Dynamic economic dispatch distributed optimization method and system for smart power grid
A smart grid and economic dispatching technology, applied in power network operating system integration, system integration technology, AC network voltage adjustment, etc., can solve problems such as poor robustness of centralized optimization strategy, large computational burden, and no consideration of dynamic constraints, etc. Achieving the effect of solving poor robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment discloses a distributed optimization method for dynamic economic scheduling of smart grids, including:
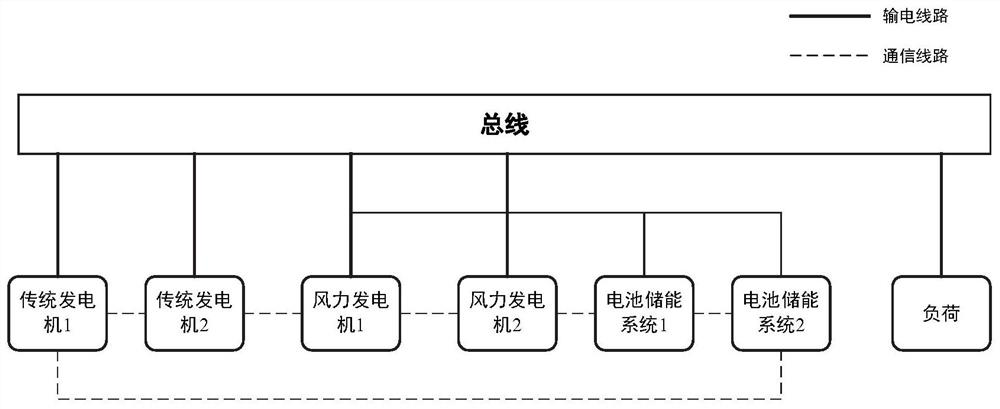
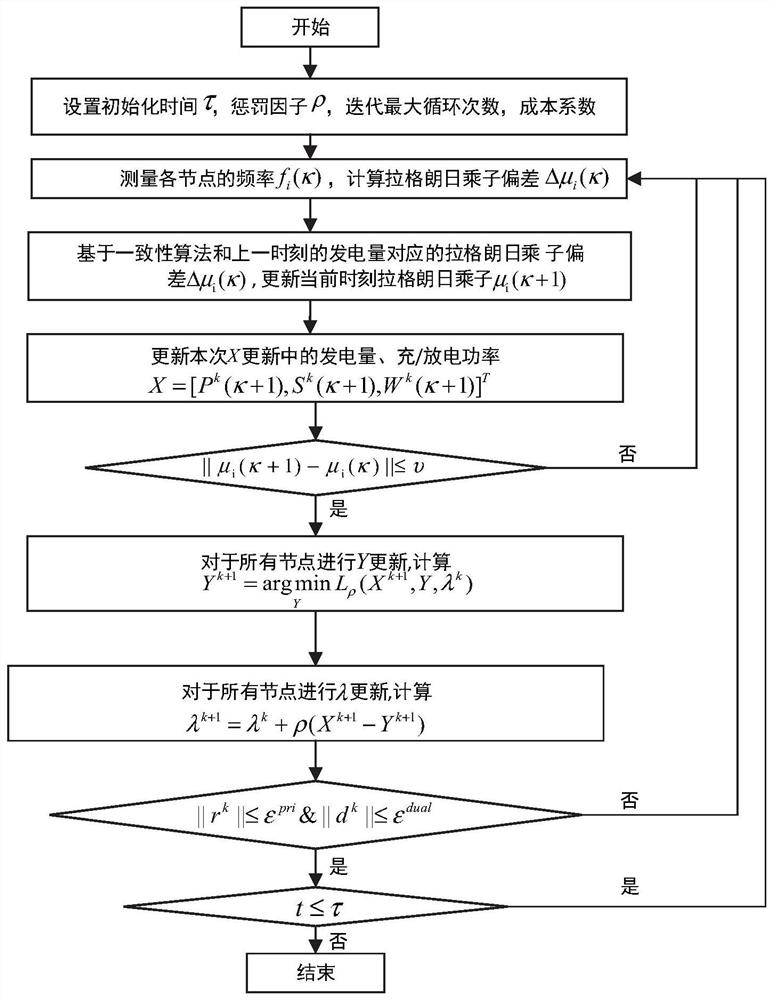
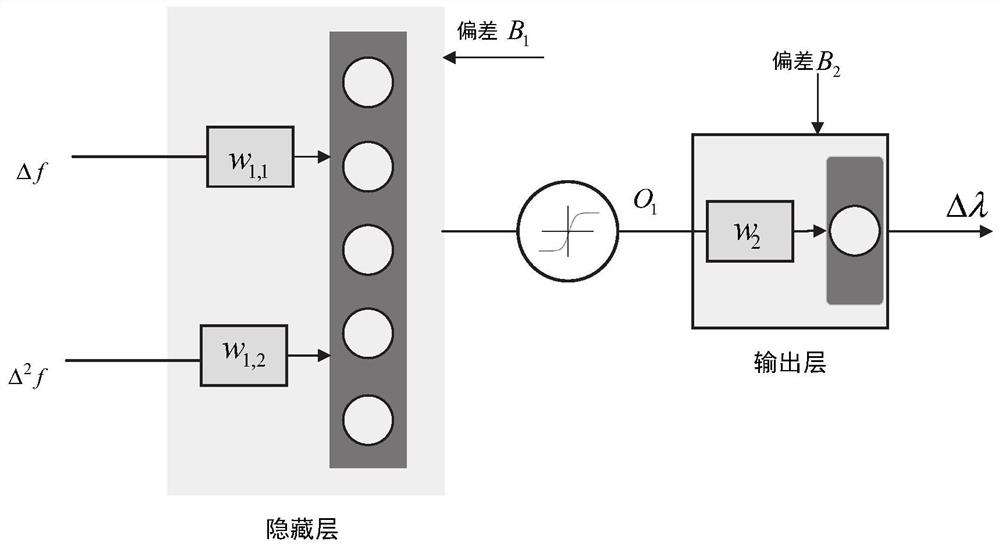
[0034] figure 1 is the system structure diagram, the solid line represents the energy transmission line, and the dotted line represents the communication topology of the system. figure 2 It is a flowchart of the optimization method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0035] Step 1: Set the initial parameters: the number of traditional generator nodes, the number of wind turbine nodes, and the number of battery energy storage system nodes are n respectively g , n w , n s , and the correlation coefficients of each unit are shown in Table 1-Table 3. The total scheduling time τ=12, the penalty factor ρ=0.8.
[0036] Initialization time t=0, scheduling time τ∈R, original residual r, dual residual d, alternating direction multiplier method optimization iteration number k=0 and maximum iteration number k max ∈R, X update iteration number κ and m...
Embodiment 2
[0121] The purpose of this embodiment is to provide a computing device, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and operable on the processor. When the processor executes the program, the method in the first embodiment above is implemented. A step of.
Embodiment 3
[0123] The purpose of this embodiment is to provide a computer-readable storage medium.
[0124] A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the program is executed by a processor, the steps of implementing the method in Example 1 are executed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com