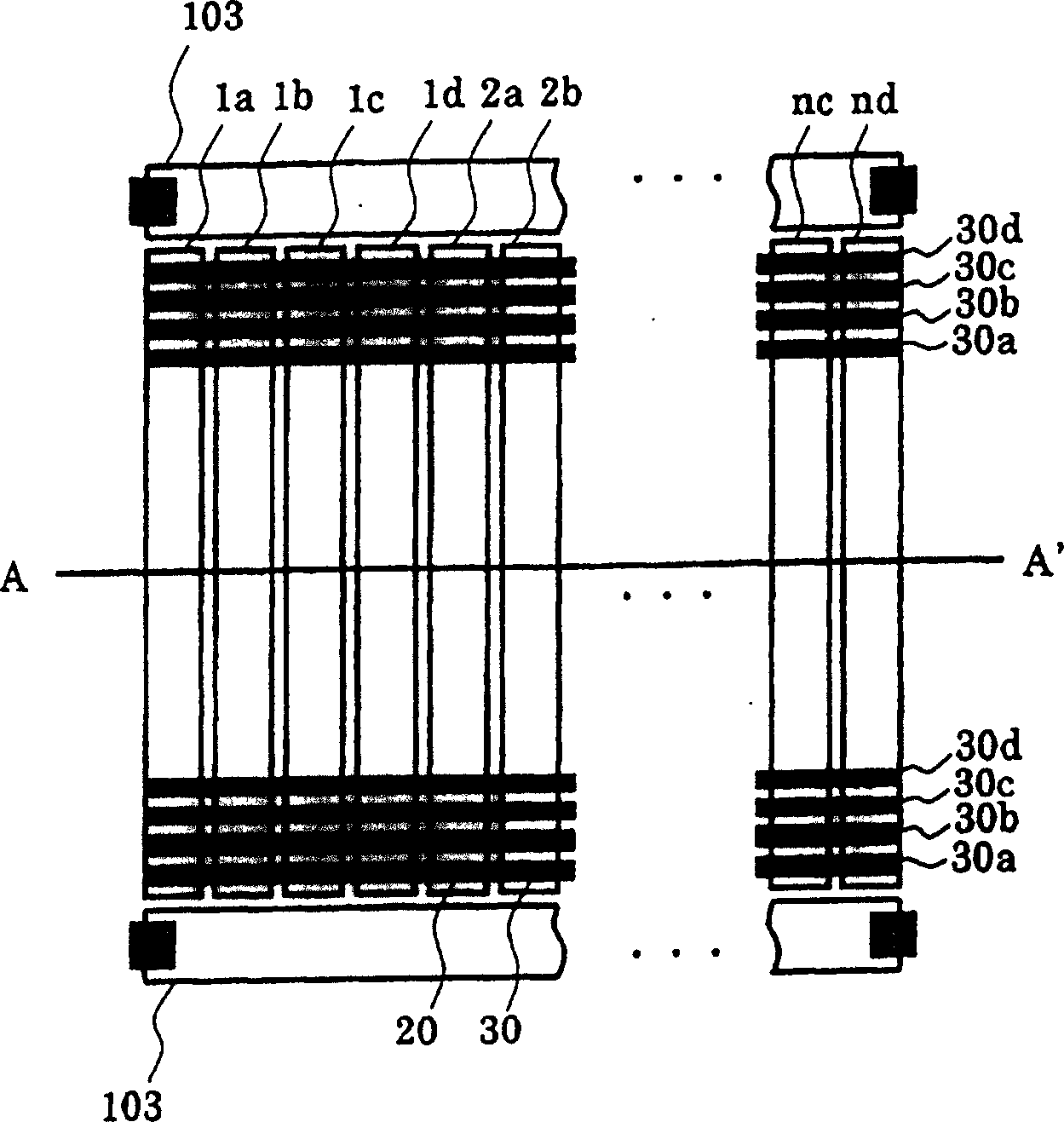
[0034] figure 1 It is a plan view showing an example of the photodiode configuration of the optical encoder according to the embodiment of the present invention.
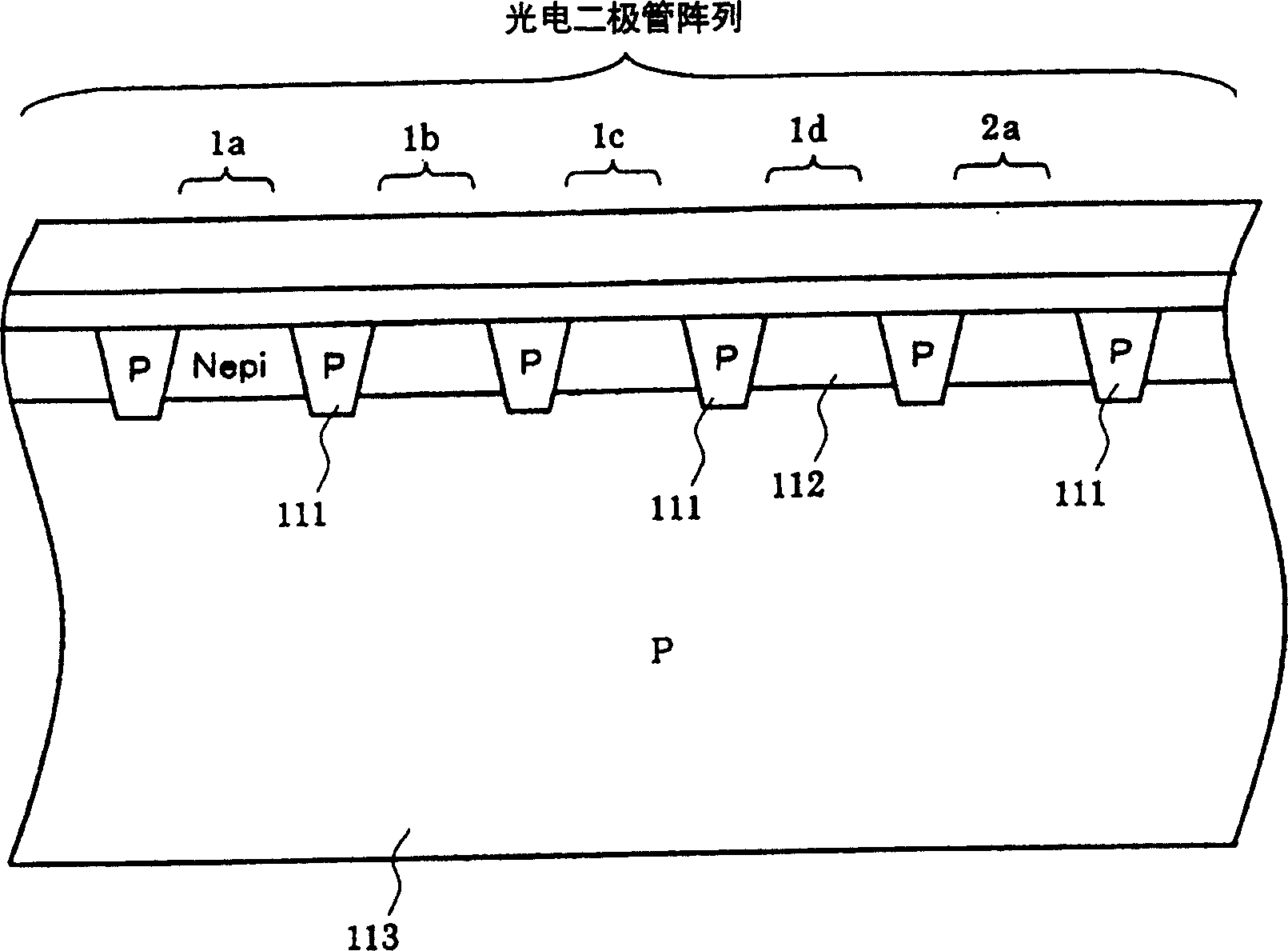
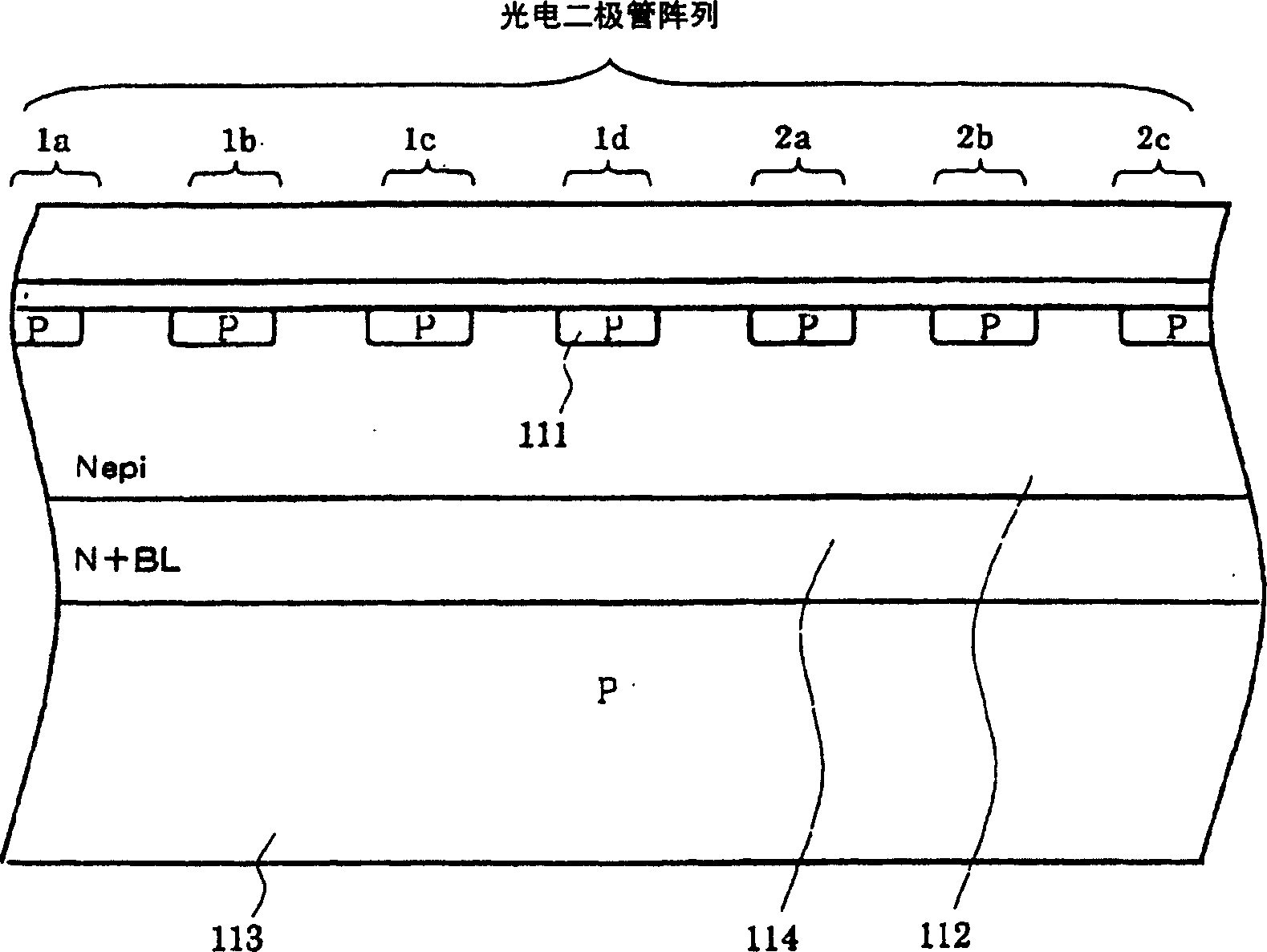
[0035] That is, also in the present embodiment, substantially rectangular signal photodiodes (1a, 1b, . . . , nd) are arranged in parallel. These signal photodiodes are sequentially connected to any one of the four-phase wiring lines 30a to 30d. That is, four-phase photodiode groups (1a-na, 1b-nb, 1c-nc, 1d-nd) connected in common are formed by the four-phase wirings 30a-30d, respectively. Furthermore, adjacent photodiodes (for example, 1a to 1d) are arranged so as to belong to different photodiode groups.
[0036] In addition, above and below these photodiodes for signals, photodiodes 103 for DC cancellation are provided. The formation of the photodiodes 103 for DC can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com