Miridae attractant and using method thereof
A technology of attractant and mirid bugs, applied in the direction of attracting pests, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve problems such as economic loss, harm, and complicated hosts of mirid bugs, and achieve low environmental pollution, good control effect, Low toxicity to humans and animals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Two-way competition experiment between Lygus green levulinate and cotton leaf odor selection:
[0022] Before the experiment, the adults of Lygus viridans were starved for 4 hours and then used for the determination of olfactory behavior. One arm of the "Y" type insect olfactory selection instrument was completely sealed with absorbent cotton, and the other two arms were respectively connected to a 250mL odor source bottle. Add 2 to 3 pieces of fresh cotton leaves to one of the taste source bottles, and add 50 μL of methyl levulinate stock solution to the other taste source bottle. The air flow rate was set at 2 L / min, and the air was ventilated for 5 min before the experiment started. In one experiment, 10 green ligus adults were put into the olfactory instrument through the top opening in the center of the olfactory instrument, all lights in the laboratory were turned off, and the results were recorded after 30 minutes. Choose a reaction.
[0023] This experiment wa...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The same method as in Example 1 is used to carry out the two-way competition experiment for diethyl phthalate and cotton leaf odor selection by Lygus lygus, and the experimental results are as shown in table 2. The selective reaction rate of diethyl phthalate was 63.96%, which was significantly higher than that of its field host cotton leaves, indicating that diethyl phthalate had better trapping activity on cotton field Lygus japonica.
[0029] Table 2 Selective responses of Lygus chlorophylla to diethyl phthalate and cotton leaves
[0030] Selective reaction rate of diethyl phthalate (%) Selective response rate to cotton leaves (%) 63.96±2.93aA 36.04±2.93bB
Embodiment 3
[0032] The three-way competition experiment of the odor selection of Lygus viridis to methyl levulinate, diethyl phthalate and compound preparations:
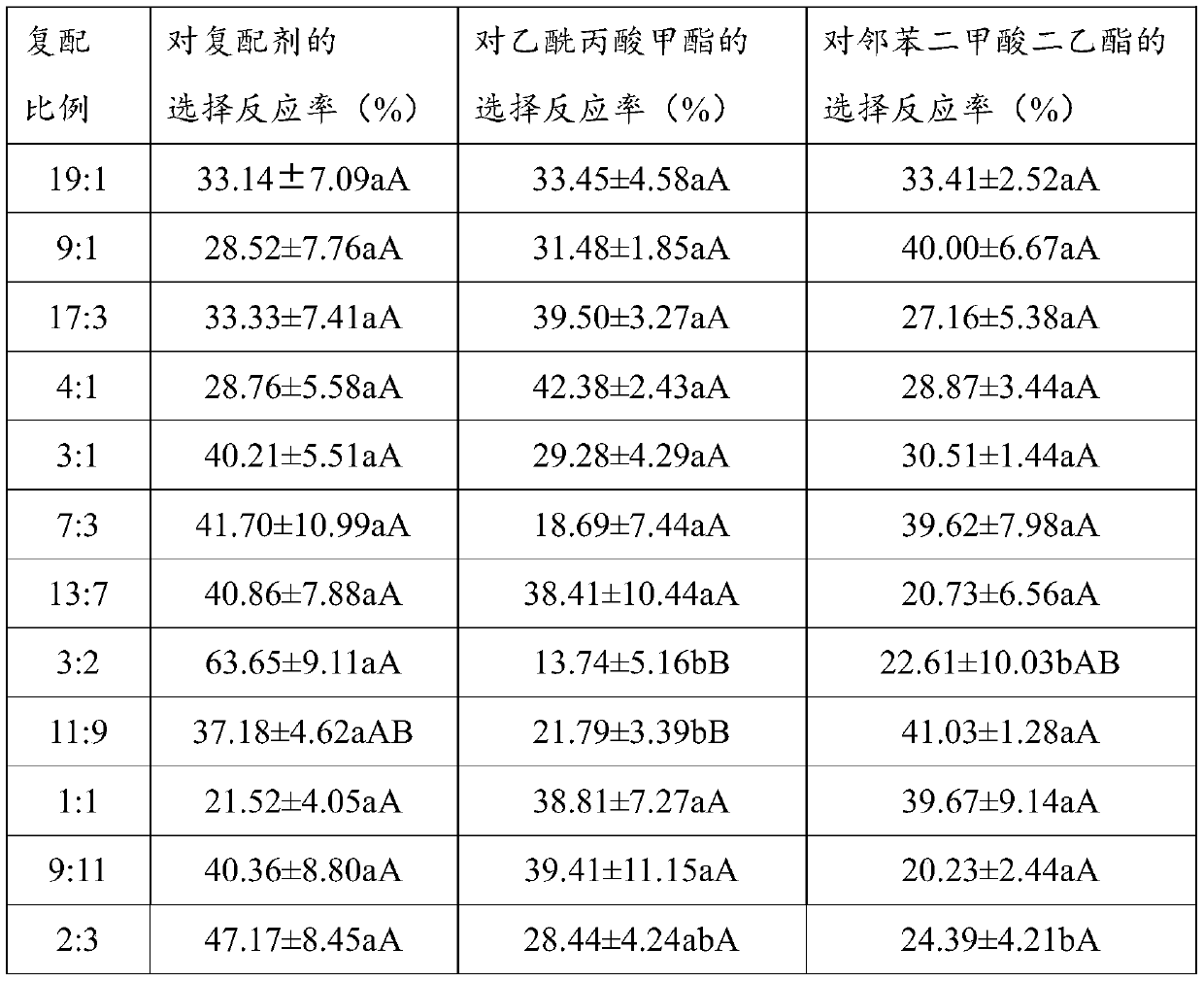
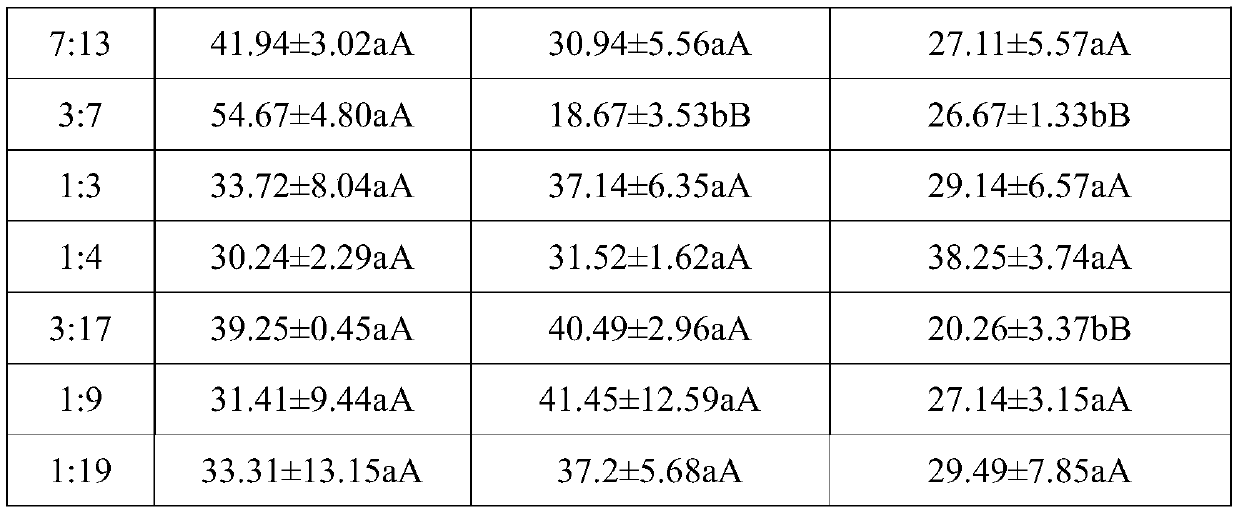
[0033] Methyl levulinate and diethyl phthalate in volume ratio 19:1, 9:1, 17:3, 4:1, 3:1, 7:3, 13:7, 3:2, 11 :9, 1:1, 9:11, 2:3, 7:13, 3:7, 1:3, 1:4, 3:17, 1:9, 1:19 to configure nineteen kinds of compound preparations, Three-way competition experiment with methyl levulinate and diethyl phthalate.
[0034] Place 50 μL of methyl levulinate stock solution, 50 μL of diethyl phthalate stock solution and 50 μL of compound preparation in the gas source bottle connected to the "Y" type insect olfactory selector, and adopt the same experiment as in Example 1 Methods and data processing methods were used to conduct experiments, and Duncan's new multiple range method was used to compare the choice responses of Lygus spp. to the three. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.
[0035] Table 3 three-way competition experiment of me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com