Quasi-static method for dynamic safety coefficient of homogeneous pure clay slope under earthquake action
A technology of safety factor and quasi-static force, which is applied in the field of slope stability evaluation, can solve problems such as differences in calculation results and determination errors of dynamic limit states, and achieve good results, improve calculation efficiency and accuracy, and have high engineering practical value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0090] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
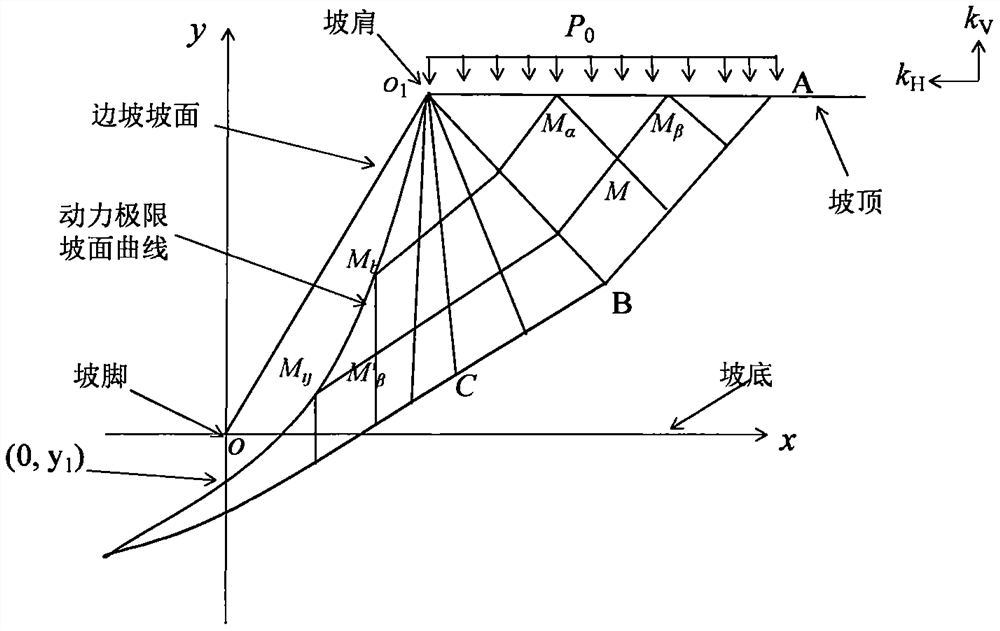
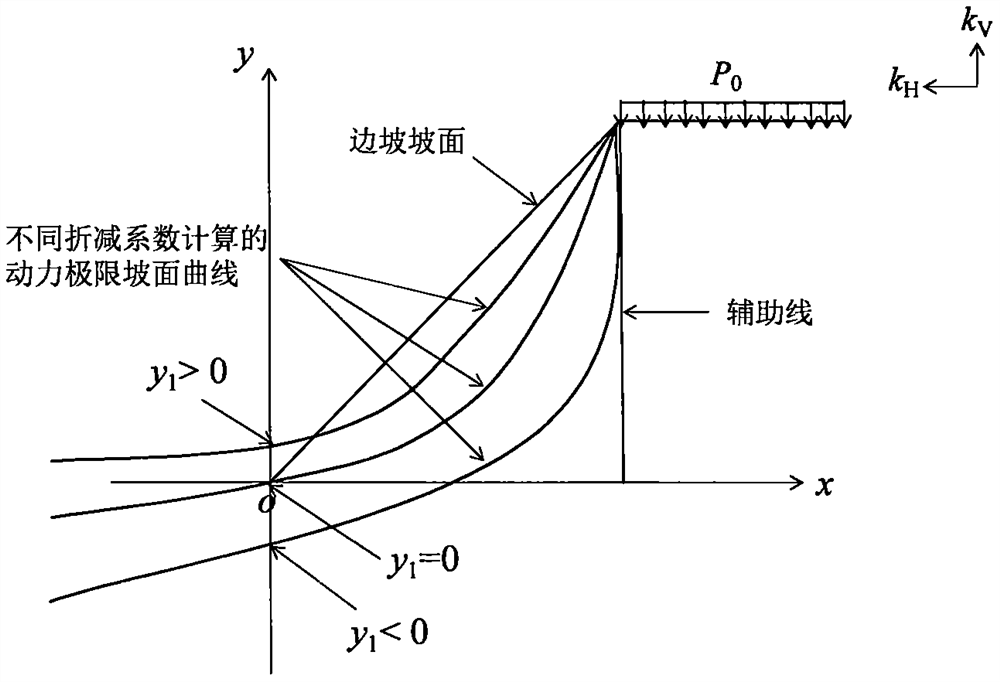
[0091] The schematic diagram of the dynamic limit slope surface curve of the homogeneous pure clay slope is shown in the theoretical calculation of the sliding line field under the earthquake action of the present invention. figure 1 .
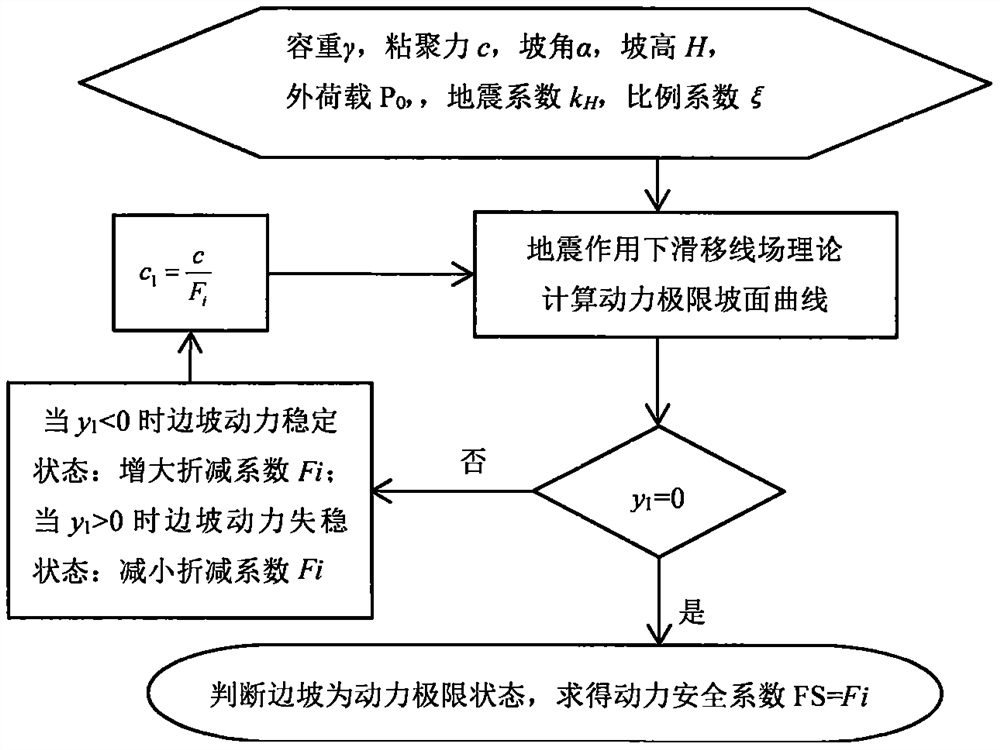
[0092] 1. A pseudo-static method for dynamic safety factor of homogeneous pure clay slope under an earthquake, is characterized in that it includes the following content:
[0093] 1) Slip line field theory under earthquake action
[0094] According to the Mohr-Coulomb criterion, the expressions of normal stress and shear stress are:
[0095]
[0096]
[0097] where σ x and σ y Denote the normal stress in the x and y directions, respectively, τ xy and τ yx represent the shear stress in the x and y directions, respectively, σ is the characteristic stress, c is the cohesion force, is the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com