Preparation method of solid-phase enriched O-GlcNAc glycopeptide
A glycopeptide and enrichment technology, applied in the field of biomolecule preparation and analysis, can solve the problems of enrichment of O-GlcNAc glycopeptides and low site specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
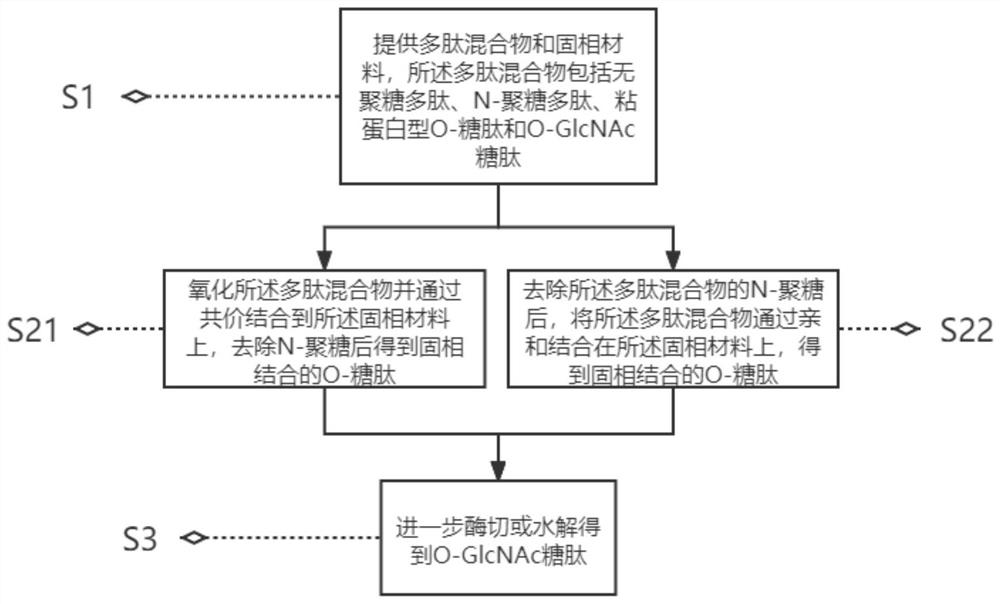
[0041] See figure 1 , the present application discloses a preparation method for solid-phase enrichment of O-GlcNAc glycopeptides, which comprises the following steps:
[0042] S1. Provide a polypeptide mixture and a solid phase material, the polypeptide mixture includes glycan-free polypeptides, N-glycan polypeptides, mucin-type O-glycopeptides and O-GlcNAc glycopeptides;
[0043] S21. Oxidize the polypeptide mixture and covalently bind to the solid phase material to obtain solid phase bound O-glycopeptides and O-GlcNAc glycopeptides after removing N-glycans;
[0044] or,
[0045] S22. After removing the N-glycans of the polypeptide mixture, affinity-binding the polypeptide mixture on the solid phase material to obtain solid phase bound O-glycopeptide and O-GlcNAc glycopeptide;
[0046] as well as,
[0047] S3. Further enzyme digestion or hydrolysis to obtain O-GlcNAc glycopeptide.
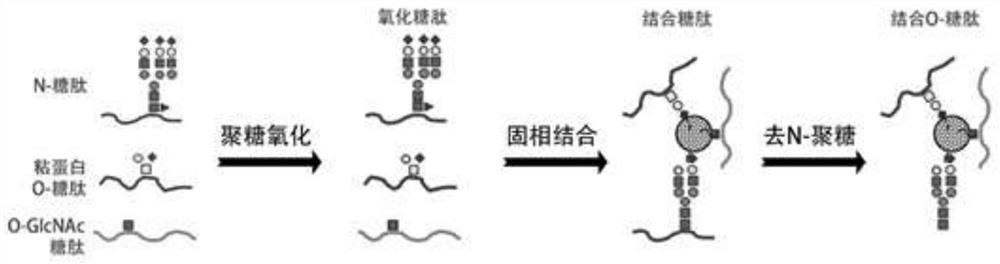
[0048] Specifically, in S21, the polypeptide mixture is oxidized and covalently bound to ...
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example One Covalent Bonding Preparation of Solid-Phase-Bound O-Glycopeptides
[0065] See figure 2 ,specific:
[0066] Freeze the tissue in dry ice or -80°C for 2-3 hours, and break the tissue immediately after taking it out;
[0067] Add 400-600 μl 1 times RIPA lysate to the tissue, use an ultrasonic breaker with 30-40% energy, break the sample for 30 seconds and put the sample in ice to cool, repeat this step 4-6 times until the sample solution is clear;
[0068] Take 2-4μl sample, dilute it 5-10 times, and test the protein concentration with BCA;
[0069] According to the concentration, take 800-1000μg protein and dissolve it in urea with a total volume of 400-600μl and a final concentration of 8M, shake the sample slightly to ensure that the protein is completely dissolved;
[0070] Add 80-100μl 120mM dithrethiol (DTT), and react at 37°C for 1-1.5 hours;
[0071] Then add 80-100μl 160mM iodoacetamide and react in dark room at room temperature for 1-1.5 hours; ...
Embodiment 2
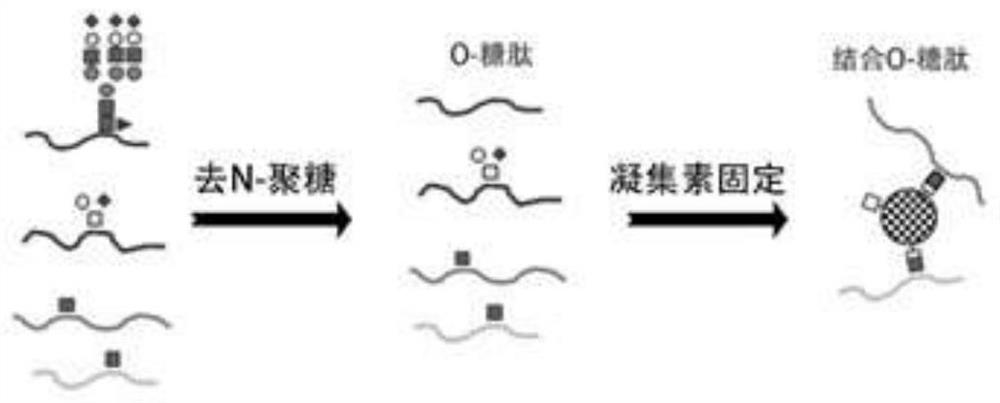
[0082] Example 2 Affinity Binding Preparation of O-Glycopeptides Binding to Solid Phase
[0083] See image 3 ,specific:
[0084] Vacuum freeze-dry 800-1000 μg of C18 purified polypeptide and redissolve in 400-600 μl PBS buffer, pH 7.2-7.6;
[0085] Add 1-2 units of N-glycosidase (PNGaseF) to the sample, react at 37°C for 4-6 hours, so that the N-glycan can be removed by enzymatic digestion, and glycan-free polypeptide, mucin-type O-glycopeptide, O- GlcNAc glycopeptides and N-glycans;
[0086] Add 20-30 μl concentrated TFA (>99%, w / v) to the sample to lower the pH to below 3.0, purify with C18 to remove N-glycans, and vacuum freeze-dry the purified sample;
[0087] Purified samples were redissolved in 400-500 μl lectin WGA buffer, i.e. 10 mM HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N'-2'-ethanesulfonic acid), 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.5;
[0088] Rinse 200-300μl WGA lectin spherical resin and 400-500μl WGA buffer 2-3 times, keep the WGA resin, and remove the washing solution;
[0089] Ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com