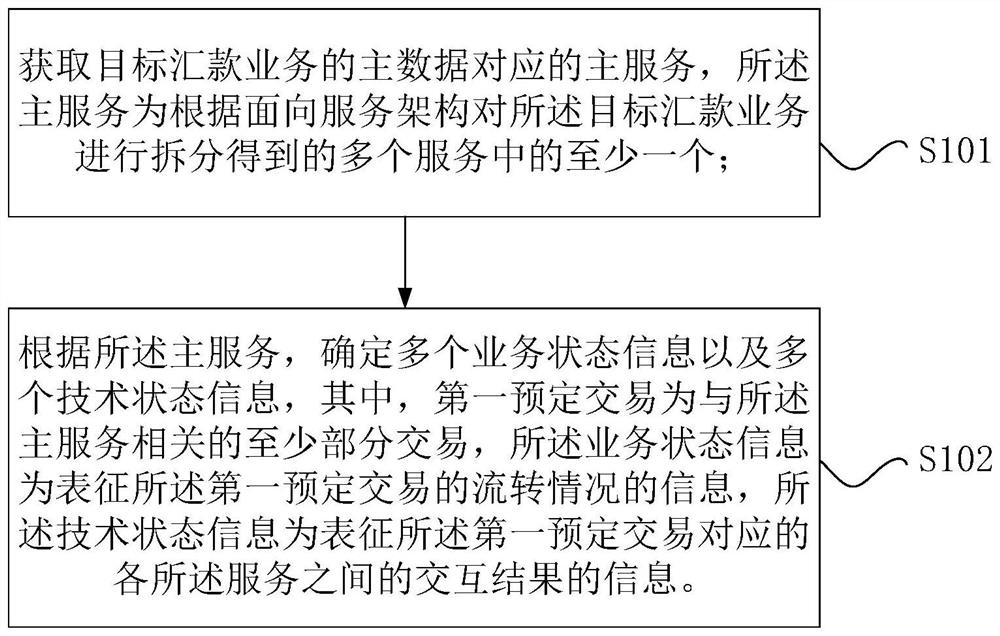
Method for determining state information of remittance service based on distributed architecture
A technology of distributed architecture and status information, applied in the fields of processors, electronic devices, and computer-readable storage media, can solve the problems of unclear and accurate remittance process status, and achieve dynamic understanding requirements, business status information and technical status. Clear and accurate information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] The remittance status flow process of the large-amount payment channel and the small-amount payment channel:
[0084] Outward remittance direction: the user applies for outward remittance, and the teller applies for verification and pending account processing after the remittance fails; different states are used to represent the business processing results; and the corresponding failure states are extracted according to different failure scenarios; the final remittance status includes: Deduction failed, reversed, liquidated / netted, queued, returned, and re-sent. The specific flow of remittance status is as follows:
[0085] (1) When the user handles RMB inter-bank remittance through the counter, the account deduction fails and the transaction ends, remittance status = deduction failure (final state); technical status information = outbound call failure or outbound call timeout / abnormal, corresponding to the failure of the associated system Response and no response;
[...
Embodiment 2
[0098] The remittance status flow process of online payment inter-bank settlement:
[0099] Remittance direction: Taking the real-time cross-bank outward remittance through the counter as an example, different statuses are used to represent the business processing results, including the status "netted" extracted according to the success scenario, and the corresponding status is extracted according to different failure scenarios. The failure status is "deduction failed", "reversed", "reversed failed", and the flow of remittance status is as follows:
[0100] (1) The user handles the inter-bank outward remittance through the counter. If the account deduction fails, the transaction ends. Remittance status = completed (final status), technical status information = outbound call timeout / abnormal;
[0101] (2) Outbound supernet front, if the outbound call fails, the remittance status = has been reversed (reset), technical status information = outbound call failed; if the outbound c...
Embodiment 3
[0109] UnionPay's remittance status transfer process:
[0110] Remittance direction: real-time transfer out, debit transfer out, and the finalized status includes deduction and deduction failure;
[0111] Remittance direction: real-time transfer-in, debit transfer-in, and the finalized status includes credited, credited failed, and sent failed. The flow of remittance status is as follows:
[0112] (1) The user uses the bank card of the First Bank to handle UnionPay remittance through the ATM (Automatic Teller Machine, ATM for short) of the First Bank. Successful call, remittance status = debited (final state); account withdrawal failed, technical status information = outbound call failed, remittance status = deduction failed (final state); account withdrawal timed out, technical status information = outbound call timeout / abnormal , remittance status = deduction failure (final state);
[0113] (2) The user uses the bank card of the First Bank to handle the UnionPay remittanc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com