Antimicrobial fiber and method of manufacturing antimicrobial fiber
A manufacturing method and antibacterial technology, applied in fiber treatment, synthetic fiber, rayon manufacturing, etc., can solve the problem of easy detachment of antibacterial particles, achieve excellent antibacterial effect, prevent discoloration, and inhibit detachment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
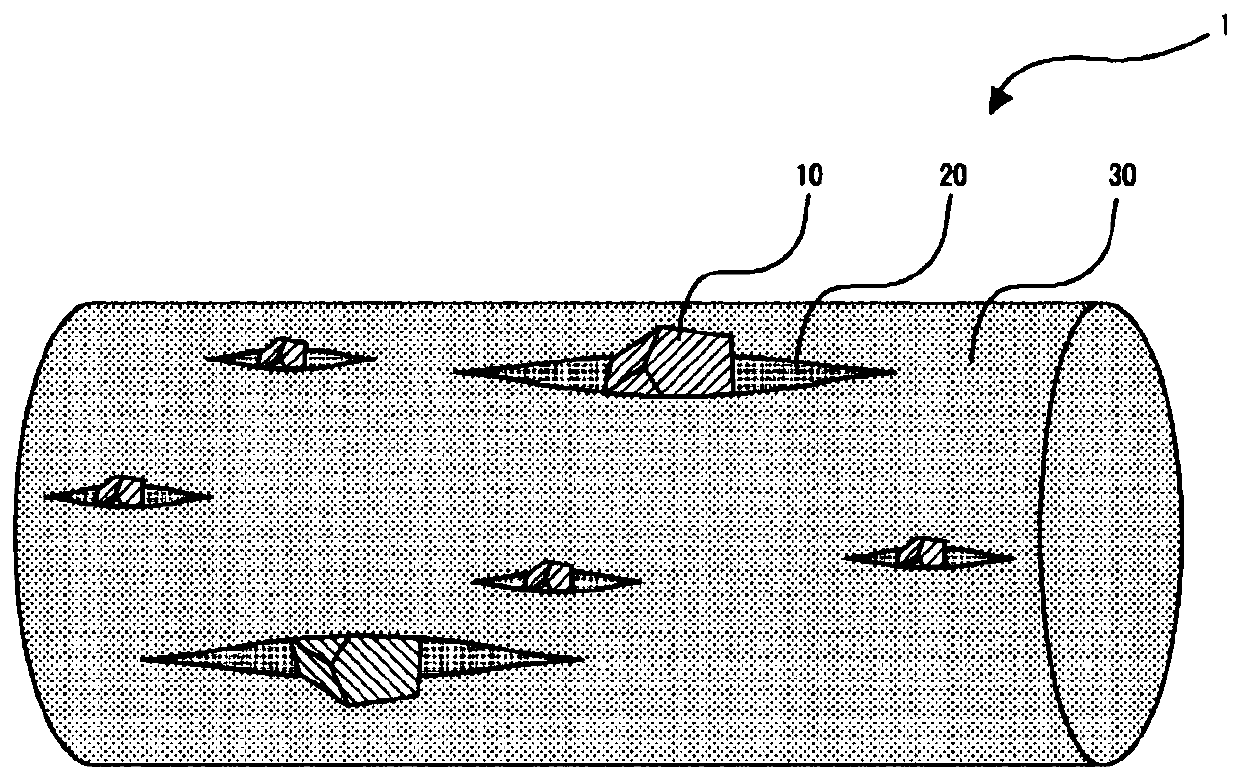
[0049] The first embodiment is an antibacterial fiber comprising a thermoplastic resin and antibacterial glass particles, on the surface of the antibacterial fiber there is a crack along the longitudinal direction of the antibacterial fiber, and the crack is sandwiched by at least one antibacterial glass particle. The state of the particle.
[0050] Hereinafter, the first embodiment will be specifically described with reference to the drawings as appropriate.
[0051] 1. Antibacterial fiber
[0052] (1) Form
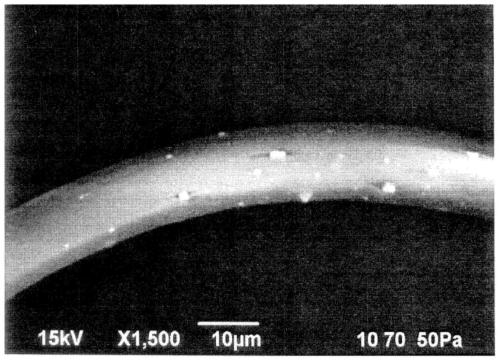
[0053] Such as figure 1 Electron micrographs (SEM images) of figure 2 As shown in the schematic diagram of FIG. 1 , the antimicrobial fiber 1 of the first embodiment is characterized by having cracks 20 along the longitudinal direction of the antimicrobial fiber on its surface.
[0054] The crack 20 in the first embodiment refers to a crack generated along the longitudinal direction of the fiber surface, and the crack 20 is a state in which at least one antibacterial ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0331] The second embodiment is the method for producing the antibacterial fiber described in the first embodiment, and is a method for producing the antibacterial fiber including a thermoplastic resin and antibacterial glass particles.
[0332] Moreover, the manufacturing method of the antibacterial fiber is characterized in that: there is a crack along the longitudinal direction of the antibacterial fiber on the surface of the antibacterial fiber, and the crack is in a state of sandwiching at least one antibacterial glass particle, and includes The following steps (a) to (d).
[0333] Step (a): Prepare a glass melt containing an antibacterial active ingredient to obtain antibacterial glass particles,
[0334] Step (b): producing an antibacterial resin composition mixed with antibacterial glass particles and a thermoplastic resin,
[0335] Step (c): The antibacterial fiber before stretching is produced directly or indirectly from the antibacterial resin component,
[0336] ...
Embodiment 1
[0432] 1. Production of antibacterial glass
[0433] (1) Melting process
[0434] P 2 o 5 The composition ratio of CaO is 50% by weight, the composition ratio of CaO is 5% by weight, Na 2 The composition ratio of O is 1.5% by weight, B 2 o 3 The composition ratio is 10% by weight, Ag 2 The composition ratio of O is 3% by weight, CeO 2 The composition ratio of ZnO was 0.5% by weight, and the composition ratio of ZnO was 30% by weight. Each glass raw material was stirred at a rotation speed of 250 rpm for 30 minutes using a universal mixer until uniformly mixed.
[0435] Next, using a melting furnace, the glass raw materials were heated at 1280° C. for 3.5 hours to obtain molten glass.
[0436] (2) Coarse crushing process
[0437] The molten glass taken out of the glass melting furnace was poured into still water at 25° C., thereby performing water pulverization to obtain coarsely pulverized glass having a volume average particle diameter of about 10 mm.
[0438] It sho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com