Power conversion device
A power conversion device and current technology, applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, electrical components, electronic switches, etc., can solve the problem of not reducing the dv/dt noise of the power conversion device, and achieve the optimization and reduction of power loss and noise noise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0068] (constitute)
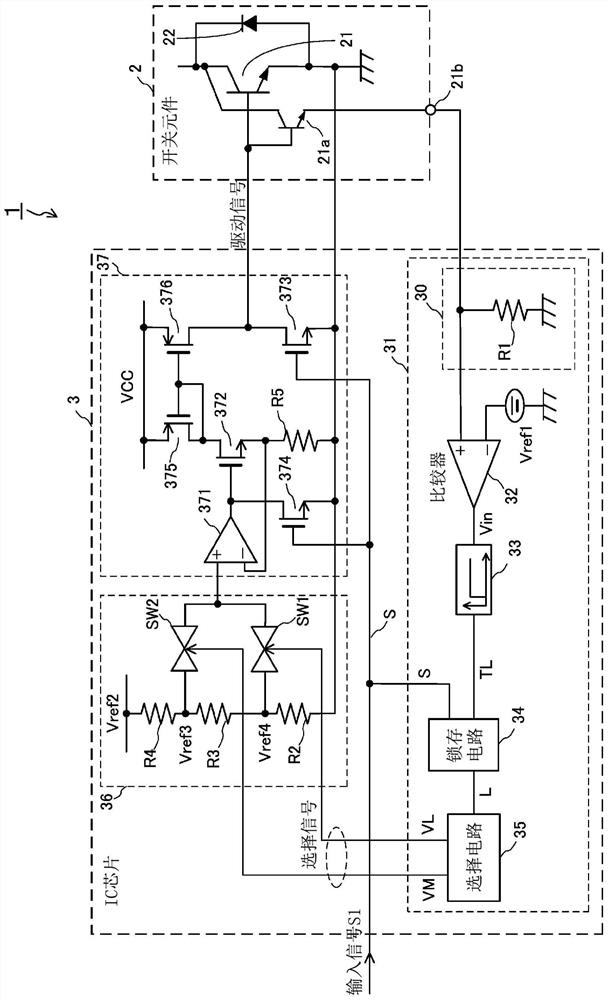
[0069] The IPM (Intelligent Power Module) 1 of this embodiment is suitable for, for example, joints of industrial robots, elevators, or power conversion devices for commercial air conditioners, such as figure 1 As shown, the configuration mainly includes a switching element 2 and an IC chip 3 .
[0070] The switching element 2 may be composed of, for example, an IGBT 21 and a freewheel diode 22 connected in antiparallel to the IGBT 21 , and may be a one-chip RC-IGBT. The IGBT 21 is turned on by a drive signal applied from the IC chip 3 to the gate (control electrode terminal), and a current (main current) flows from the collector to the emitter to supply constant power to a load not shown. The emitter of IGBT21 is connected to the reference potential of IC chip 3 mentioned later. Moreover, IGBT21a for current sensing is connected in parallel with IGBT21, and outputs a sense current at a fixed ratio according to a main current.
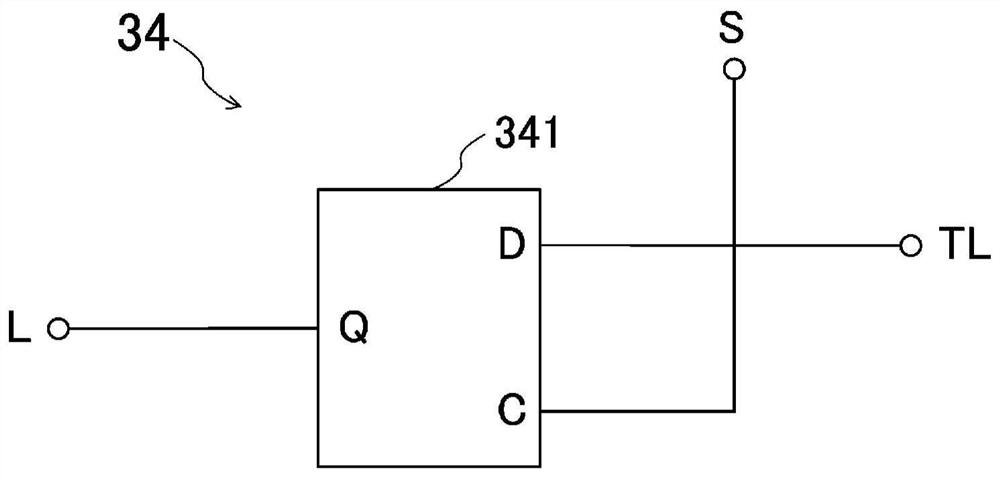
[0071] The IC chip 3 i...
no. 2 approach
[0110] Next, a second embodiment will be described.
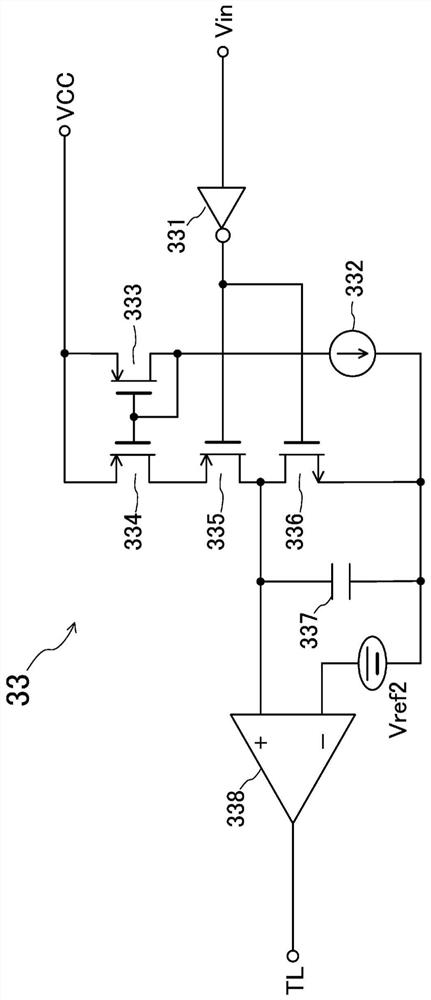
[0111] Image 6 It is a configuration diagram of the power conversion device of the second embodiment. and figure 1 The difference is that the constant current source 38 is provided on the side of the connection point of the resistance element R1 that converts the sense current into a voltage, and the sense terminal 21b. Otherwise with figure 1 are the same, and therefore the same elements are attached with the same symbols and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0112] The constant current output from the constant current source 38 flows to the reference potential through the resistance element R1. Thus, the sensing voltage value increases by the amount of voltage generated by the constant current value and the resistance value of the resistance element R1.
[0113] Actually, about 10% of the rated current of the IGBT is sometimes specified as a small current range. In this case, to figure 1 When the low current ...
no. 3 approach
[0119] Next, a third embodiment will be described.
[0120] Figure 8 It is a configuration diagram of the power conversion device of the third embodiment. and figure 1 The difference is that constant current sources and P-type A series circuit of MOSFETs.
[0121] Hereinafter, the configuration of this embodiment will be described in detail.
[0122] exist Figure 8 Among them, the source of the P-type MOSFET 377 is connected to the output terminal of the constant current source 39 and the non-inverting input terminal of the comparator 32 . The drain of the P-type MOSFET 377 is connected to the reference potential. The gate of the P-type MOSFET 377 is connected to one end of the resistance element R1 and the sensing terminal 21b. The other end of the resistance element R1 is connected to a reference potential.
[0123] In addition, the source of the P-type MOSFET 378 is connected to the output terminal of the constant current source 40 and the inverting input terminal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com