Compositions and methods for treatment of dominant retinitis pigmentosa
A technology of retinal pigments and compositions, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, gene therapy, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
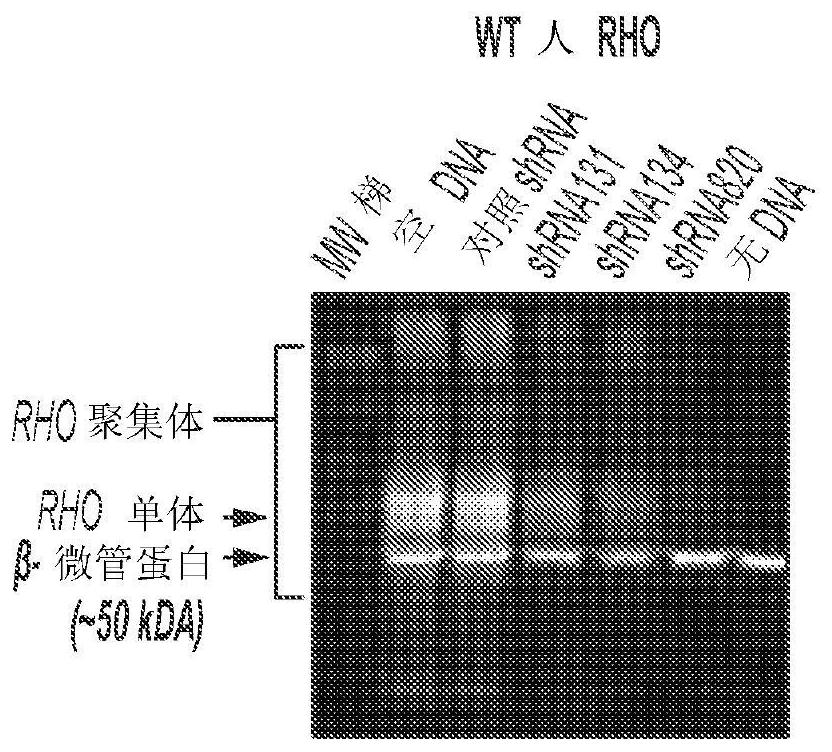
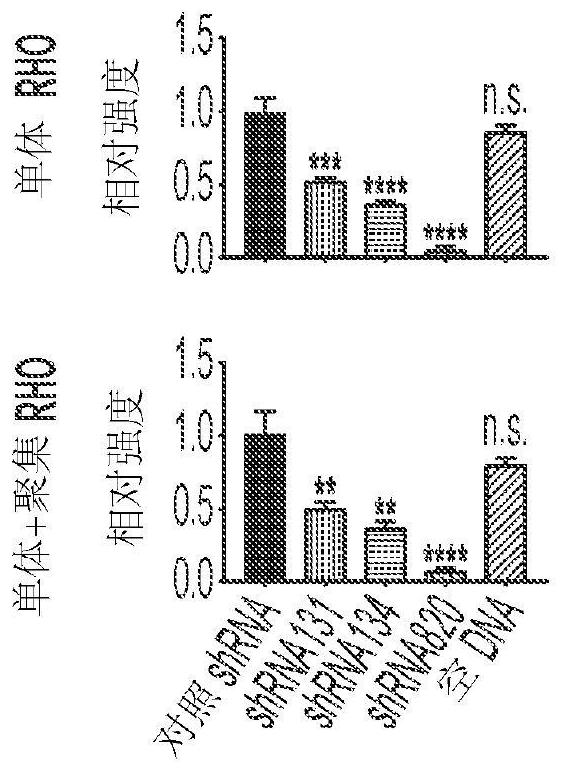
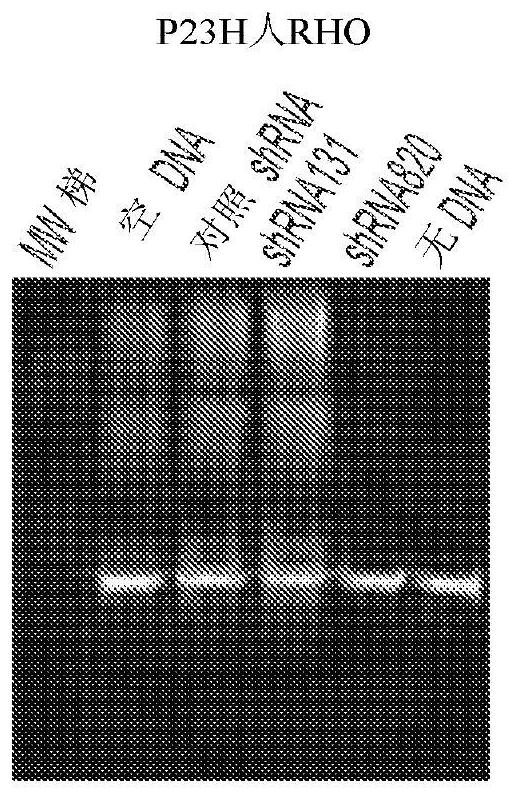
[0109] Hereditary retinal degenerations are caused by mutations in >250 genes that affect photoreceptor cells or the retinal pigment epithelium and cause vision loss. For autosomal recessive and X-linked retinal degenerations, remarkable progress has been made in the field of gene therapy, as evidenced by the increasing number of clinical trials and the recent commercialization of the first gene therapy for congenital forms of blindness. However, despite enormous efforts to develop treatments for the most common form of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP), caused by mutations in >150 rhodopsin (RHO) genes, translation to the clinic has been slow. Stand still. Here, for the first time, a highly potent novel short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting human (and canine) RHO in a mutation-independent manner is identified. This shRNA was combined with a human RHO surrogate cDNA made resistant to RNA interference in a single adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector, and this constru...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Example 2: Constructs protect mice from retinal degeneration
[0175] AAV-shRNA 820 -RHO 820 The constructs provided long-term protection against retinal degeneration in the RHO-adRP mouse model.
[0176] C57Bl / 6 mice transgenic for human P23H RHO undergo retinal degeneration due to the presence of the mutant rhodopsin gene even in the presence of dim red light without exposure to bright light (33, 34, 43). At 1 month of age, mice of this genotype were treated with AAV2 / 5-GFP or scAAV2 / 5-RHO 820 -shRNA 820 Subretinal injections were administered in one eye. Two groups of mice were analyzed at different intervals: a) before treatment, b) 1 month after injection, c) 2 months after injection, and d) 3 months after injection. Subretinal injection induced transient retinal detachment, which eventually resolved. The fellow eye was not treated.
[0177] OCT analysis was performed at monthly intervals for three months in P23H RHO mice to determine the effect of vehicle t...
Embodiment 3
[0186] Example 3: Analysis of mRNA Sequences Expressed by Vector Constructs
[0187] To determine the type of short mRNA sequences derived from AAV constructs, scAAV2 / 5-RHO 820 -shRNA 820 The construct transfected HEK293T cells. After 48 hours, total RNA was extracted. Extracted RNA was size fractionated and short RNA sequences were subjected to RNA sequencing. for shRNA 820 RNA molecules of their sequence are analyzed to determine their size as well as their 5' and 3' ends (see Figure 24 ).
[0188] A summary of the sequencing reads is shown in Figure 25 middle. The sequence (UAG) at the 5' end of the guide strand in 73% of the RNA molecules was identical to the expected sequence. 13% of the molecules were shortened by one nucleotide at the 5' end. 52% had 2 extra uridines at the 3' end, while 10% had 1 extra uridine at the 3' end. 13% of the molecules had an extra UUA codon at the 3' end. SEQ ID NO: 40 to 46 are provided as derived from shRNA 820 Sequences of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com