Synthetic resin stent
A synthetic resin and network-forming technology, which can be used in stents, medical science, prostheses, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to perform and poor followability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
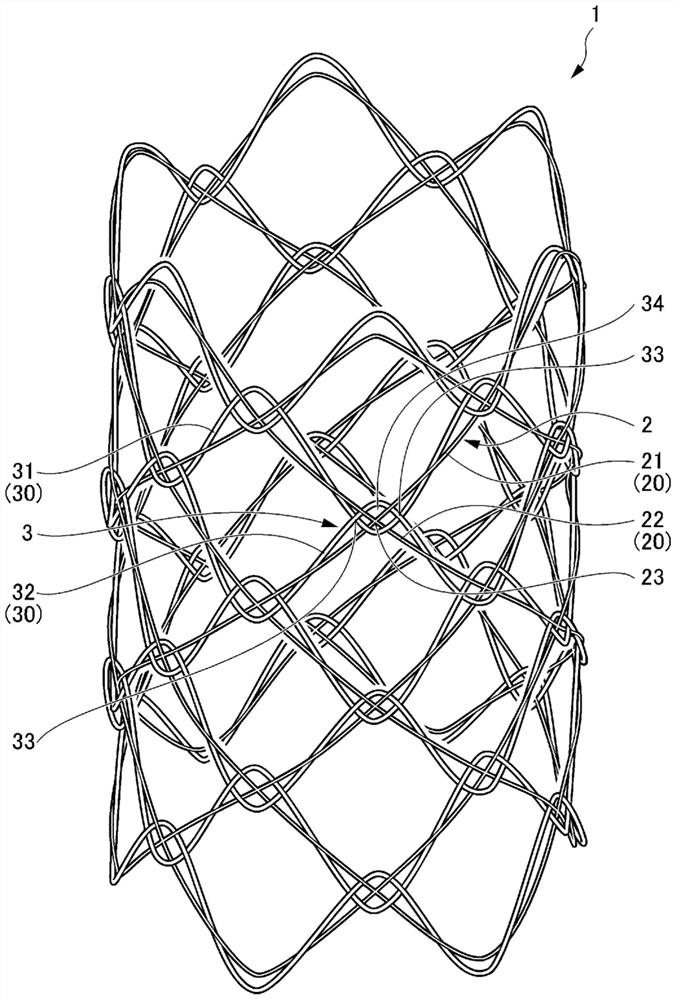
[0031] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , the biodegradable stent 1 of the first embodiment will be described.
[0032] figure 1 It is a perspective view showing the biodegradable stent 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. figure 2 yes figure 1 An enlarged view of the biodegradable scaffold 1 shown.
[0033] The synthetic resin stent of this embodiment is a biodegradable stent 1 made of biodegradable fibers, such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the mesh-shaped cylindrical portion 2 (first knitting configuration portion) and the wave-shaped knitting portion 3 (second knitting configuration portion) knitted and arranged on the mesh-shaped cylindrical portion 2 are provided.
[0034] The mesh-shaped cylindrical part 2 is formed into a cylindrical shape by weaving a plurality of fibers 20 into a mesh shape, and has a plurality of rhombic holes formed by the fibers 20 and arranged in an orderly manner on the outer periphery. The mesh of the mesh-...
no. 2 approach
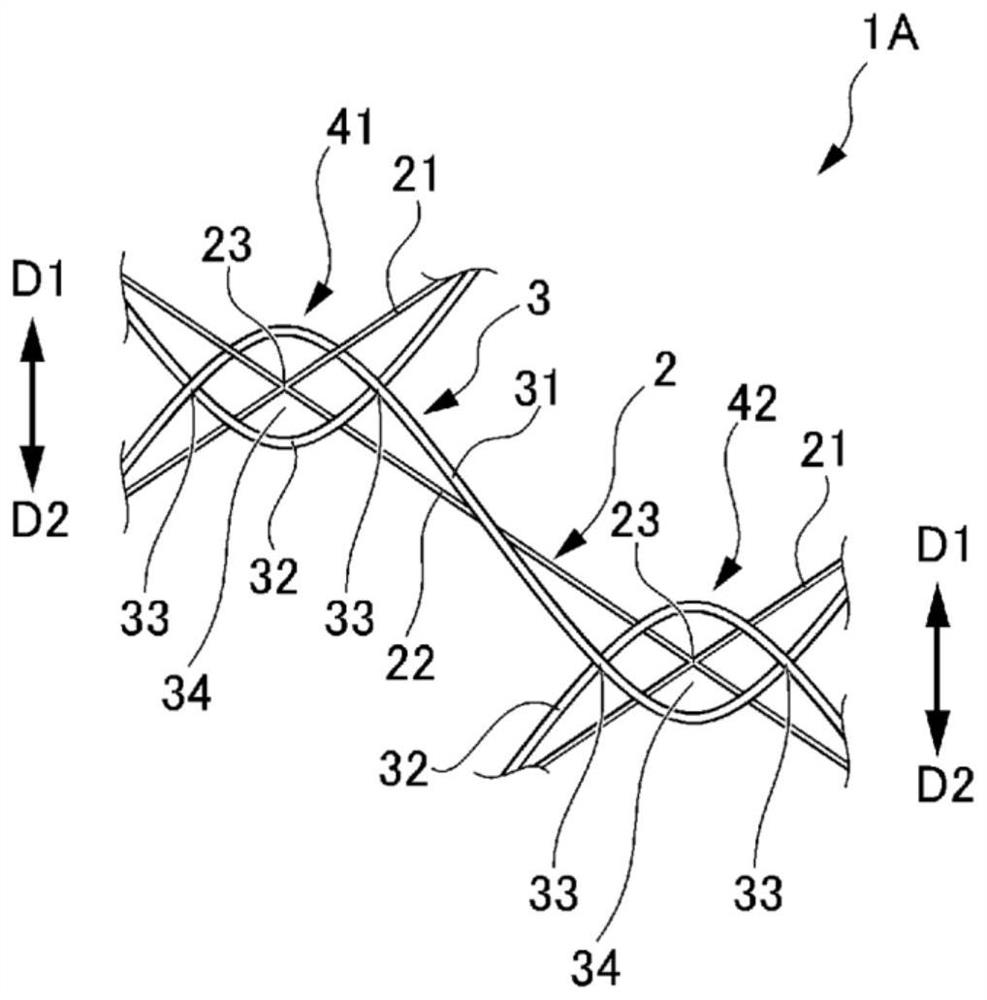
[0066] The biodegradable stent 1A of the second embodiment will be described below. image 3 It is a figure which shows the biodegradable stent 1A of 2nd Embodiment.
[0067] Such as image 3 As shown, the biodegradable stent 1A of the second embodiment has a first hook portion 41 ( image 3 in the left side) and the second hook part 42 ( image 3 in the right side) to form. The plurality of first hook portions 41 and the plurality of second hook portions 42 of the biodegradable stent 1A are arranged alternately in a helical shape in the circumferential direction.
[0068] because image 3 The structure of the illustrated first hooking portion 41 is the same as that of the first hooking portion 41 described in the first embodiment, so description thereof will be omitted.
[0069] The structure of the second hook portion 42 will be described below.
[0070] Such as image 3 As shown, at the second hooking portion 42, like the first hooking portion 41 of the first embodim...
no. 3 approach
[0080] The biodegradable stent 1B of the third embodiment will be described below. Figure 4 It is a figure which shows the biodegradable stent 1B of 3rd Embodiment.
[0081] In the biodegradable stent 1B of the third embodiment, compared with the biodegradable stent 1 of the first embodiment, the wave-shaped braided portion 3 (the first braided portion) woven into the mesh-shaped tubular portion 2 (the first braided portion) is In the second braided structure part), for the rows in which the plurality of first hooking parts 41 are arranged in a row in the circumferential direction, they are not arranged next to each other in the axial direction of the biodegradable stent 1A, but separated by a certain interval. and configured separately.
[0082] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the wave-shaped braided portion 3 has a plurality of first hooking portions 41 in the axial direction of the mesh-shaped tubular portion 2 having a plurality of first intersection points 23, and has a ro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com