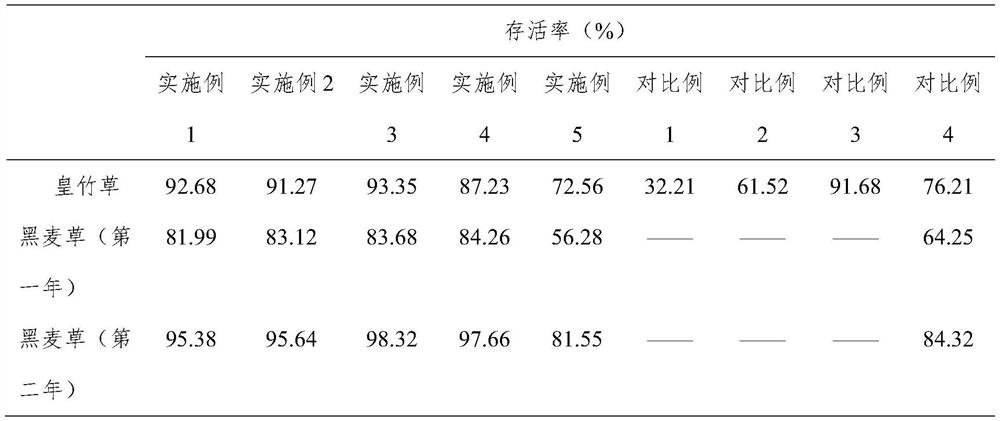
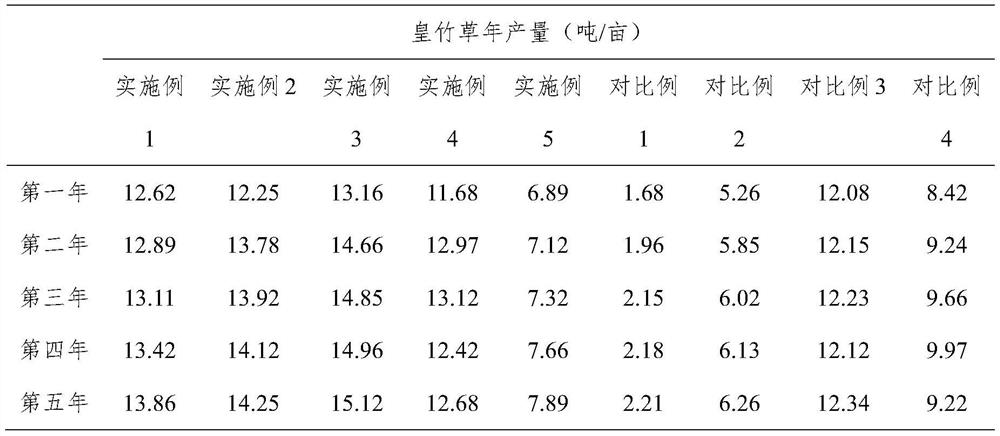
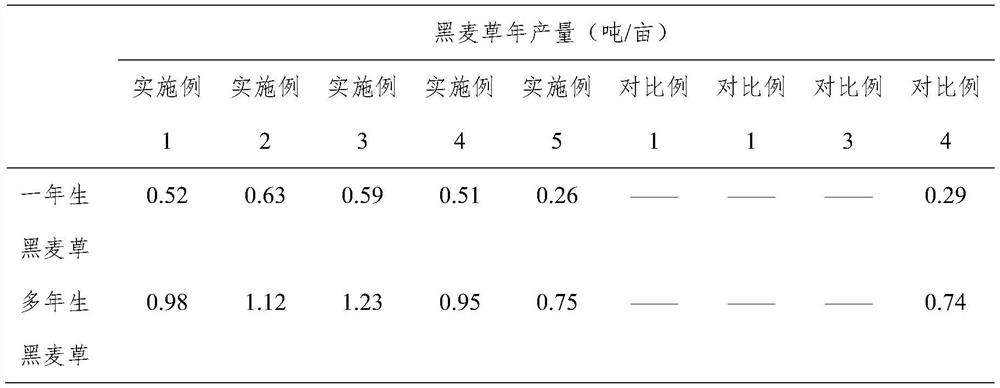
The method of planting grass in rare earth tailings and the comprehensive treatment method of rare earth tailings
A technology of rare earth tailings and pasture, applied in the field of resources and environment, can solve the problems of unrepaired soil, soil acidification, few repair measures, etc., to improve plant survival rate and growth rate, increase organic matter content, and increase fertilization depth Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Step 1. Collect cow dung. Collect cow dung from the cattle farm, control the drinking water and rainwater for beef cattle breeding not to enter the cow dung, and the cow urine enters the biogas digester for fermentation to obtain biogas slurry.
[0042] Step 2, preparing cow dung-based bed bait. Place the above-mentioned cow dung in a fermentation tank, add vermicompost and navel orange dregs to ferment for 4.5 days, the mass ratio of cow dung, vermicompost and navel orange dregs is 100:12.5:7.5, and ferment to obtain cow dung for cultivating earthworms Bed bait.
[0043] Step 3, preparing vermicompost. The above-mentioned cow dung-based bed bait is placed in strips on the ground with good drainage and shade to obtain a cultured base bed for cultivating earthworms. The length of the cultured base bed is controlled to be 4m, the width is 0.25m, and the height is 0.25m. Add 13.5kg of earthworms in the culture bed, water the culture bed every day, keep its humidity at a...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The differences between this embodiment and Implementation 1 are as follows:
[0049] In step 2, the mass ratio of cow dung, vermicompost and navel orange residue is 100:13.5:8.5, and fermented for 4 days to obtain cow dung-based bed bait.
[0050] In the step 3, the length of the earthworm breeding base bed is controlled to be 4.6m, the width is 0.28m, and the height is 0.26m, and 14.2kg of earthworms are added in the culture base bed, and the culture base bed is watered every day to keep its humidity at 53%. About 22 days for breeding;
[0051] In step 4, in the rare earth tailings area (115° 58' east diameter, 26° 39' north latitude, 1200-1250 meters above sea level), each horizontal field is ditched with a width of 32cm; others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0052] In step 6, annual ryegrass is sown in the first year, with a sowing area of 0.64 kg per mu; in the second year, perennial ryegrass is interplanted, with a sowing area of 0.63 kg per mu; t...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The differences between this embodiment and Implementation 1 are as follows:
[0055] In step 2, the mass ratio of cow dung, vermicompost and navel orange residue is 100:15:10, and fermented for 3 days to obtain cow dung-based bed bait.
[0056] In the step 3, the length of the earthworm breeding base bed is controlled to be 5m, the width is 0.3m, and the height is 0.3m, and 15kg of earthworms are added in the culture base bed, and the culture base bed is watered every day to keep its humidity at about 53%. Breeding for 25 days;
[0057]In step 4, in the rare earth tailings area (116° 38' east diameter, 26° 29' north latitude, 1100-1120 meters above sea level), each horizontal field is ditched with a width of 35 cm; others are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0058] In the first year in step 6, annual ryegrass is sown and planted, with a sown area of 0.7 kg per mu; in the second year, perennial ryegrass is interplanted with a sown area of 0.75 kg per mu; others are t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com