Motor rotating speed control method for food processor
A food processing machine and motor speed technology, which is applied to the estimation/correction of motor parameters, applications, and home appliances, etc. Problems such as poor experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
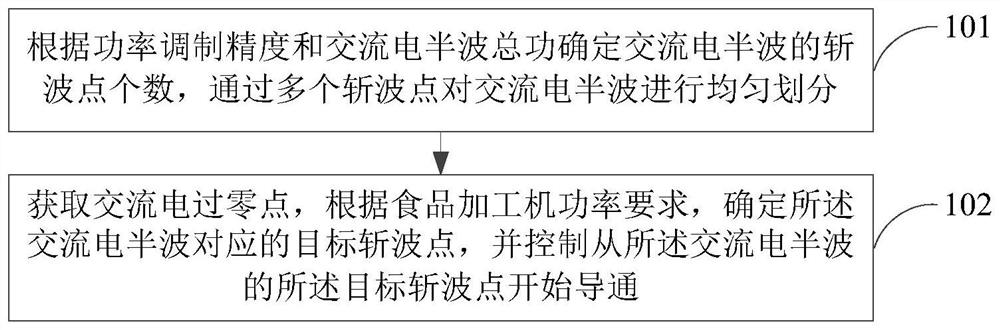
[0041] to combine figure 1 As shown, in an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, this embodiment provides a motor speed control method for a food processor, such as figure 1 As shown, the power modulation method for the food processor includes step 101 and step 102 .
[0042] Step 101: Determine the number of chopping points of the AC half-wave according to the power modulation accuracy and the total power of the AC half-wave, and evenly divide the AC half-wave through multiple chopping points;
[0043] When adjusting the power of the food processor, in order to quickly and accurately realize the modulation of the power of the food processor, improve the accuracy of the power modulation, and avoid fluctuations in the power of the food processor, and fluctuations around the target power situation.
[0044] In the scheme of this embodiment, the number of chopping points of the AC half-wave is determined according to the power modulation accuracy and the total power of...
Embodiment 2
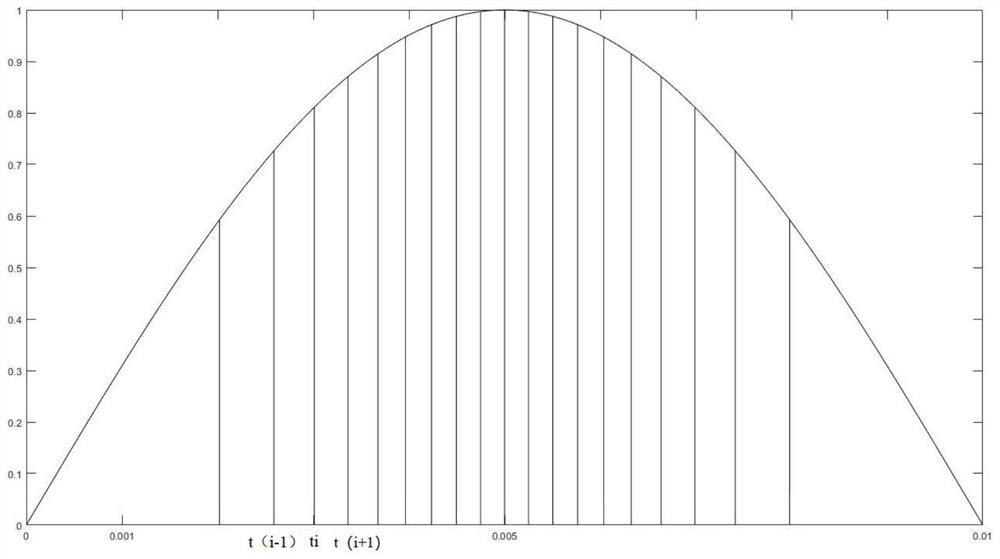
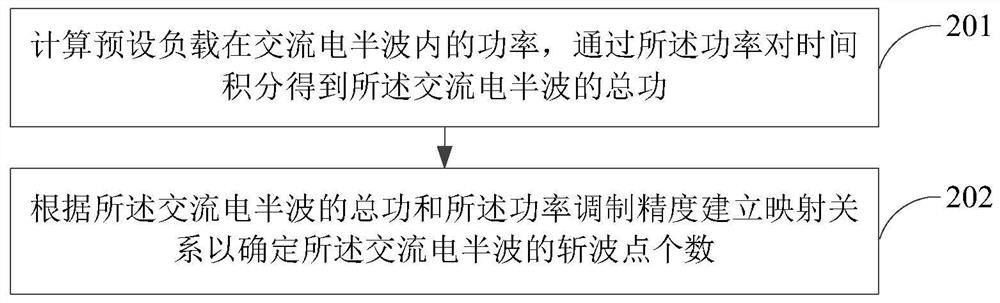
[0057] In this embodiment, the number of chopping points of the AC half-wave is determined by establishing a mapping relationship between the total power of the AC half-wave and the power modulation accuracy, such as image 3 As shown, in the scheme of this embodiment, the power modulation method for the food processing machine determines the number of chopping points of the alternating current half wave according to the power modulation accuracy and the total power of the alternating current half wave, and evenly conducts the alternating current half wave through multiple chopping points. The division includes step 201 and step 202 .
[0058] Step 201: Calculate the power of the preset load in the AC half-wave, and integrate the power with time to obtain the total work of the AC half-wave.
[0059] Most of the existing food processing machines are powered by 220V, 50HZ mains electricity. In this embodiment, 220V, 50HZ mains electricity is used as an example, and the AC wavefo...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The difference between Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 of this embodiment is that, on the basis of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, it is given to determine the alternating current half-wave Example scheme of the corresponding target chopping point.
[0080] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the power modulation method for the food processor in this embodiment includes step 301 and step 302 .
[0081] Step 301: Calculate the difference between the preset power and the actual power of the food processor.
[0082] Specifically, in this embodiment, voltage detection can be realized through the voltage detection module of the food processor. For the preset load R, the actual power of the preset load can be obtained. When the food processor is working, different processing stages have different power Requirements, and then can calculate the difference between the preset power and the actual power under the current working state of the food processor.
[0083]It should be noted that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com