Discrete fracture modeling method based on multi-point geostatistics
A technology of geostatistics and discrete fractures, which is applied in the field of oil and gas development, can solve problems such as failure to simulate fractures, failure to consider spatial configuration relations, and influence on fracture simulation accuracy, so as to ensure structural effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that, as long as there is no conflict, each embodiment and each feature in each embodiment of the present invention can be combined with each other, and the formed technical solutions are all within the protection scope of the present invention.
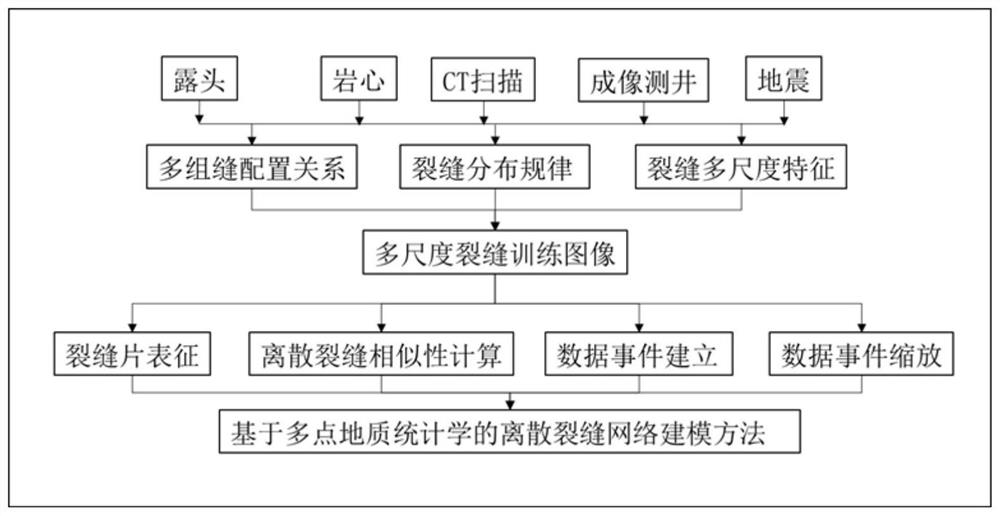
[0045] like figure 1 As shown, the discrete fracture modeling method based on multi-point geostatistics of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0046] Step 1. Establishment of discrete fracture training images based on multi-scale fractal theory; wherein, step 1 includes:
[0047] Step 1.1. Characterization of multi-scale fractures;
[0048] Step 1.2. Quantitative relationship characterization of fracture scale features;
[0049] Step 1.3. Establishment of multi-scale training images based on multi-scale fractal theory.
[0050] Step 2. Multi-point geos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com