Determination of a change in the refraction error of an eye
A technique for refractive errors and eyes, which is applied in the direction of eye testing equipment, eye examination, comprehensive refractometer, etc., can solve the problem that the reproducibility of choroid is not enough to be able to actually verify the size of the influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
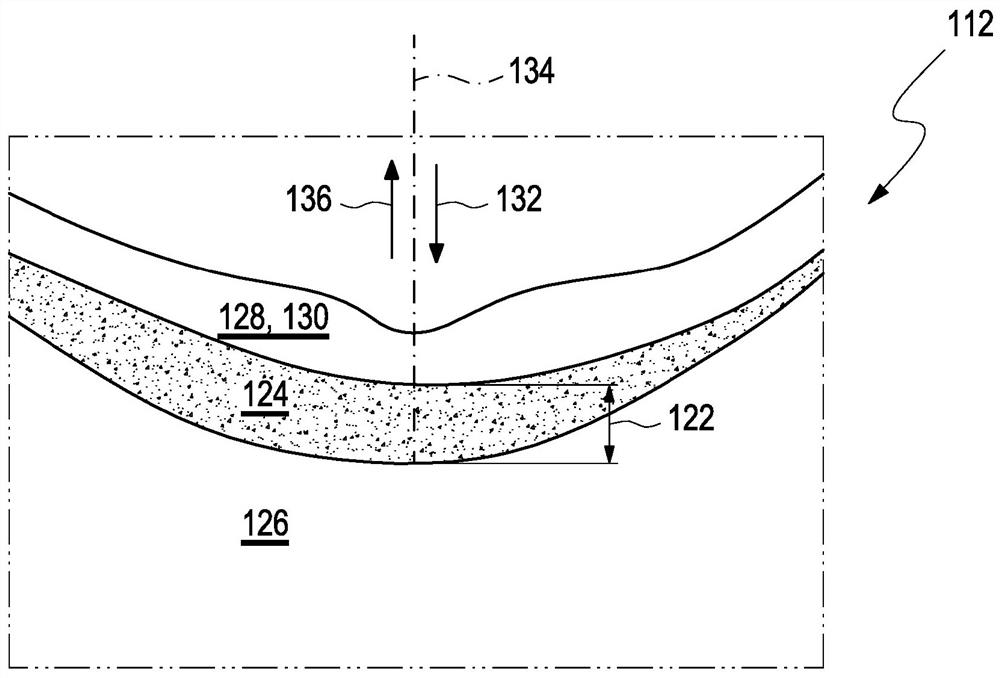
[0088] figure 1 A preferred exemplary embodiment of an apparatus 110 for determining changes in refractive error of an eye 112 of a user 114 is schematically shown. The apparatus 110 comprises a measuring device 116 , preferably an optical measuring device 118 , in particular a device 120 for optical coherence tomography, arranged to capture the layer thickness 122 of the choroid 124 of the eye 112 of the user 114 . However, other types of measuring devices, in particular acoustic or photoacoustic measuring devices, are conceivable. like figure 2 As shown schematically in , the choroidea 124 represents the intermediate layer that is disposed between the sclera 126 and the retina 128, particularly between the sclera 126 and the retinal pigment epithelium layer 130, on the side of the eye 112 away from light incidence. between.
[0089] The apparatus 120 for optical coherence tomography facilitates imaging methods for generating two- or three-dimensional recordings of biolo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com