Microsatellite instability analysis method and analysis device
A microsatellite instability and instability technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problem of deep false positives in sequencing, and achieve the effect of high sensitivity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Screening of microsatellite markers
[0054] In this example, the pan-cancer NGS panel MED1CDx developed by Medtech Translational Medicine Research (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. was used to screen microsatellite markers. The MED1CDx chip was modified with gene capture probes, covering the exon regions of 601 genes. And some introns and intergenic regions, the total length is about 2.8Mb, including 23323 possible microsatellite sites with repeat sequence length ≥5 nucleotides.
[0055] Sites with single-base repeat length ≥15 nucleotides and double-base or polynucleotide repeat unit repeat times ≥8 were selected, and 138 microsatellite sites were finally obtained as MSI detection markers.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 The read length ratio distribution of different repeat lengths of microsatellite loci
[0057] (1) After the sequencing data (fastq files) of tumor samples and healthy samples are subjected to quality control filtering, they are compared to the human reference genome, and the alignment files (BAM files) of tumor samples and healthy samples are obtained respectively;
[0058] (2) Create a sequence list Lmi for each microsatellite site Mi (i=1, 2, 3, ... 138), each unit of the list is the sequence of 5 bases upstream of the microsatellite site + (microsatellite Repeat unit × n) + sequence Sn of 5 bases downstream of the microsatellite site, where n is an integer from 0 to (140÷repeat unit length);
[0059] (3) Analyze each pair of read lengths (read pair) in the BAM file of step (1), when at least one read length (read) is compared to a range of 2 kb of a microsatellite site, the read The pair is extracted, and finally the total number of reads Rmi covering the...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Comparison of the distribution of microsatellite reads in tumor samples and healthy samples
[0063] Set the read ratio distribution of repeat sequences of different lengths at the microsatellite locus Mi in the tumor samples of the subject as Pni, and the read ratio distribution of repeat sequences of different lengths at the microsatellite locus Mi in the healthy samples as Qni, then the two Its KL divergence is:
[0064] KL(Pi||Qi)=Pni×log(Pni÷Qni)
[0065] KL(Qi||Pi)=∑Qni×log(Qni÷Pni)
[0066] The KL divergence is asymmetric, let Mi=(Pi+Qi)÷2, then the JS divergence of the two is:
[0067] JSD(Pi||Qi)=(KL(Pi||Mi)+KL(Qi||Mi))÷2
[0068] =(∑Pni×log(Pni÷(Pni+Qni))+∑Qni×log(Qni÷(Pni+Qni)))÷2+log2
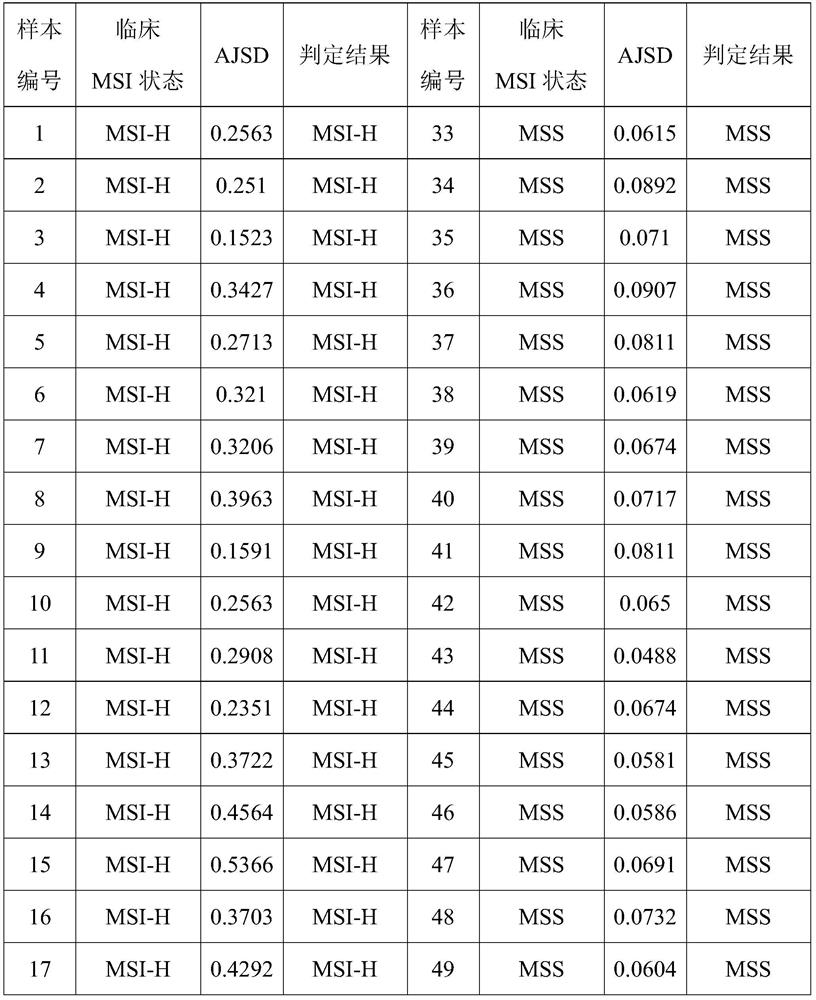
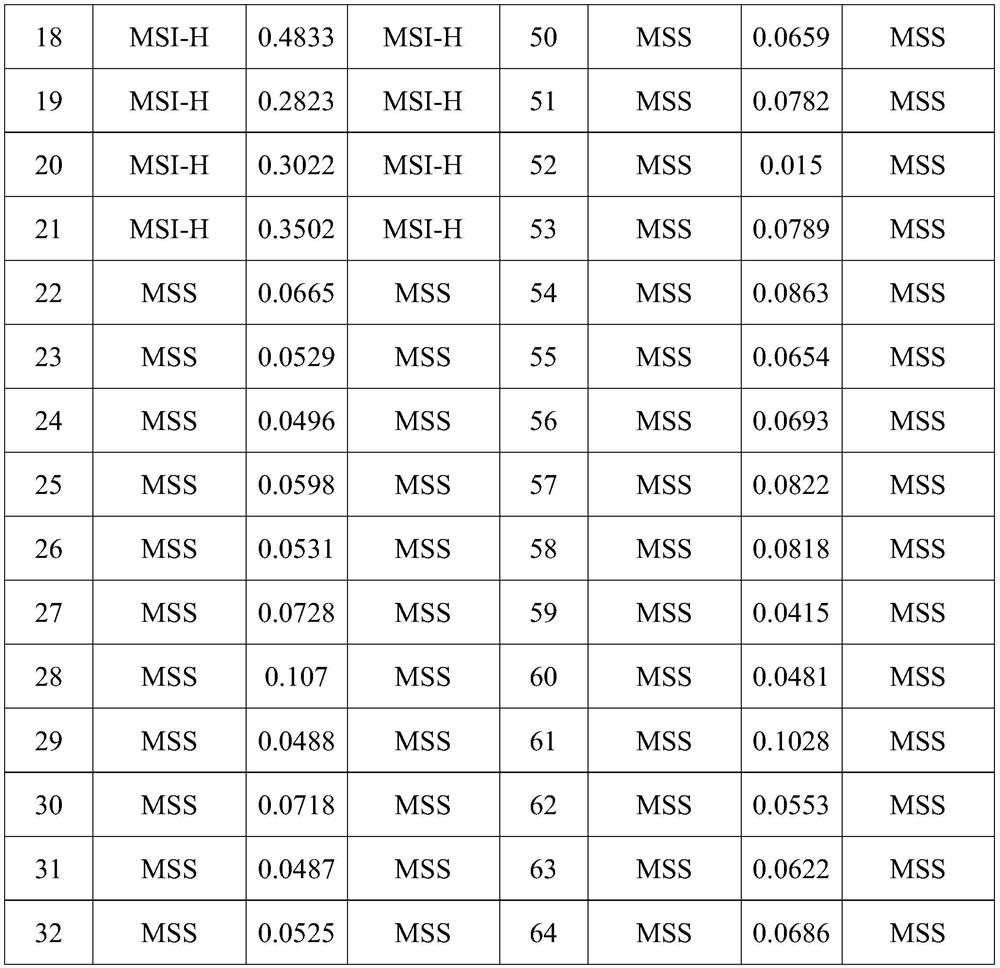
[0069] The mean JSD of the subjects' 138 microsatellite loci was
[0070] AJSD=(∑JSD(Pi||Qi))÷138
[0071] Based on the accumulated data, the subject was judged to be MSI-H when AJSD ≥ 0.12.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com