Image display device
A technology for image display devices and bus electrodes, which is applied in the direction of image/graphic display tubes, electrode devices and related components, screen tubes, etc., and can solve problems such as increased step difference, increased film resistance value, and disconnection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
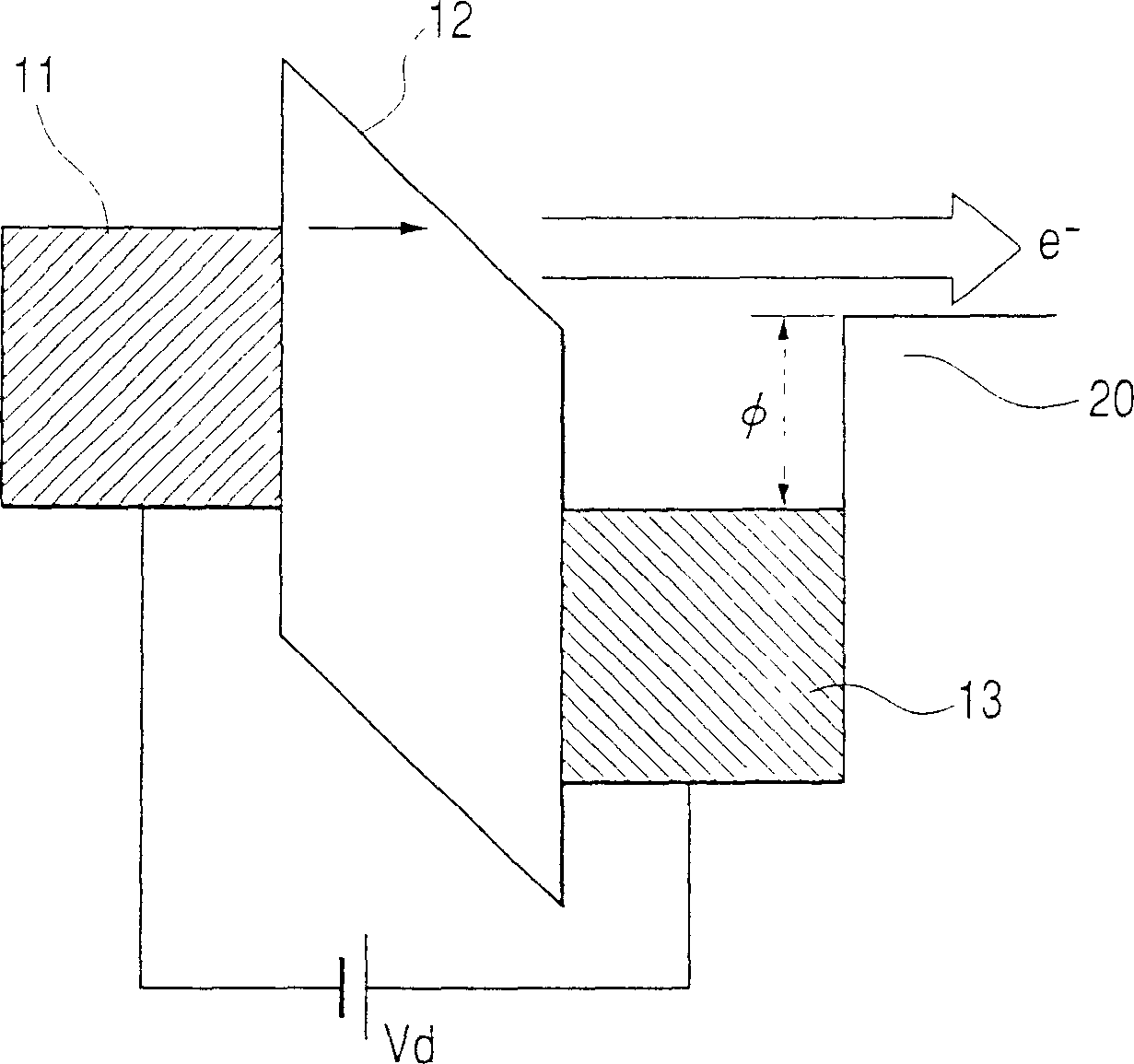
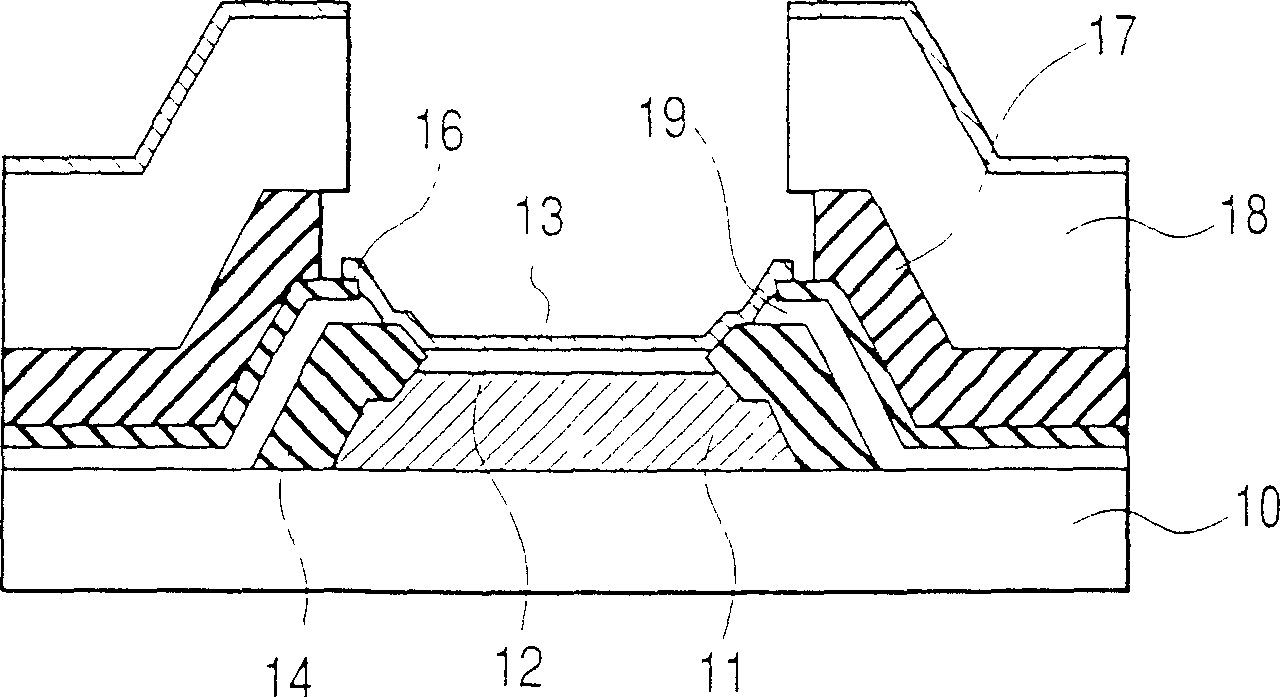
[0043] As the first embodiment of the present invention to achieve the above object, taking the MIM type as an example, it is described that the upper part is formed by stacking the first metal layer (upper bus electrode), the second metal layer, and the insulating layer in this order from the upper bus electrode. Thin-film electron source (cathode) in case of laminated film of bus electrode and overhang structure.
[0044] First, use Figure 4-15 A method of forming a thin-film electron source will be described.
[0045] First, a metal film for the lower electrode is formed on an insulating substrate 10 such as glass. As the lower electrode material, Al and Al alloys are used. The reason why Al and Al alloys are used is that a high-quality insulating film can be formed by anodic oxidation. Here, an Al—Nd alloy doped with 2 atomic weight % of Nd was used. For film formation, for example, a sputtering method is used. The film thickness was 300 nm. After film formation, th...
no. 2 Embodiment
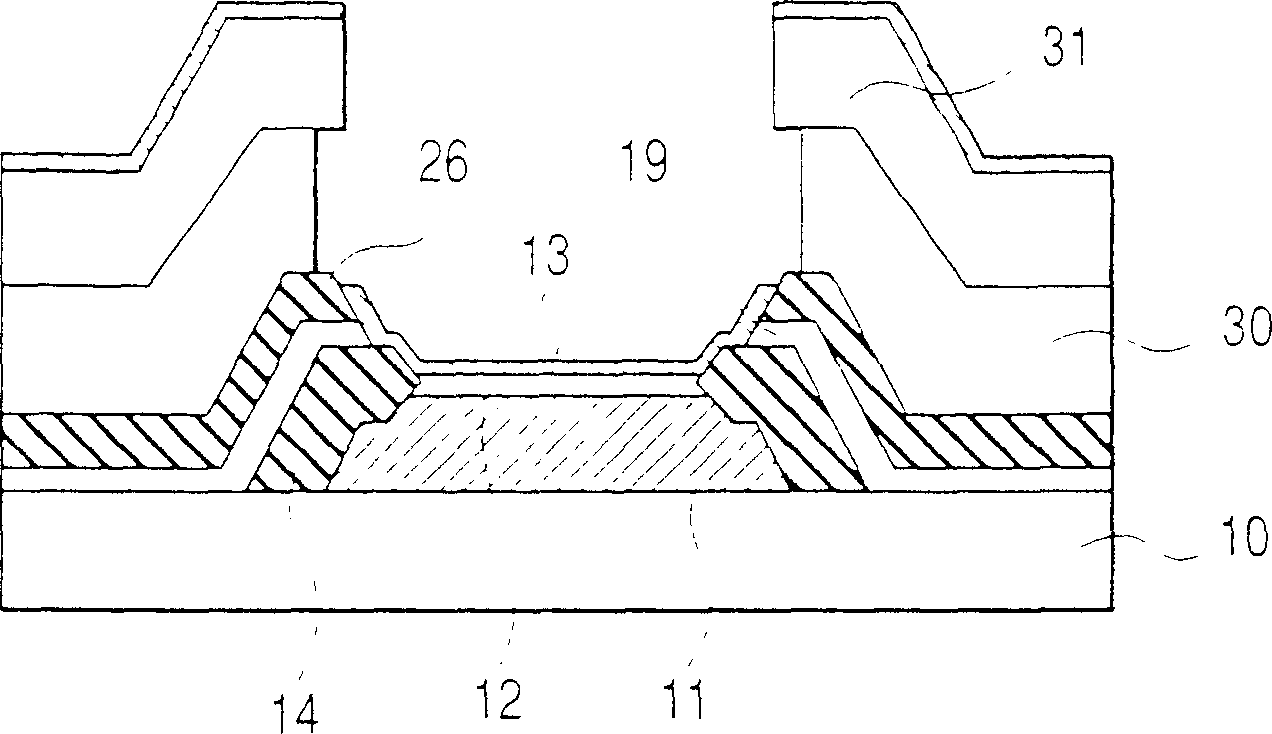
[0058] As a second embodiment of the present invention that achieves the above object, the MIM type is used as an example to explain that the laminated film constituting the upper bus electrode and the overhang structure is that the first metal layer (upper bus electrode) is sequentially laminated from the upper bus electrode side. ), an insulating layer, and a thin-film electron source in the case of a second metal layer (surface electrode).
[0059] First, the electron acceleration layer 12 was formed according to the same procedure as in Example 1. Next, the second protective insulating layer 19 and the first metal layer 26 are formed into films. As the second protective insulating layer 19 , for example, Si oxide is used, and the film thickness is 40 nm. On the other hand, as the material of the first metal layer 26, an Al—Nd alloy is used. In addition, as the first metal layer 26, Cr or a Cr alloy or the like may be used. The film thickness is 300nm ( Figure 16 ).
...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0067] As a third embodiment of the present invention that achieves the above object, the MIM type is used as an example to explain that the laminated film constituting the upper bus electrode and the overhang structure is that the first metal layer (upper bus electrode) is sequentially laminated from the upper bus electrode side. ), a thin-film electron source in the case of the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer.
[0068] First, the first metal layer (upper bus electrode) 26 is processed and formed so as to be perpendicular to the lower electrode 11 by the same procedure as in the second embodiment. Here, an Al—Nd alloy is used as the material of the first metal layer 26 . In addition, Cr or a Cr alloy or the like may be used as the first metal layer. The film thickness is 300nm ( Figure 17 ).
[0069] Next, the first insulating layer 30 and the second insulating layer 31 which are laminated films of the overhang structure are formed ( Figure 23 ). ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com