Method for promoting colonization of azotobacter chroococcum in plant rhizosphere
A nitrogen-fixing bacterium and plant root technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as differences in chemotaxis, restrictions on popularization and application, differences in plant chemotaxis and growth-promoting effects, etc., to achieve increased numbers, wide application prospects, and promotion of biological The effect of film formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
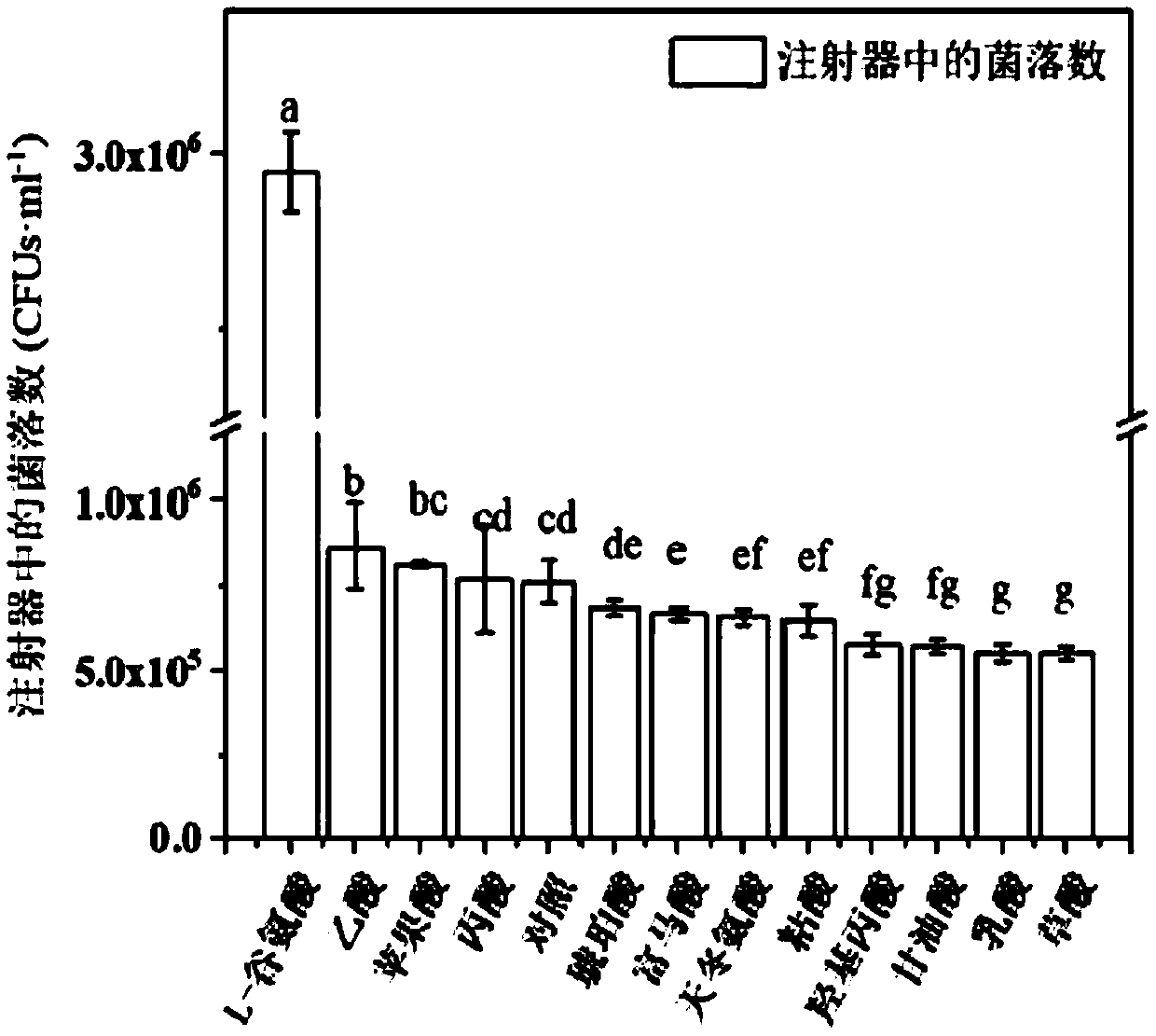
[0037] Example 1 Chemotaxis of Organic Acids in Different Root Exudates to Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663
[0038] The present invention selects 12 kinds of organic acids (L-glutamic acid, acetic acid, malic acid, propionic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, aspartic acid, mucic acid, hydroxypropionic acid, glyceric acid) on the basis of previous studies. , lactic acid and oxalic acid), to study its chemotactic effect on Azotobacter phenus, the specific experimental methods and experimental results are as follows:
[0039] 1. Experimental method
[0040] Use a pipette to draw 100 μL of the aqueous solution of Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663 after the logarithmic phase of growth and centrifugation and resuspension, and use a syringe to draw 200 μL with a concentration of 30 μmol L -1 12 kinds of organic acids, set sterile water as the blank control. After inserting the needle of the syringe into the tip of the pipette, let it stand in the ultra-clean bench for 2 hours, pull out ...
Embodiment 2
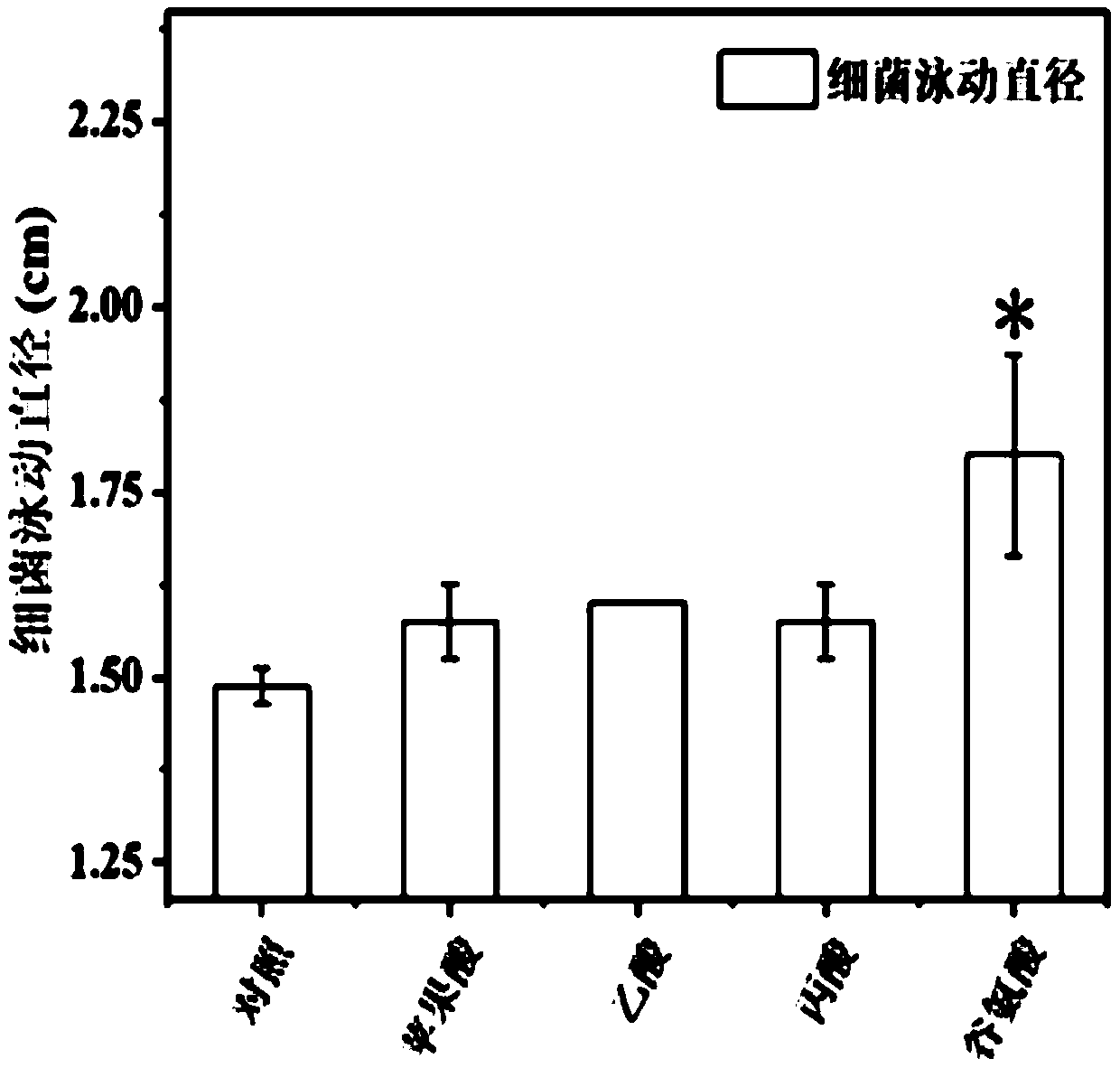
[0043] Example 2 Effects of Organic Acids in Different Root Exudates on Group Swimming of Nitrogenus Pherogenus 22663
[0044] For the 4 kinds of organic acids (L-glutamic acid, acetic acid, malic acid and propionic acid) screened in Example 1 that have a positive chemotaxis effect on Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663, their group swimming effect on Azotos sphaeroides was studied , the specific experimental methods and experimental results are as follows:
[0045] 1. Experimental method
[0046] Prepared with 30μmol·L -1 For the SOC medium of organic acid (the blank control is sterile water), place an 8mm sterile filter paper in the center of the solid medium, and absorb 5mL of the enriched Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663 in the center of the filter paper, and then place it in the biochemical Cultivate in the incubator at 28°C for 4 days, measure the colony diameter from 3 different directions, set up 3 parallels, and calculate the average value ± standard deviation of the diamete...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 The in vitro recruitment effect of L-glutamic acid on Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663 in plant roots
[0050] According to the L-glutamic acid that screened in Example 2 has a positive chemotactic effect and a strong group swimming effect on Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663, study its in vitro recruitment effect on Azotos sphaeroides 22663 in plant roots, specific experimental methods And the experimental results are as follows:
[0051] 1. Experimental method
[0052] Prepare 1 / 4 concentration Hoagland nutrient solution, add 50mL nutrient solution and 1% (0.5g) agar to each tissue culture bottle to make a solid medium. The amaranth seeds were soaked in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 30 minutes, placed on the surface of the center of the tissue culture bottle, and cultivated for 4 days. After the tender leaves grow, suck 10 μL of the enriched Azotobacter sphaeroides 22663 bacterial suspension (OD600=0.4) at a place 2 mm away from the root of the plant, and a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com