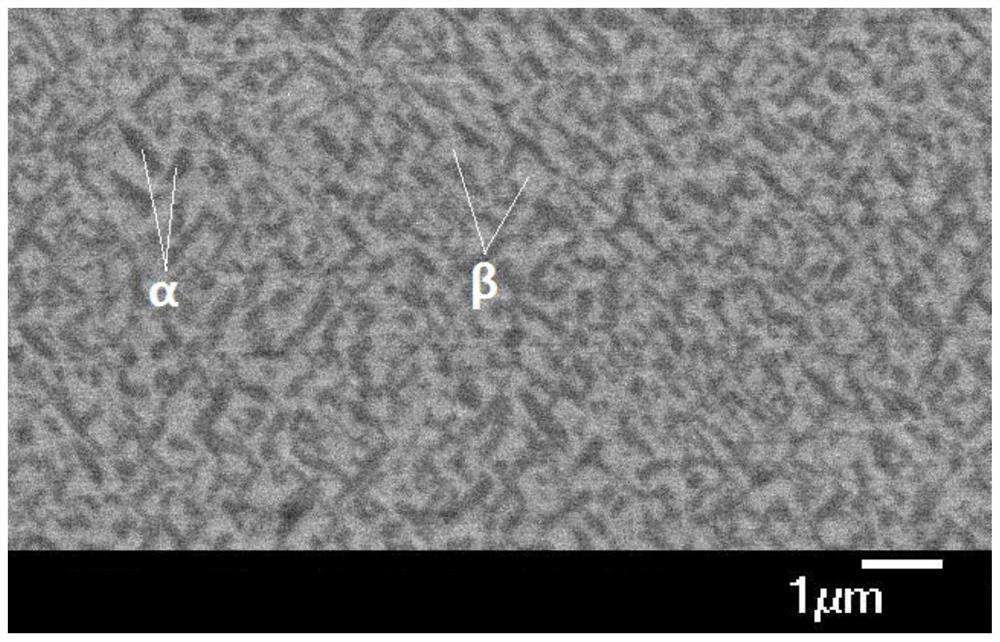
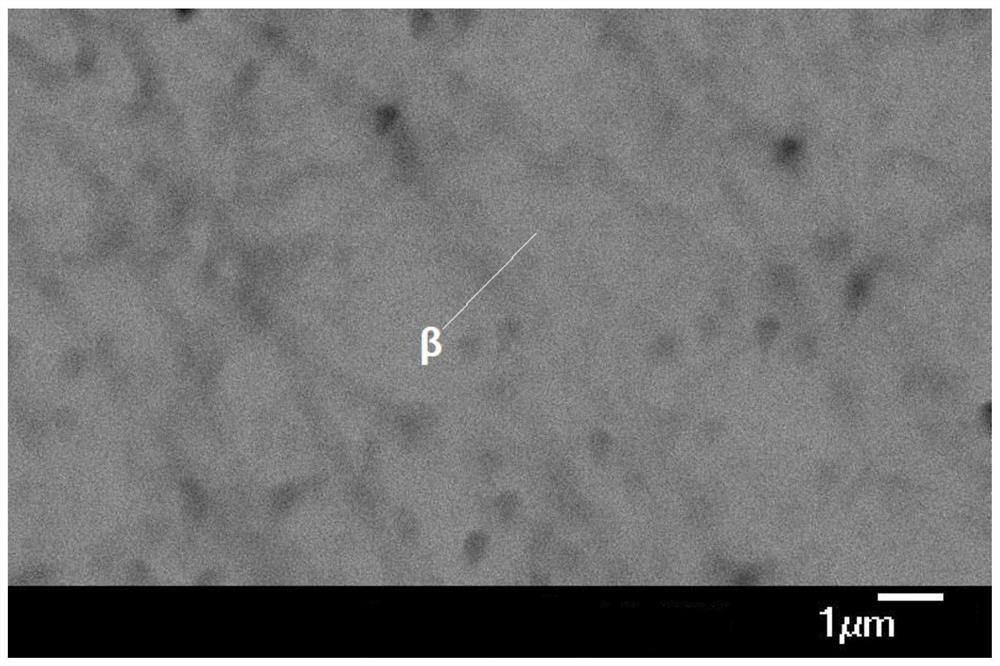
A method for preparing high-strength titanium alloy rods for additive manufacturing powder making
A technology of additive manufacturing and titanium alloy, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, heat treatment equipment, etc., can solve the problems of unstable performance of Ti185 alloy rods, high-speed rotating rods breaking and flying out, unstable performance, etc., and achieve sphericity High, high uniformity, good quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. Mix the titanium alloy raw materials to obtain a mixture; the titanium alloy raw materials are Fe-80V alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, and Ti-32Fe alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm Ti-50Al alloy and titanium sponge with a particle size of 10mm to 30mm;
[0037] Step 2. Put the mixed material obtained in step 1 into a mold and press to obtain an electrode block; the pressing pressure is 60 tons, and the electrode block is a cylindrical electrode block with a cross-sectional diameter of 75 mm;
[0038] Step 3. The electrode block obtained in step 2 is subjected to intermediate frequency induction melting to obtain a cylindrical blank; the process of the intermediate frequency induction melting is as follows: the electrode block is placed in an intermediate frequency induction melting furnace, and the vacuum degree in the furnace is kept at 0.7×10 -3 Pa...
Embodiment 2
[0068] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0069] Step 1. Mix the titanium alloy raw materials to obtain a mixture; the titanium alloy raw materials are Fe-80V alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, and Ti-32Fe alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm Ti-50Al alloy and titanium sponge with a particle size of 10mm to 30mm;
[0070] Step 2. Put the mixture obtained in step 1 into a mold and press it to obtain an electrode block; the pressing pressure is 70 tons, and the electrode block is a cylindrical electrode block with a cross-sectional diameter of 80 mm;
[0071] Step 3. The electrode block obtained in step 2 is subjected to intermediate frequency induction melting to obtain a cylindrical blank; the process of the intermediate frequency induction melting is as follows: the electrode block is placed in an intermediate frequency induction melting furnace, and the vacuum degree in the furnace is kept at 0.9×10 -3 Pa, wi...
Embodiment 3
[0078] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0079] Step 1. Mix the titanium alloy raw materials to obtain a mixture; the titanium alloy raw materials are Fe-80V alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, and Ti-32Fe alloy with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm, with a particle size of 3 mm to 5 mm Ti-50Al alloy and titanium sponge with a particle size of 10mm to 30mm;
[0080] Step 2. Put the mixture obtained in step 1 into a mold and press to obtain an electrode block; the pressing pressure is 50 tons, and the electrode block is a cylindrical electrode block with a cross-sectional diameter of 70 mm;
[0081]Step 3. The electrode block obtained in step 2 is subjected to intermediate frequency induction melting to obtain a cylindrical blank; the process of the intermediate frequency induction melting is as follows: the electrode block is placed in an intermediate frequency induction melting furnace, and the vacuum degree in the furnace is kept at 0.8×10 -3 Pa, heated...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com