Damping force adjustment type shock absorber
A damping force and buffer technology, applied in shock absorbers, shock absorbers, liquid shock absorbers, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to adjust the damping force in extremely small and low-speed areas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0024] A first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. For convenience, the figure 1 The up and down directions in are directly referred to as "up and down directions".
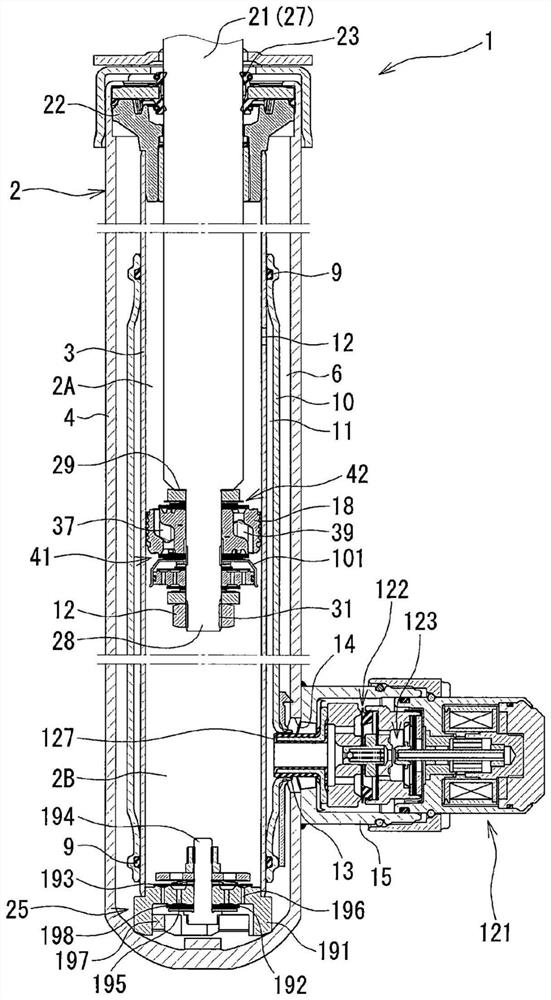
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, the damping force adjustable shock absorber 1 of the first embodiment is a so-called control valve laterally mounted type damping force adjustable shock absorber in which the damping force adjusting mechanism 121 is mounted laterally on the cylinder 2 . The cylinder 2 has an inner cylinder 3 and an outer cylinder 4 arranged coaxially with the inner cylinder 3 . Between the inner cylinder 3 and the outer cylinder 4, a storage chamber 6 is formed. It should be noted that oil (working fluid) is sealed in the inner tube 3 , and oil and gas are sealed in the storage chamber 6 .
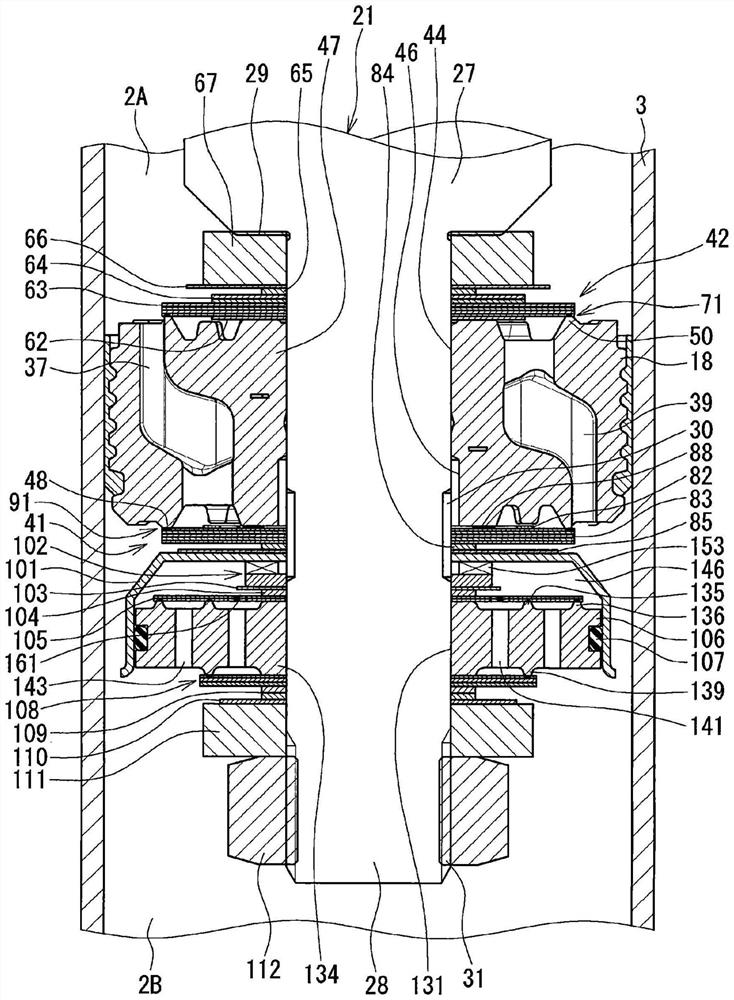
[0026] In the inner cylinder 3 of the cylinder 2, a piston 18 is slidably embedded, and the piston 18 divides the inner cylinder 3 into two cylinder upper...
no. 2 approach
[0088] Next, refer to Figure 7 A second embodiment will be described. Here, differences from the first embodiment will be described. It should be noted that the same designations and reference numerals are used for the same parts as those of the first embodiment, and overlapping descriptions will be omitted.
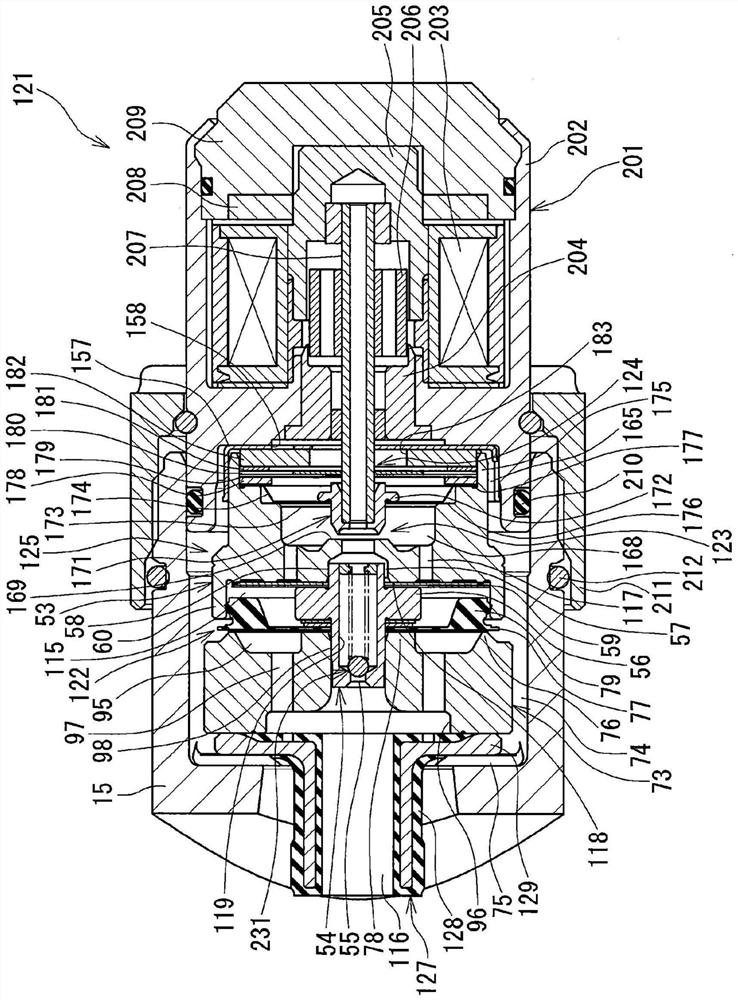
[0089] The first embodiment has a pilot pin 54 (introduction orifice forming member) in which an introduction orifice 55 is formed on a bottom portion 237 , and on the inner peripheral side of a cylindrical portion 238 of the pilot pin 54 (the shaft hole 119 of the pilot pin 54 ). , is equipped with a very small low-speed valve 231 (low-speed valve mechanism). In addition, in the first embodiment, the pilot chamber 115 is formed on the back side of the main disc valve 77 by bringing the packing 79 of the main valve 122 into slidable contact with the inner peripheral surface of the cylindrical portion 60 of the pilot body 53 . (back pressure chamber). That is, the ma...
no. 3 approach
[0100] Next, refer to Figure 8 A third embodiment will be described. Here, differences from the first embodiment and the second embodiment will be described. It should be noted that the same names and reference numerals are used for the common parts as those of the first embodiment and the second embodiment, and overlapping descriptions will be omitted.
[0101] In the damping force adjustment mechanism 242 of the second embodiment, the rigid body main valve 243 (the introduction orifice forming member) formed with the introduction orifice 55 is seated on the annular seat portion 76 formed in the main body 73 , thereby , a valve chamber 265 is formed between the main body 73 and the rigid body main valve 243 . In addition, in the second embodiment, the micro low speed valve 241 (low speed valve mechanism) having the micro low speed disc 258 is provided at the bottom 244 of the rigid main valve 243 .
[0102] In contrast, in the damping force adjustment mechanism 272 of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com