A method for co-processing lead glass and waste catalyst
A waste catalyst and co-processing technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problem of high energy consumption in smelting, achieve obvious environmental and economic benefits, improve capture efficiency, and achieve high capture efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
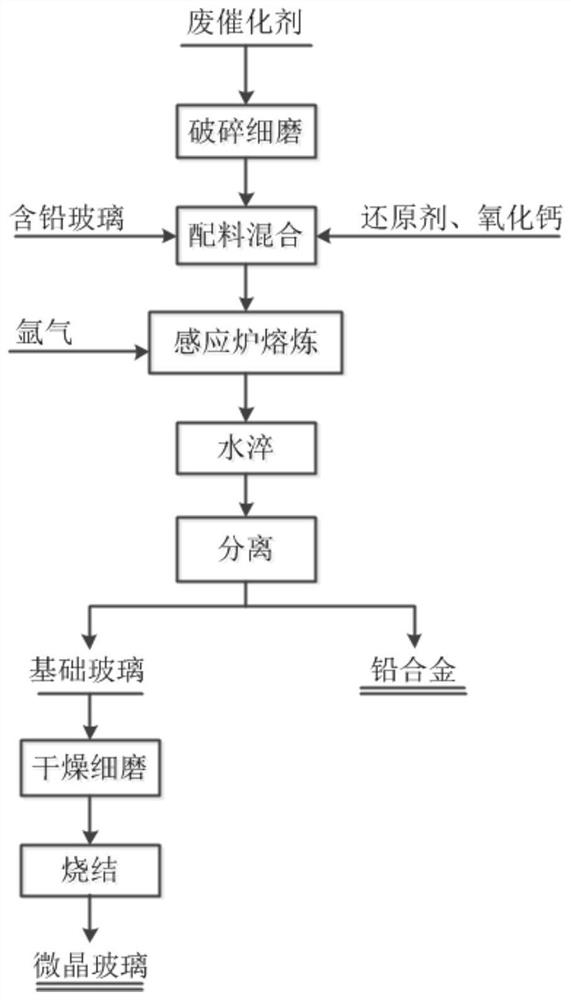
[0032] use figure 1 The shown method for co-processing of lead glass and spent catalyst, which treats spent catalyst and lead glass, includes the following steps:
[0033] Crush the lead glass and waste catalyst to 0.074-0.178mm, take 200g of waste catalyst, add 200g of lead glass, 60g of calcium oxide, 4g of anthracite, and add 5g of cellulose as a binder, mix evenly in the mixing tank, and use powder The tablet press compresses the mixture into The cylindrical sample was loaded into a graphite crucible.
[0034] The material was smelted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, the sample was heated to 1400°C, and argon gas was sprayed above the melt at a flow rate of 0.5 L·min. -1. After smelting for 2 hours, pour the upper glass liquid into water and dry to obtain 335g of basic glass particles. The metal melt at the bottom of the crucible and the crucible are placed in the air to cool, and 35.4g of lead alloy is obtained after separating the slag phase.
[0035]...
Embodiment 2
[0038] use figure 1 The shown co-processing method from lead glass and spent catalyst, which treats spent catalyst and lead glass, includes the following steps:
[0039] Crush the lead glass and waste catalyst to 0.074-0.178mm, take 200g of waste catalyst, add 300g of lead glass, 100g of calcium oxide, 7.5g of anthracite, and 8g of cellulose, mix them evenly in the mixing tank, and use a powder tablet machine to make the mixture evenly. pressed The cylindrical sample was loaded into a graphite crucible.
[0040] The material is smelted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, the sample is heated to 1500°C, and argon gas is sprayed above the melt, and the argon gas flow rate is 0.4L·min -1 . After smelting for 4 hours, pour the upper glass liquid into water, and dry to obtain 432g of basic glass particles. The metal melt at the bottom of the crucible and the crucible are placed in the air to cool, and 52.7g of lead alloy is obtained after separating the slag phase. ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] use figure 1 The shown co-processing method from lead glass and spent catalyst, which treats spent catalyst and lead glass, includes the following steps:
[0045] Crush the lead glass and waste catalyst to 0.074-0.178mm, take 200g of waste catalyst, add 250g of lead glass, 130g of calcium oxide, 5g of anthracite, and 6g of cellulose, mix them evenly in a mixing tank, and press the mixture with a powder tablet machine. to make The cylindrical sample was loaded into a graphite crucible.
[0046] The material was smelted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, the sample was heated to 1300°C, and argon gas was sprayed above the melt at a flow rate of 0.8 L·min. -1 . After smelting for 3 hours, pour the upper glass liquid into water and dry to obtain 426g of basic glass particles. The metal melt at the bottom of the crucible and the crucible are placed in the air to cool, and 44.7g of lead alloy is obtained after separating the slag phase.
[0047] The base gla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com