Multi-target tracking method for solving distributed label fusion
A multi-target tracking and tag fusion technology, applied in the field of distributed multi-sensor multi-target detection and tracking, can solve the problems of ineffective fusion of sensors and inconsistency of sensor tags
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] This embodiment provides a multi-target tracking method that solves distributed label fusion, and the multi-target tracking method is based on including:
[0047] Step 1. Run the LMB filter on each local sensor separately to obtain the locally estimated LMB posterior information, and set a threshold for the local information to perform pruning and truncation to reduce computational complexity;
[0048] Step 2, for each sensor label, carry out label consistency through label matching;
[0049] Step 3, share the LMB posterior information of each sensor and adjacent sensors, and perform arithmetic mean fusion on the shared information according to the label;
[0050] Step 4: Extract the target state and target track according to the fusion result.
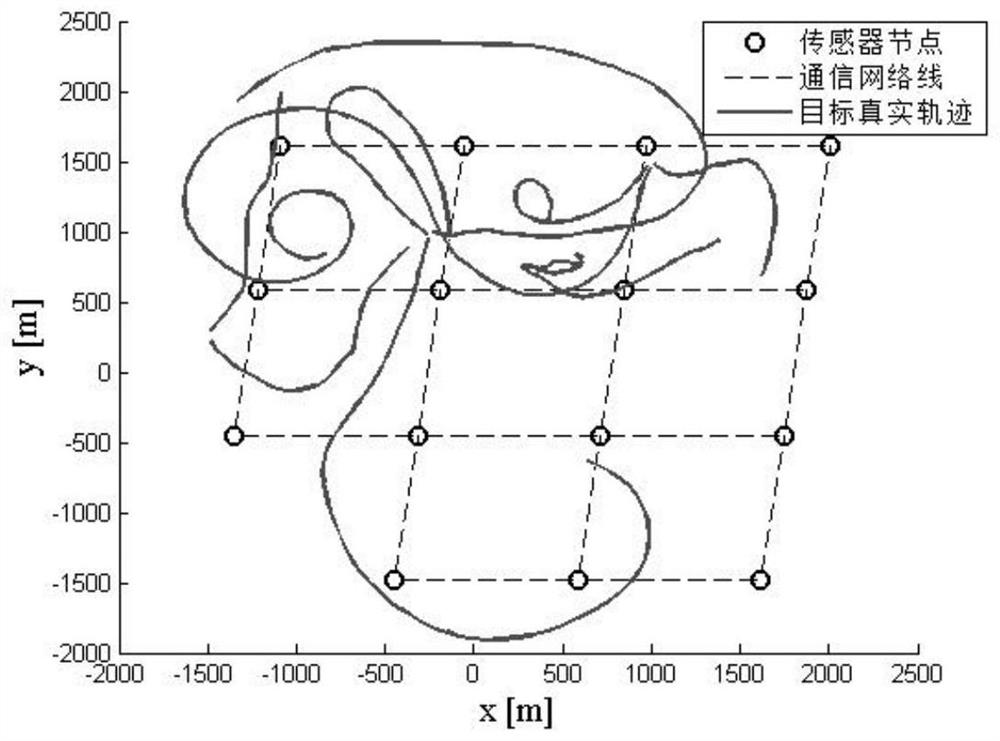
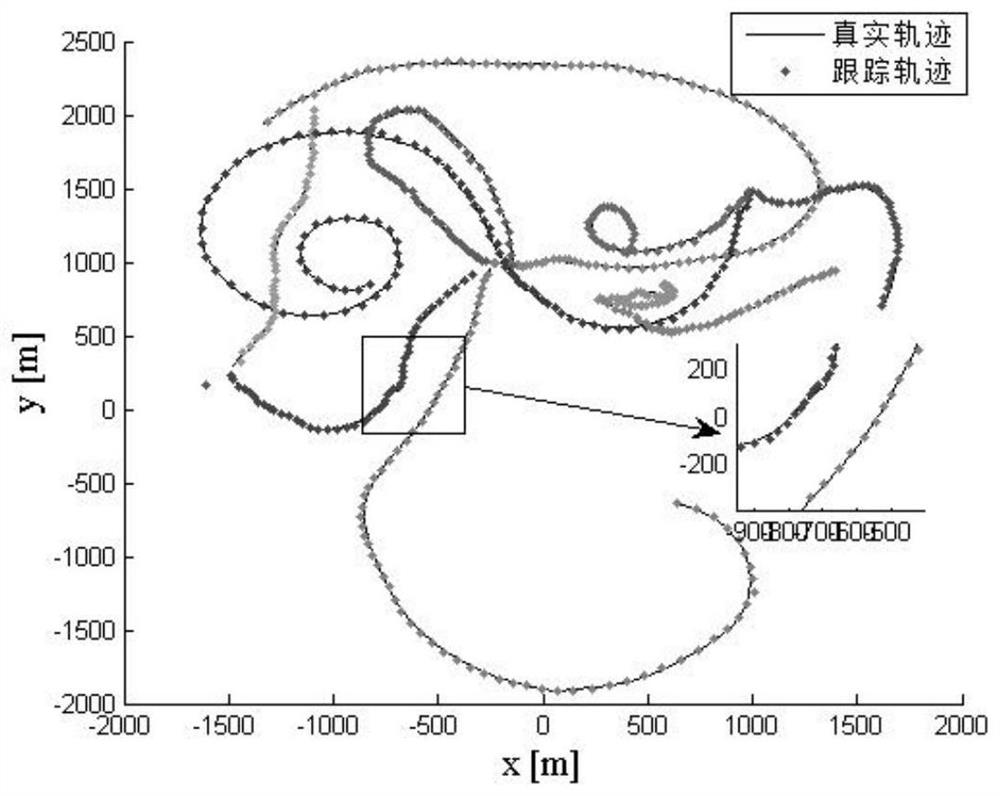
[0051] All steps, conclusions, and simulation diagrams of this embodiment are verified and confirmed on MATLAB-R2018a. Such as figure 1 , the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0052] Step 1: Initialize system ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com