Oligonucleotides and methods for treating neurological diseases
A technology of oligonucleotides and nucleotides, applied in nervous system diseases, biochemical equipment and methods, gene therapy, etc., can solve problems such as early polyadenylation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0486] Example 1: Initial design and selection of STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides
[0487] Antisense oligonucleotides complementary to STMN2 RNA were designed and tested to identify STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) capable of acting as inhibitors of STMN2 transcripts including cryptic exons.
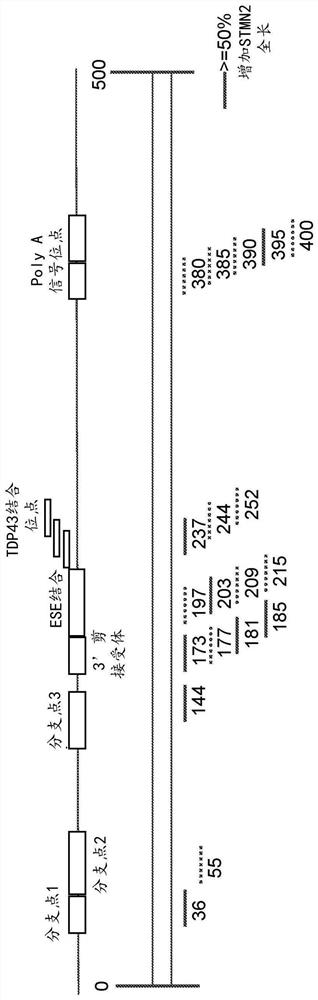
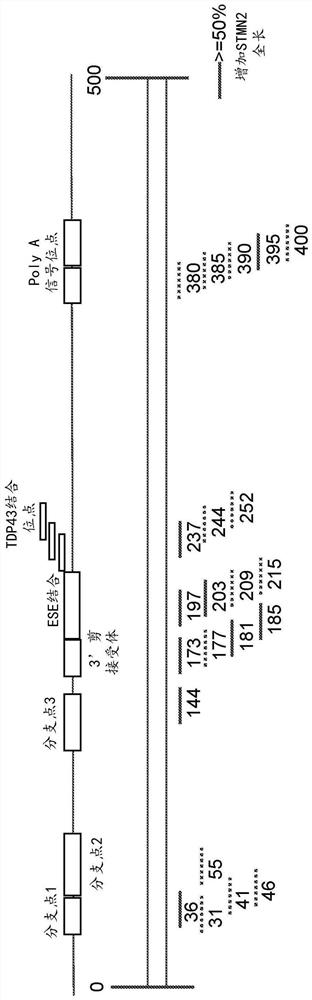
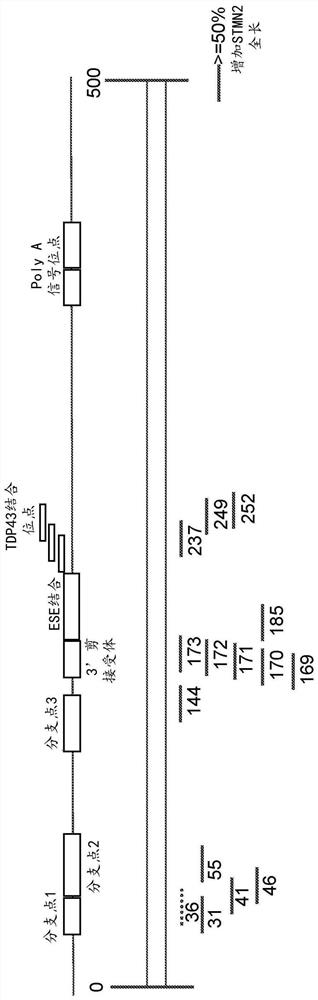
[0488] Figures 1A-1C Portions of the STMN2 transcript and STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides designed to target certain portions of the STMN2 transcript are depicted. Specifically, regions of the STMN2 transcript include branch points (eg, branch points 1, 2, and 3), 3' splice acceptor regions, ESE binding regions, TDP43 binding sites, and PolyA regions. STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides were identified based on the position of the STMN2 transcript to which the STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides correspond. E.g, Figure 1A STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides targeting positions 36 to 60 of the STMN2 transcript, including branch point 1, are depicted. Similarly, different STMN2 antise...
Embodiment 2
[0495] Example 2: Method for evaluating STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides
[0496] STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides were evaluated in SY5Y cells and human motor neurons. Specifically, Examples 3, 4 and 5 below describe the results resulting from the evaluation of STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides in SY5Y cells. Examples 6 and 7 below describe the results resulting from the evaluation of STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides in human motor neurons.
[0497] STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides were evaluated in SY5Y cells. Cells were plated in 6- or 96-well plates and grown to 80% confluence. Antisense oligonucleotides (AON) to TDP43 were transfected with RNAiMax (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to express the cryptic exon, thereby preventing transcription of the full-length STMN2 (STMN2-FL) product. Vehicle was treated with RNAiMax alone. Positive controls included cells treated with TDP43 siRNA alone ("siRNA TDP43") and / or TDP43 AON alone ("AON TDP43" or "TDP43 AON"). s...
Embodiment 3
[0517] Example 3: STMN2 antisense oligonucleotides restore full-length STMN2 and reduce STMN2 transcripts with cryptic exons in SY5Y cells
[0518] Figure 1B and 1C demonstrated the effectiveness of STMN2 AONs targeting distinct regions of the STMN2 transcript with cryptic exons. Particularly, Figure 1B STMN2 AONs designed and evaluated in SY5Y cells are described. Figure 1C STMN2 AONs designed and evaluated in human motor neurons are depicted. STMN2 AONs represented by solid lines produced cells with more than 50% increased STMN2-FL mRNA expression compared to TDP43 AONs treated alone. STMN2 AONs represented by dashed lines produced cells with less than 50% increased STMN2-FL (full length) mRNA compared to TDP43 AONs treated alone.
[0519] about figure 2 , when treated with 500 nM TDP43 AON, TDP43 transcripts were reduced by ~52% and STMN2-FL by ~57%. 500 nM treatment of STMN2 AON with SEQ ID NO:36 increased TDP43 levels by 25% and STMN-FL levels by 55% (rescue to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com