A phase-sensitive selective j-spectroscopy method for suppressing axial peaks
A selective, spectral method technology, applied in the direction of using nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum for measurement, using magnetic variable measurement, instrument, etc., can solve the problems of narrow chemical shift distribution, complex split peak pattern, high axial peak intensity, etc. High resolution and the effect of improving spectral resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
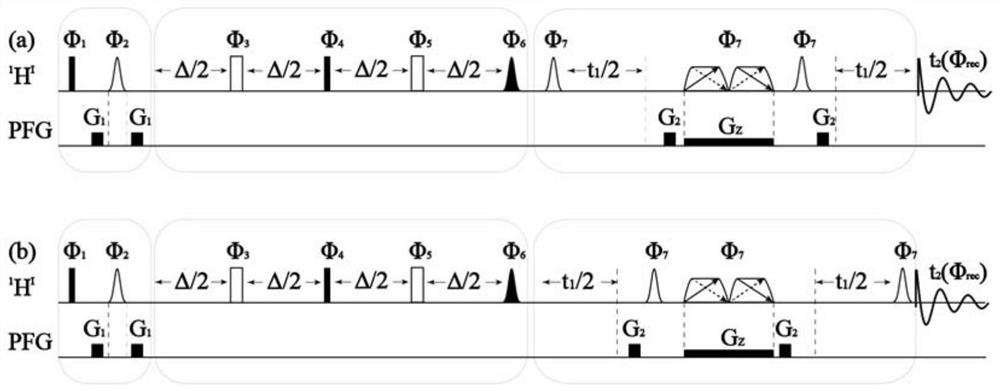
[0023] The following embodiments will further illustrate the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
[0024] A phase-sensitive and selective J spectrum method for suppressing axial peaks described in the embodiment of the present invention, the main steps are:
[0025] 1) collecting the NMR one-dimensional spectrum of the sample;
[0026] 2) Measure the pulse width of the 90-degree hard pulse of the sample;
[0027] 3) Determine the range of hydrogen spectrum that needs to be analyzed;
[0028] 4) Take the frequency of the S nucleus to be measured in the hydrogen spectrum as the excitation center of the selectively excited 180-degree soft pulse, set the power and time of the selectively excited 180-degree soft pulse, and set the dephase gradient G 1 ;
[0029] 5) Take the central frequency of the hydrogen spectrum to be analyzed as the excitation center of the hard pulse, and set the power and time of the 90-degree and 180-degree hard pulse;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com