A kind of adenylated protein a6 mutant and its encoding gene and application
A technology for adenylylating proteins and coding genes, which is applied in the field of catalytic synthesis of polymyxins, to achieve the effect of improving activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Construction of unmutated adenylated protein A6 expression plasmid
[0043] (1) Using the total genome of Paenibacillus polymyxa (CICC 21777) preserved in the laboratory as a template, design the upstream and downstream primers F / R with homologous fragments recombined with pET-28a(+) for PCR amplification, and the PCR product use 1%
[0044] Agarose gel electrophoresis detection. After detecting the target product, use a small amount of DNA purification kit to recover the target fragment for future use.
[0045] F: CTTTAAGAAGGAGATATAATGGCTTTTTGAAAAAGAAACG
[0046] R: CTCGAGTGCGGCCGCAAGCCGCTCGGCTTCATTGCGGGGAGC
[0047] (2) The expression plasmid pET-28a(+) was extracted, digested with Nco I and EcoR I, and recovered for use.
[0048] (3) The above-mentioned recovery and standby vectors and fragments were recombined with SoSoo kit, and transferred into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells to obtain recombinant expression plasmid pET-28a+A6 cloned strain. ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Prediction of key amino acid residues by sequence alignment
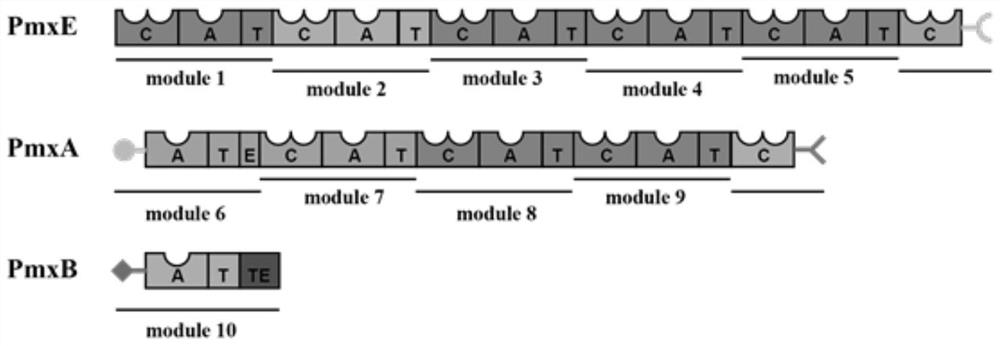
[0050] In order to predict the key residues related to the substrate-binding pocket of adenylylated proteins, the five amino acid sequences of GrsA, SlgN1, CmiS6, IdnL1, and DltA whose protein structures and active sites have been determined by X-ray diffraction were downloaded from NCBI. Their PBD numbers are 1AMU, 4GR5, 5JJP, 5JJQ, and 3DHV, respectively. These amino acid sequences were compared with the amino acid sequence of A6 in Example 1 and the amino acid sequence encoding the adenylation domain B-A6 in the polymyxin B biosynthesis gene cluster module 6 (GenBank: JN660148.1). Yes, the key residues that may be related to the substrate specificity of the A domain of this module from the preliminary screening are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1: Results of active site prediction by multiple sequence alignment
[0052]
[0053] Conclusion: The laboratory-derived adenylation protein A6 (...
Embodiment 3
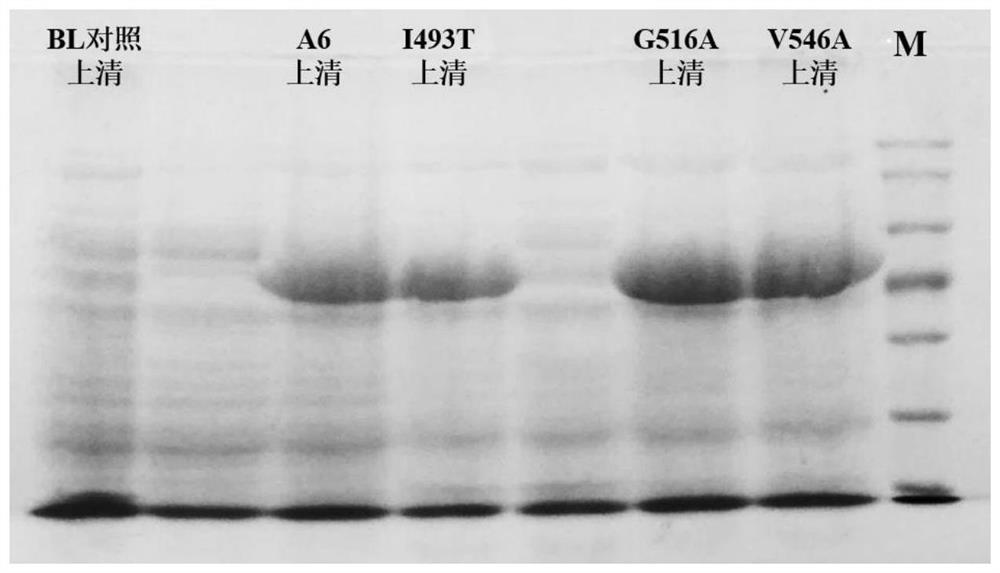
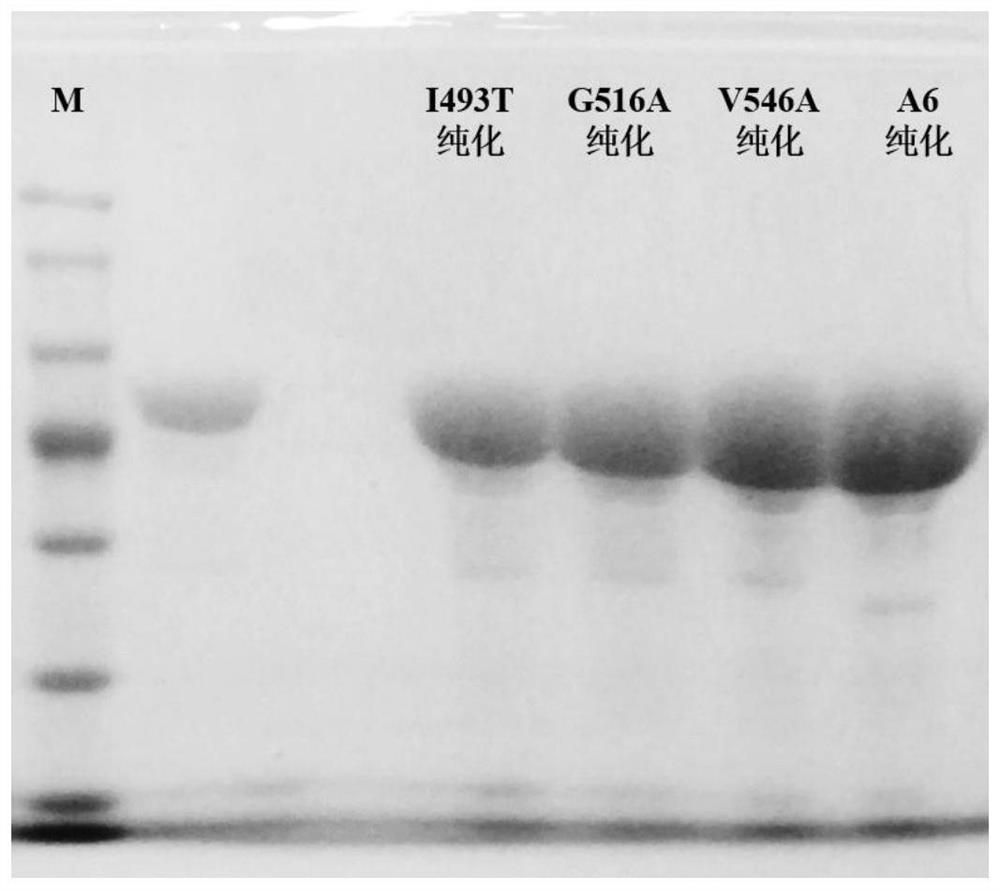
[0054] Example 3: Construction of adenylylated protein mutant expression plasmid
[0055] (1) Using the pET-28a+A6 expression plasmid constructed in Example 1 as a template, design site-directed mutagenesis primers I493T-F / R, V514I-F / R, G516A-F / R, and V546A-F / R to reverse to PCR. The specific site-directed mutagenesis primers are as follows (underlined are the mutation sites):
[0056] I493T-F: A G TCGCCGCCGTAATCGCAT
[0057] I493T-R: ATGCGATTACGGCGGCGA C TTTGCCTCCAACGTACAG
[0058] V514I-F: TA T GAGCTTCGTTAAGCTGG
[0059] V514I-R:
[0060] CCAGCTTAACGAAGCTC A TAACGGGAGGCTCTGCGGT
[0061] G516A-F: T G CCGTTACGAGCTTCGTTA
[0062] G516A-R:
[0063] TAACGAAGCTCGTAACGG C AGGCTCTGCGGTATCGGC
[0064] V546A-F: A G CAATCGAAGCTTCGGTAG
[0065] V546A-R:
[0066] CTACCGAAGCTTCGATTG C TACGACGCTTTGGGATGC
[0067] (2) PCR products were detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. After detection of the target product, Dpn I enzyme was added to digest the template, and a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com