Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein delation analogs
An analogue and permeability technology, applied in the direction of bactericidal/permeability enhancing protein, peptide/protein component, animal/human protein, etc., can solve the problem that the loss of survival of Gram-negative bacteria has not been reversed, and the correlation has not been obtained clarification and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1rBPI(10-193)C132ApING 1742。 Embodiment 2pING 1742CHO and rBPI(10-193)C132A。 Embodiment 3
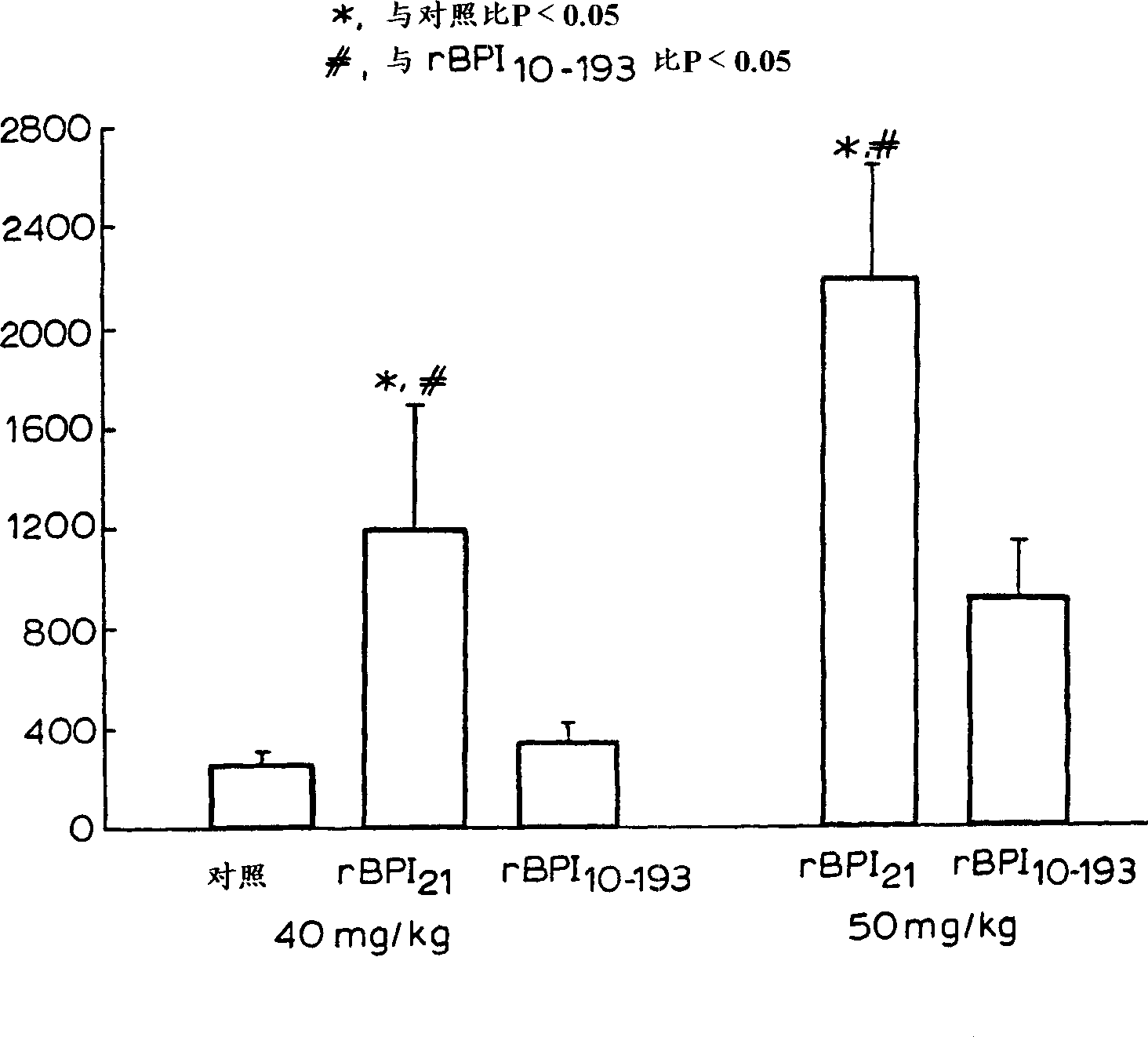
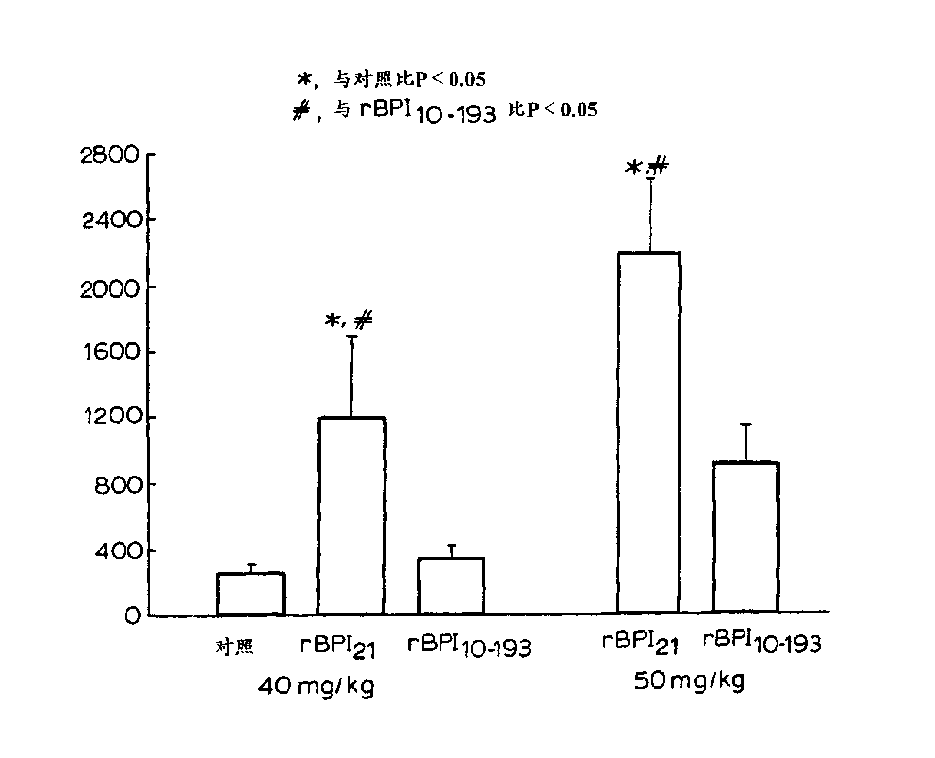
[0032] Other aspects and advantages of the invention will become apparent from the following illustrative examples. Example 1 describes the construction of the expression vector pING1742 encoding rBPI(10-193)C132A. Example 2 describes the transformation of CHO cells with pING 1742 and the selection of the highest producing clone secreting rBPI(10-193) C132A. Example 3 describes the preparation and purification of rBPI(10-193)C132A in 2-L and 500-L fermentors. Example 4 describes the effect on rBPI(10-193)C132A and rBPI 21 analysis of biochemical characteristics. Embodiment 5, 6 and 7 describe and rBPI respectively 21 In vitro LPS-binding activity was compared in the following assays, including competition binding assay assays and assays measuring complex formation rates using velocity nephelometric assays, bactericidal activity, and LPS neutralizing activity of rBPI(10-193)C132A. Example 8 highlights the in vivo activity of rBPI(10-193)C132A.
Embodiment 1
[0034] Construction of expression vector pING1742
[0035] The rBPI(10-193)C132A expression vector, pING 1742, was constructed as follows. First, the expression vector pING 4115 was constructed by ligating the following fragments, including the BamHI-BsaI fragment containing the pING 3174neo gene and the BsaI-XhoI fragment containing the CMV promoter and rBPI from pING 4144 21 gene and the XhoI-BamHI fragment containing the 3' untranslated region of the mouse (Kaba) light chain from pING 4537 (pING 3174, pING 4144 and pING4537 are described in US Patent No. 5,420,019, incorporated herein by reference). The resulting pING4155 vector contains the encoding rBPI fused to the human IgG enhancer, the human CMV promoter, and the 3' untranslated region of the mouse (Kaba) light chain 21 gene. It also contains the neo gene encoding neomycin phosphotransferase for screening against the antibiotic Geneticin ) (G418) resistant transformants.
[0036] Vector pING1732 wa...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Transformation of CHO cells with pING 1742
[0042] CHO-K1 cells (American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) License No. CCL 61) were adapted for growth in serum-free Ex-Cell 301 medium as follows. CHO-K1 cells cultured in Ham's F12 medium were trypsinized, centrifuged and resuspended in Ex-Cell 301 medium. Cells were cultured in 125ml culture flasks at 100rpm and passaged every two to three days with 125ml or 250ml culture flasks.
[0043] These Ex-Cell 301 -adapted CHO cells were transfected with pING1742 by electroporation. Before transfection, pING1742 was digested with NotI which linearized this plasmid. 48 hours after recovery the cells were treated with approximately 10 4 cells / well were seeded in 96-well plates containing Ex-Cell 301 medium supplemented with 0.6 mg / mL G418 (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD). At approximately 2 weeks, supernatants from approximately 250 wells containing single colonies were screened for the presence of BPI-reactive ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com